Practice Free H12-831_V1.0-ENU Exam Online Questions
The interface address of an OSPFv3 router is 2000::1/128.
In which of the following types of LSAs is this prefix likely to appear? (Multiple choice)
- A . Inter-Area-Prefix-LSA
- B . Router-LSA
- C . Inter-Area-Router-LSA
- D . AS-External-LSA
As shown in the figure, R1, R2, and R3 run WPLS, and the administrator configures a static LSP from the 1.1.1.0/24 network segment to the 3.3.3.0/24 network segment.
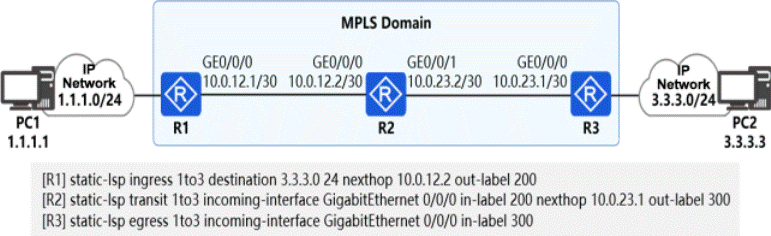
Which of the following descriptions of this scene are correct? (Multiple choice)
- A . R3 will perform MPLS forwarding on the traffic sent from PC2 to PC1.
- B . R1 will perform MPLS forwarding on the traffic sent from PC1 to PC2.
- C . PC1 cannot access PC2
- D . PC2 can access PC1
Which of the following descriptions about OSPFv3 are correct? (Multiple choice)
- A . OSPFv3 Router LSA and Network LSA do not contain IP addresses
- B . In broadcast, NBMA, and P2MP networks, neighbors are no longer identified by IP addresses, but only by Router IDs.
- C . OSPFv3 supports multiple processes on a link
- D . The flooding scope of LSA is added to the LSA message of OSPFv3
When IP packets pass through the WPLS network, the WPLS device will process the TTL. If the topology uses the uniform process Hub-PE ing mode as shown in the figure, please match the TTL values during the packet transmission process one by one.
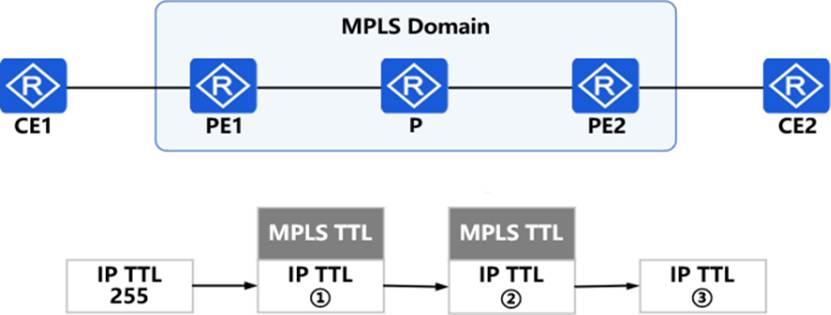

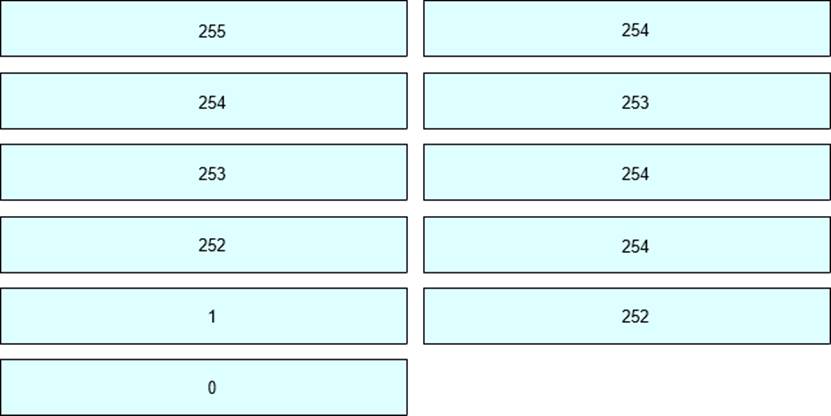
In the OSPF network shown in the figure, the link cost value has been marked in the figure, R1 enables OSPF IP FRR, then which of the following descriptions is wrong?
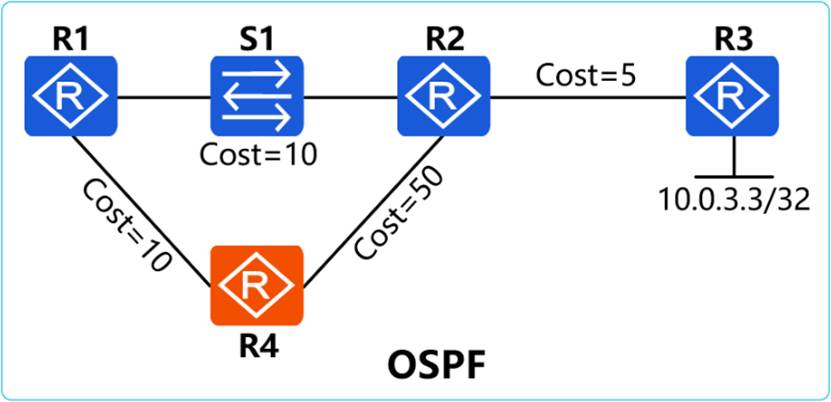
- A . If the link between R1 and S1 is disconnected, R1 will directly use the backup path to reach R3 because FRR is enabled on R1.
