Practice Free GES-C01 Exam Online Questions
An AI engineer is building an automated pipeline in Snowflake that processes various types of textual data using Cortex AI functions. To ensure the pipeline’s stability and avoid failures due to exceeding LLM context windows, they integrate SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX.COUNT_TOKENS and TRY_COMPLETE. Consider the following code snippets and statements about context window management in Snowflake Cortex.

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
- E . Option E
A,C,E
Explanation:
Option A is correct.
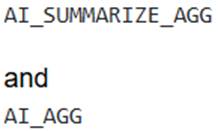
functions are explicitly stated as not being subject to context window limitations. This means input length is less of a concern for truncation for these specific functions, though

has a 200,000-token context window,
mistral -7b
has a 32,000-token context window) before invoking the LLM function.
Option D is incorrect. The

controls the maximum number of *output* tokens the model can generate, not the input tokens.
Option E is correct.
TRY_COMPLETE is a helper function that returns NULL instead of raising an error if the operation cannot be performed. Integrating COUNT_TOKENS before TRY_COMPLETE can proactively identify potential token overflow issues, thus helping to prevent the operation from failing or returning NULL, and enhancing pipeline stability.
A global enterprise has Snowflake accounts in various regions, including a US East (Ohio) account where a critical application is deployed. They need to use AI_COMPLETE with the claude-3-5-sonnet model for real-time customer support, but this model is not natively available in US East (Ohio) for direct AI_COMPLETE usage. The Snowflake administrator considers enabling cross-region inference.
Which statements accurately reflect the considerations and characteristics of cross-region inference in Snowflake Cortex?

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
- E . Option E
B,C
Explanation:
Option B is correct because setting the parameter to ‘ANY_REGION’ enables inference requests to be CORTEX_ENABLED_CROS_ REGION processed in a different region from the default, thereby allowing access to models not natively supported in the local region .
For example, claude- 3 – 5- sonnet is available in AWS US East 1 (N. Virginia), which could be accessed from US East (Ohio) via cross-region inference.
Option C is 3-5 Csonnet correct as cross-region inference is explicitly not supported in U.S. SnowGov regions for either inbound or outbound inference requests.
Option A is incorrect because user inputs, service generated prompts, and outputs are not stored or cached during cross-region inference.
Option D is incorrect; latency depends on the cloud provider infrastructure and network status, and testing is recommended.
Option E is incorrect because CORTEX_ENABLED_CROSS_REGION is an account-level parameter, not a session parameter.
A data analyst is setting up a new Cortex Analyst-powered conversational app for business users. They want to understand how the "Suggested Questions" feature behaves under different semantic model configurations to ensure an optimal user experience.
Which of the following statements accurately describe the behavior of the "Suggested Questions" feature in Cortex Analyst based on the semantic model configuration?
- A . If the semantic model does not include a Verified Query Repository (VQR), Cortex Analyst will always return a blank list of suggested questions.
- B . When a semantic model contains a VQR, Cortex Analyst prioritizes returning up to five suggested questions from the VQR that are semantically similar to the user’s input.
- C . Setting the
flag on verified queries within a VQR ensures that only up to three of these marked questions are returned, regardless of user input. - D . In the absence of a VQR, Cortex Analyst uses underlying Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate up to three suggested questions, which are guaranteed to be answerable.
- E . If multiple verified queries in a VQR are marked with

, Cortex Analyst will return all of them when configured in Customizable Mode, even if there are more than five.
B,E
Explanation:
Cortex Analyst’s ‘Suggested Questions’ feature operates in different modes. If a semantic model does not include a Verified Query Repository (VQR), Cortex Analyst uses Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate up to three suggested questions, which may not always be answerable. Therefore, option A is incorrect because it returns a blank list, and option D is incorrect because the LLM-generated questions are not guaranteed to be answerable. When a semantic model has a VQR defined, Cortex Analyst suggests up to five questions from the VQR based on their similarity to the user’s input, making option B correct. Furthermore, in Customizable Mode, if verified queries in the VQR are marked with
![]()
, Cortex Analyst will return all of these flagged questions, regardless of their quantity or similarity to user input, making option E correct and option C incorrect.
A multinational corporation is implementing Document AI to automate the processing of purchase orders from various global suppliers. These purchase orders vary significantly in layout and are often submitted in English, German, and Spanish. The data engineering team aims to optimize the preparation phase for effective model training and deployment. Considering Document AI’s ‘Question optimization best practices’ and general document preparation guidelines, which of the following is a ‘critical consideration’ for successful implementation?
- A . For multilingual support, it is mandatory to externally translate all non-English purchase orders to English before uploading them to an internal stage, as Document AI only formally supports English.
- B . The training dataset should be highly diverse, representing various layouts, data variations (including potential NULLs), and containing documents in all target languages (English, German, Spanish) to ensure robust model performance.
- C . To simplify prompt engineering, define generic questions such as ‘What is the total amount?’ irrespective of document layout, as Document AI’s foundation model is expected to handle most layout variations through its zero-shot capabilities.
- D . For maximum efficiency in defining data values for complex extractions (e.g., lists of line items), prioritize spending extensive time on crafting highly precise and detailed natural language prompts to guide the model.
- E . Document AI model builds can only support a single document layout type; therefore, separate model builds must be created for each distinct purchase order layout from different suppliers.
B
Explanation:
Optimizing Document AI involves careful preparation of both the questions and the training data.
– ‘ ‘Option ‘ is incorrect. While Document AI formally supports English, it also supports processing documents in Spanish, French, German, Portuguese, Italian, and Polish, especially if the model is trained appropriately. External translation is not mandatory; questions should be written in English, using native terms when appropriate, and the model trained for the specific language documents.
– ‘‘Option B" is correct. To improve model training, it is crucial that the uploaded documents represent a real use case, and the dataset consists of diverse documents in terms of both layout and data. This includes variation in information, not just all documents containing the same data or presented in the same form. When dealing with multilingual documents, training the model appropriately with diverse language examples is key for successful extraction .
– “Option is incorrect. Document AI best practices emphasize specificity in questions. While zero-shot capabilities exist, relying on generic questions for diverse layouts without additional training or specificity can lead to inaccurate results .
– “Option is incorrect. For complex extractions like lists of line items, the best practice is ‘Show, don’t tell’. This means showing the expected result through annotations and fine-tuning across the training set, rather than relying solely on elaborate prompt engineering. – ‘ ‘Option is incorrect. Document AI model builds are designed to handle the entire range and diversity of document types for a specific use case, not just a single layout. The goal is often to have a single model for a document type (e.g., invoices) even with layout variations. Training with diverse documents, including different layouts, is a best practice.
A Gen AI Specialist is setting up AI Observability for a new generative AI application in Snowflake to monitor its performance and debug issues. The application is built in Python.
Which of the following prerequisites must be met to enable tracing for this application?
- A . The Python environment must have the TRULENS_OTEL_TRACING environment variable set to o before connecting to Snowflake.
- B . The account role used must be granted the SNOWFLAKE. CORTEX_USER database role.
- C . The Python project requires installation of trulens-core and trulens-connectors-snowflake packages, with versions earlier than 2.1.2.
- D . The role used for creating and executing runs must have the CREATE EXTERNAL AGENT privilege on the schema.
- E . The application must run exclusively within a Snowflake Notebook for observability features to function.
B,D
Explanation:

A financial analyst is concerned about the rising costs of their Document AI pipeline, which uses ‘invoice_model!PREDlCT’ to extract data from daily financial reports. They observe that their assigned ‘LARGE virtual warehouse is running continuously, even during periods of low document ingestion, contributing significantly to their bill. They want to investigate how to reduce costs effectively for their existing Document AI setup.

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
- E . Option E
B
Explanation:

