Practice Free GES-C01 Exam Online Questions
A financial institution uses Snowflake Cortex Analyst with strict role-based access control (RBAC) on their Snowflake-hosted LLMs. The security team has granted specific ‘CORTEX-MODEL-ROLE application roles to different analyst teams, ensuring they only access approved models.
A new requirement arises to enable Azure OpenAI GPT models for Cortex Analyst to leverage a specific feature. An administrator proceeds to execute:
![]()
Which of the following statements accurately describe the implications of this change?

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
- E . Option E
B,C
Explanation:
Option B is correct because when is ‘ TRUE, cortex Analyst can use Azure OpenAI models, but this setting is incompatible with model-level RBAC, meaning RBAC is not available for any models used by Cortex Analyst when this parameter is enabled.
Option C is correct because if Azure OpenAI models are opted in for Cortex Analyst, semantic model files (which are metadata) and user prompts will be processed by Microsoft Azure, a third party, thus transmitting them outside Snowflake’s governance boundary. Customer data itself is not shared.
Option A is incorrect because the parameter is incompatible with model-level RBAC for ‘all’ models used by Cortex Analyst.
Option D is incorrect as the parameter specifically controls the use of Azure OpenAI models within Cortex Analyst.
Option E is incorrect because this parameter can only be set by the ‘ ACCOUNTADMIN’ role.
A data engineering team is implementing a Document AI solution to automate the extraction of vendor invoice details. They have already published a Document AI model build, ‘vendor_invoice_model’, located in New invoices are uploaded to an internal stage, ‘fin db.invoice_processing_schema.raw invoices_stage’. The ‘invoice_pipeline role’ is responsible for executing the ! PREDICT method on these staged documents as part of an automated task.
Which of the following USAGE privileges are essential for to successfully execute the ! PREDICT method and process documents from the specified stage, assuming the required SNOWFLAKE.DOCUMENT_INTELLIGENCE_CREATOR role is already granted?
A)
![]()
B)
![]()
C)
![]()
D)
![]()
E)
![]()
- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
- E . Option E
A,B,C
Explanation:

A data engineering team is developing a Cortex Analyst semantic model in YAML for an e-commerce platform. They need to ensure high accuracy for common queries, improve literal matching for product names, and understand limitations for supported data types.
Which of the following statements correctly describe aspects of semantic model configuration or capabilities for these requirements?
- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
- E . Option E
A,C
Explanation:
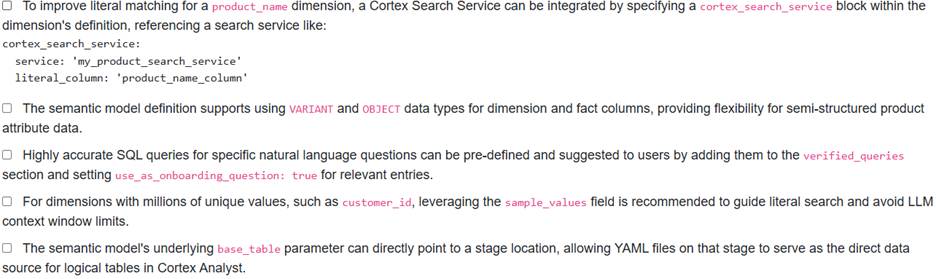
Option A is correct. Cortex Search Services can be integrated into a dimension’s definition (using the field with ‘service’ and fields) to improve literal matching by performing semantic search over the underlying column. This is specifically useful for ‘fuzzy’ searches of product names.
Option C is correct. The ‘verified_querieS section allows pre-defining accurate SQL queries for specific natural language questions. Setting ‘use_as_onboarding_question true’ for entries ensures these queries are used when relevant and presented as suggested questions to users, or as onboarding questions.
Option B is incorrect because ‘VARIANT, ‘OBJECT, ‘GEOGRAPHY, and ‘ARRAY’ data types are currently not supported for dimension, fact, or metric columns in a semantic model.
Option D is incorrect; the ‘sample_values’ field is recommended for dimensions with relatively low-cardinality (approximately 1-10 distinct values) to aid in semantic search for literals, not for high-cardinality dimensions like millions of customer IDs.
Option E is incorrect because a ‘ base_table’ in a semantic model must refer to a physical database table or a view, not directly to a stage location.
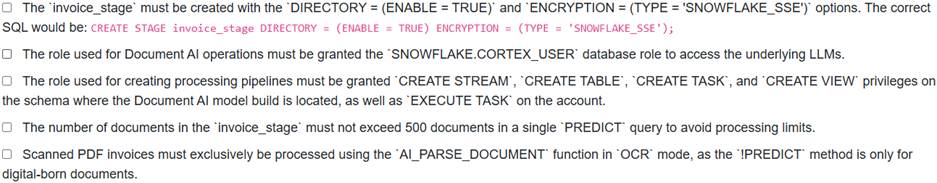
A data engineer is setting up a Document AI pipeline to extract information from scanned invoices stored in an internal stage named ‘invoice_stage’. They have created the stage using ‘CREATE STAGE and uploaded several PDF documents. However, when attempting to run the extraction query, they encounter an error message: ‘File extension does not match actual mime type. Mime- Type: application/octet-stream’. Additionally, they anticipate a privilege issue might arise for pipeline automation.
Which of the following conditions must be met to resolve the current error and ensure proper setup for Document AI extraction and subsequent pipeline creation?
- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
- E . Option E
A,C
Explanation:

A data architect is designing a workflow to programmatically extract highly structured data from various text inputs using Snowflake Cortex AI’s AI_COPIPLETE function through its REST API. They require the output to strictly adhere to a complex JSON schema for downstream processing and need to manage associated costs.
Which of the following statements accurately describe aspects of this approach?

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
- E . Option E
A,C,D
Explanation:

A developer is building an interactive chat application in Snowflake leveraging the COMPLETE (SNOWFLAKE. CORTEX) LLM function to power multi-turn conversations.
To ensure the LLM maintains conversational context and generates coherent responses based on prior interactions, which of the following methods correctly implements the passing of conversation history to the COMPLETE function?

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
- E . Option E
B
Explanation:
To provide a stateful, conversational experience with the ‘COMPLETE (SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX)’ function, all previous user prompts and model responses in the conversation must be passed as part of the argument. This argument is an array of objects, with each object representing a turn in the conversation and containing a ‘role’ (‘system’, ‘user’, or ‘assistant’) and a ‘content’ key, presented in chronological order.
Option A is less effective as it loses the structured conversational context that roles provide.
Option C is incorrect because ‘COMPLETE’ does not retain any state from one call to the next; conversational history must be explicitly managed and passed.
Option D describes a non-existent parameter for the ‘COMPLETE function.
Option E, while fine-tuning is a Snowflake Cortex capability, it is used to customize a model for a specific task over time, not for real-time maintenance of dynamic conversational context in a multi-turn chat.
A security-conscious data scientist in an Azure East US 2 (Virginia) account wants to fine-tune a mistral -7b model for a specific text summarization task and then deploy it for real-time inference using the Cortex REST API. The mistral-7b base model is natively available for fine-tuning in Azure East US 2 (Virginia). For subsequent inference using the fine-tuned model, they need to understand the regional and cross-region inference considerations.
Which of the following statements are correct?

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
- E . Option E
A,B,D,E
Explanation:

A data engineering manager needs to audit Cortex LLM function costs to identify specific SQL queries that are unexpectedly high in token consumption for the ‘llama3.1-8b’ model. They require granular analysis of prompt, completion, and guardrail token usage for these queries.
Which of the following Snowflake methods or views would provide the necessary insights?

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
- E . Option E
B,D
Explanation:

A development team is implementing a document retrieval system in Snowflake. They plan to store document embeddings and use VECTOR_L2_DISTANCE to find the most relevant documents for a given query embedding.
Considering Snowflake’s capabilities, which of the following statements are true regarding the use of vector types and VECTOR_L2_DISTANCE? (Select all that apply)
- A . Document embeddings, which are typically float arrays, can be stored in a VARIANT column to leverage Snowflake’s flexible schema capabilities, and then cast to VECTOR when calling VECTOR_L2_DISTANCE
- B . O When defining a table column for 1024-dimensional float embeddings, the SQL type specification VECTOR(FLOAT, 1024) is valid.
- C . Using the Snowpark Python library, developers can directly invoke
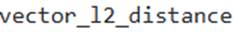
on DataFrame columns containing VECTOR data. - D . VECTOR columns can be designated as clustering keys to improve performance for queries involving VECTOR_L2_DISTANCE in ORDER BY clauses.
- E . To prevent issues with direct vector comparisons, explicitly using VECTOR_L2_DISTANCE is recommended over operators like
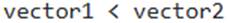
, as direct comparisons are byte-wise lexicographic.
B,C,E
Explanation:
Option A is incorrect. Vectors are explicitly not supported in
VARIANT
columns.
Option B is correct. The
VECTOR
data type supports elements of type
FLOAT
and a dimension up to 4096. Therefore,
VECTOR(FLOAT, 1024)
is a valid type specification.
Option C is correct. The Snowpark Python library supports the
VECTOR
data type and provides functions like
vector_12_distance
for distance calculations on DataFrame columns.
Option D is incorrect. The
VECTOR
data type is not supported as a clustering key.
Option E is correct. Direct vector comparisons using operators like
![]()
are byte-wise lexicographic and do not produce semantically expected results for numerical comparisons; dedicated vector similarity functions like
VECTOR_L2_DISTANCE
should be used instead.
A data science team is fine-tuning a mistral-lb model within Snowflake Cortex using proprietary customer interaction logs.
Which of the following principles and practices apply to this fine-tuning process concerning data privacy, model ownership, and subsequent inference?
- A . The proprietary customer interaction logs used for fine-tuning are leveraged by Snowflake to improve the base mistral -7b model for all customers.
- B . The resulting fine-tuned model is exclusively available to the data science team and cannot be accessed by other Snowflake customers.
- C . The fine-tuning process occurs entirely within Snowflake’s security and governance boundaries, ensuring the data never leaves the Snowflake environment.
- D . The fine-tuned model, which is a CORTEX_FINETUNED type, can be shared with other Snowflake accounts using secure data sharing.
- E . The fine-tuned model is fully managed by the Snowflake Model Registry API, allowing programmatic management of its lifecycle.
B,C,D
Explanation:
Cortex Fine-tuning is a fully managed service that lets you fine-tune popular LLMs using your data, all within Snowflake. Your Usage and Customer Data (including inputs and outputs) are NOT used to train, re-train, or fine-tune Models made available to others. Fine-tuned Models built using your data can only be used by you.
Therefore, Option A is incorrect.
Options B and C are correct, as the fine-tuned model is exclusive to the customer, and the process is managed within Snowflake’s boundaries.
Option D is also correct because models generated with Cortex Fine- tuning (CORTEX_FINETUNED type) can be shared using Data Sharing.
Option E is incorrect because Cortex Fine-Tuned LLMs appear in the model registry’s Snowsight UI, but are not managed by the model registry API.