- B . If the link between R1 and S1 is disconnected, check the neighbor relationship on R1 and the neighbor relationship between R1 and R2 becomes Down
- C . If the link between R2 and S1 is disconnected, R1 will recalculate the optimal path to R3
- D . If the link between R1 and S1 is disconnected, R1 will recalculate the optimal path to reach R3
In the OSPFv3 network shown in the figure, area 1 is a stub area, area 2 is a normal area, and area 3 is an NSSA area. The IPv6 address of the R6 Lopback0 interface is 2000::6/128. The Router ID of each device is 10.0.X.X, where X is the device number. "stub no-summary" is configured in area 1 of R2.
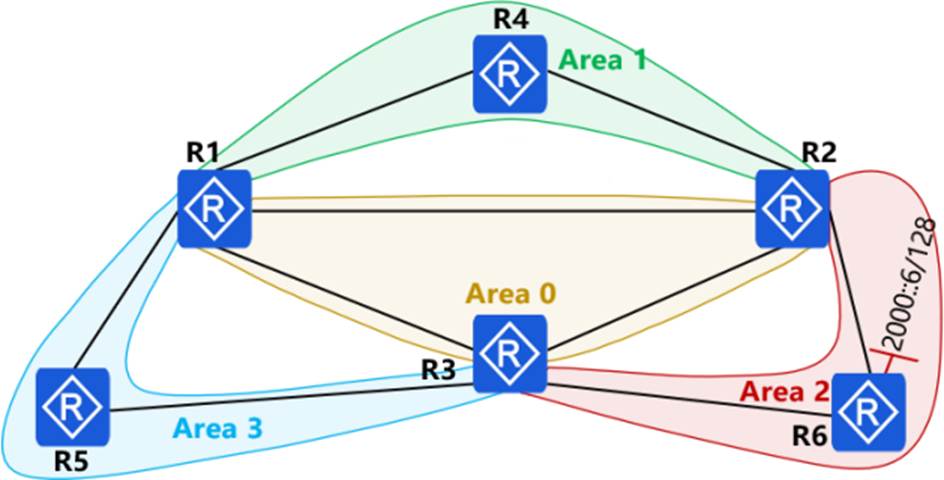
Which of the following descriptions is correct?
- A . The R4 LSDB contains the Inter-Area-Prefix-LSA describing 2000::6/128 generated by R1.
- B . The path for R4 to send data packets to 2000::6 is R4-R2-R6
- C . There is no route entry for 2000::6/128 in R4’s routing table.
- D . The path for R4 to send data packets to 2000::6 is R4-R1-R5-R3-R6
By default, the IS-IS LSP refresh interval is which of the following?
- A . 1200s
- B . 900s
- C . 3600s
- D . 10s
In the network shown in the figure, R1 and R2 are configured with single-hop BFD detection. The network engineer found that the BFD session was Down, so he queried the configuration related to R1 and R2 BD. The configuration information has been marked in the figure. According to the configuration information, the reason for the BFD session Down is that the time parameters configured on R1 and R2 do not match.
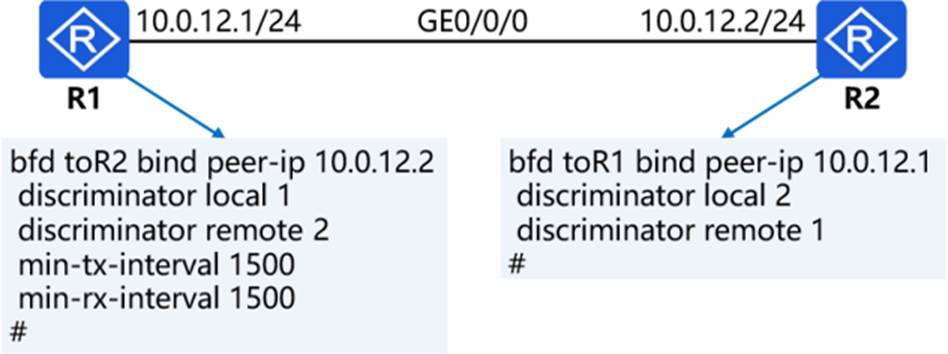
- A . True
- B . False
The business route of an enterprise is transmitted in the network, and part of the configuration of PE1 and PE2 is shown in the figure. At this time, CE1 adds a new business network segment and announces it to Area1 of OSPF 10.
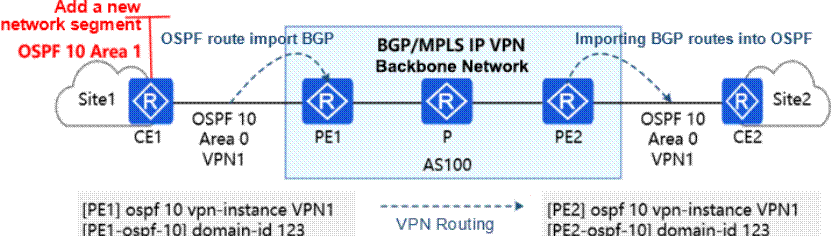
In this scenario, which type of LSA will CE2 receive, which will contain the service network segment newly announced by CE1?
- A . True
- B . False
On the network shown in the figure, IS-IS runs on R1, R2, R4, and R5, and the area ID is 49.0001. IS-IS runs on R3 and R6, and the area ID is 49.0002. In AS 65000, R1, R3, R4, and R6 each establish iBGP peer relationships with R2 and R5. R2 and R5 are RRs (Route Reflectors), and R1, R4, R3, and R6 are clients. The iBGP peer relationships are established using Loopback0 on each router, and the router ID is 10.0.0.X/32, where X is the number of the router. R1 and R4 import the external route 192.168.1.0/24 to BGP through the import-route command, and R3 and R6 import the external route 192.168.2.0/24 to BGP through the import-route command.
Which of the following statements are true?
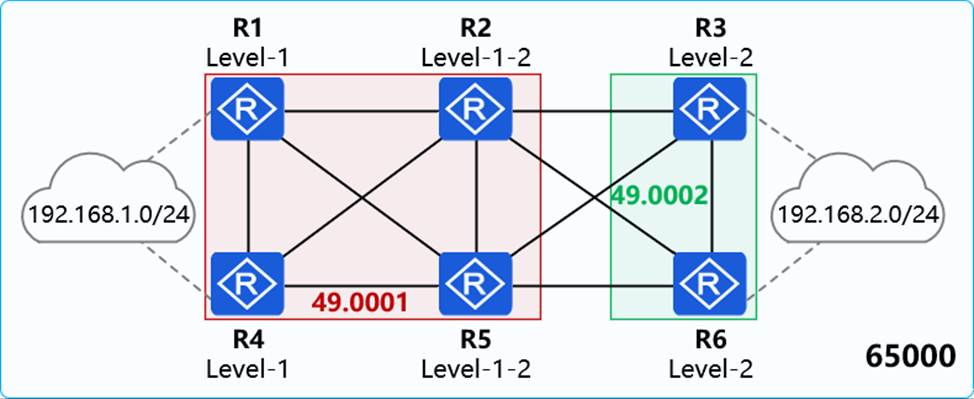
- A . The routing table of R4 contains two equal-cost default routes.
- B . The route 192.168.1.0/24 in the routing table of R3 has two next hops.
- C . The routing table of R1 does not contain the route 192.168.2.0/24.
- D . For 192.168.1.0/24, R3 preferentially selects the BGP route received from R2, and R6 preferentially selects the BGP route received from R5.
B, D
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed In-Depth
This question involves a network topology with IS-IS, iBGP, and route reflection, and we need to determine which statements are true, allowing for multiple correct answers. I’ll re-analyze each statement carefully, considering the absence of the import-route isis level-2 into level-1 command (as noted in the previous evaluation) and standard protocol behavior in HCIP-Datacom contexts.
Network Overview:
IS-IS Configuration:
IS-IS runs on R1, R2, R4, and R5 in area 49.0001 (Level-1/Level-2).
IS-IS runs on R3 and R6 in area 49.0002 (Level-2 only, as implied by the figure).
Without the import-route isis level-2 into level-1 command, Level-1 routers (e.g., R1, R4) cannot directly learn Level-2 routes (e.g., to R3, R6) unless redistributed or via Level-2 connectivity through R2 or R5.
BGP Configuration:
AS 65000 uses iBGP with R2 and R5 as Route Reflectors (RRs), and R1, R3, R4, and R6 as clients.
iBGP peer relationships use Loopback0 addresses with router IDs of 10.0.0.X/32, where X is the router number (e.g., R1 = 10.0.0.1/32, R3 = 10.0.0.3/32, etc.).
R1 and R4 import the external route 192.168.1.0/24 into BGP using import-route.
R3 and R6 import the external route 192.168.2.0/24 into BGP using import-route.
Topology Insights:
The figure shows R2 and R5 as central hubs connecting Level-1/Level-2 IS-IS areas and serving as RRs for iBGP.
R1 and R4 are in area 49.0001 (Level-1/Level-2), while R3 and R6 are in area 49.0002 (Level-2).
External routes (192.168.1.0/24 and 192.168.2.0/24) are injected into BGP and distributed via iBGP.
Analyzing Each Statement:
