Practice Free FCSS_NST_SE-7.6 Exam Online Questions
In the SAML negotiation process, which section does the Identity Provider (IdP) provide the SAML attributes utilized in the authentication process to the Service Provider (SP)?
- A . SP Login dump
- B . Authentication Response
- C . Authentication Request
- D . Assertion dump
Refer to the exhibit.
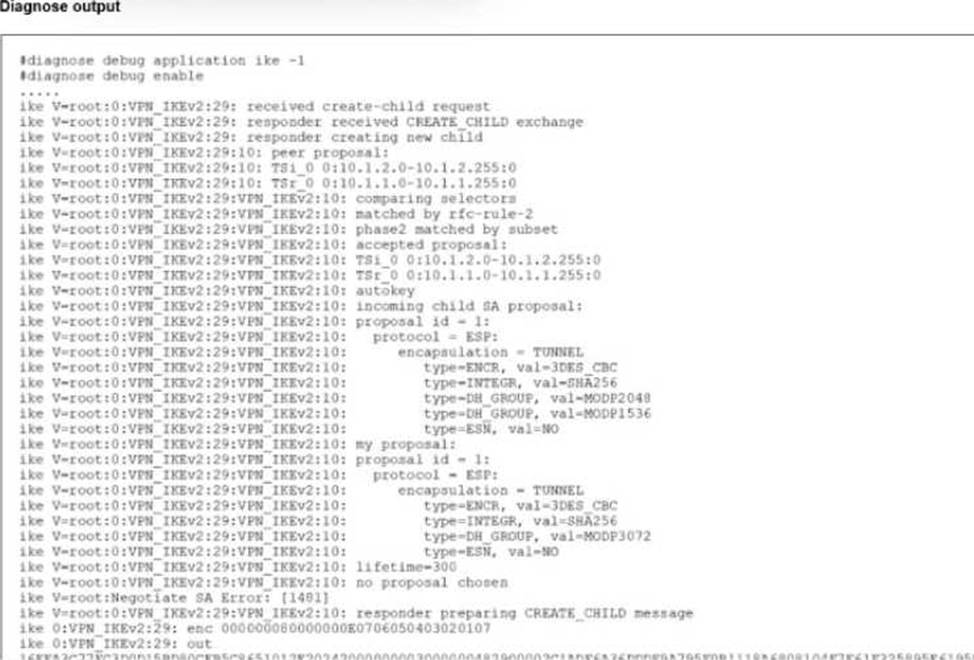
An IPsec VPN tunnel using IKEv2 was brought up successfully, but when the tunnel rekey takes place the tunnel goes down.
The debug command for IKE was enabled and, in the exhibit, you can review the partial output of the debug IKE while attempting to bring the tunnel up.
What is causing. The tunnel to be down?
- A . A Diffie-Hellman mismatch
- B . Blocked traffic on UDP port 500
- C . A mismatch m the Phase 1 negotiations
- D . A mismatch in the Phase 2 negotiations
A
Explanation:
To determine the cause of the failure, we must analyze the IKEv2 debug output provided in the exhibit (image_ad3dc6.jpg):
Identify the Negotiation Phase:
The debug log shows: responder received CREATE_CHILD exchange.
In IKEv2, the CREATE_CHILD_SA exchange is used to create new Child SAs (Phase 2) or to rekey existing ones.
The fact that the tunnel was previously "brought up successfully" implies the initial IKE SA (Phase 1) is stable, and this error is occurring specifically during a rekey event, which often involves Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS).
Analyze the Proposals (The Mismatch):
Incoming Proposal (Remote Peer):
The remote peer sends a proposal containing two Diffie-Hellman groups: type=DH_GROUP, val=MODP2048 (Group 14) and type=DH_GROUP, val=MODP1536 (Group 5).
My Proposal (Local FortiGate):
The local FortiGate configuration expects: type=DH_GROUP, val=MODP3072 (Group 15).
Result of the Negotiation:
The debug output concludes with: no proposal chosen and Negotiate SA Error.
This error occurs because the local FortiGate cannot find a common Diffie-Hellman group between what it requires (Group 15) and what the peer is offering (Groups 14 or 5).
While this is technically a mismatch occurring during the Phase 2 (Child SA) creation, "A Diffie-Hellman mismatch" (Option A) is the precise root cause identified in the logs.
Why other options are incorrect:
B: The log shows received create-child request, confirming that UDP traffic is reaching the device and is not blocked.
C: The failure is in the CREATE_CHILD exchange (Phase 2/Rekey), not the IKE_SA_INIT or IKE_AUTH (Phase 1) exchanges.
D: While the mismatch is occurring within the Phase 2 definitions, Option A is the specific technical reason for the no proposal chosen error shown in the DH_GROUP lines.
Reference: FortiGate Security 7.6 Study Guide (IPsec VPN): "Phase 2 parameters… if Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS) is enabled, a Diffie-Hellman exchange is performed again. Both peers must match the DH Group."
Refer to the exhibit.

An IPsec VPN tunnel using IKEv2 was brought up successfully, but when the tunnel rekey takes place the tunnel goes down.
The debug command for IKE was enabled and, in the exhibit, you can review the partial output of the debug IKE while attempting to bring the tunnel up.
What is causing. The tunnel to be down?
- A . A Diffie-Hellman mismatch
- B . Blocked traffic on UDP port 500
- C . A mismatch m the Phase 1 negotiations
- D . A mismatch in the Phase 2 negotiations
A
Explanation:
To determine the cause of the failure, we must analyze the IKEv2 debug output provided in the exhibit (image_ad3dc6.jpg):
Identify the Negotiation Phase:
The debug log shows: responder received CREATE_CHILD exchange.
In IKEv2, the CREATE_CHILD_SA exchange is used to create new Child SAs (Phase 2) or to rekey existing ones.
The fact that the tunnel was previously "brought up successfully" implies the initial IKE SA (Phase 1) is stable, and this error is occurring specifically during a rekey event, which often involves Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS).
Analyze the Proposals (The Mismatch):
Incoming Proposal (Remote Peer):
The remote peer sends a proposal containing two Diffie-Hellman groups: type=DH_GROUP, val=MODP2048 (Group 14) and type=DH_GROUP, val=MODP1536 (Group 5).
My Proposal (Local FortiGate):
The local FortiGate configuration expects: type=DH_GROUP, val=MODP3072 (Group 15).
Result of the Negotiation:
The debug output concludes with: no proposal chosen and Negotiate SA Error.
This error occurs because the local FortiGate cannot find a common Diffie-Hellman group between what it requires (Group 15) and what the peer is offering (Groups 14 or 5).
While this is technically a mismatch occurring during the Phase 2 (Child SA) creation, "A Diffie-Hellman mismatch" (Option A) is the precise root cause identified in the logs.
Why other options are incorrect:
B: The log shows received create-child request, confirming that UDP traffic is reaching the device and is not blocked.
C: The failure is in the CREATE_CHILD exchange (Phase 2/Rekey), not the IKE_SA_INIT or IKE_AUTH (Phase 1) exchanges.
D: While the mismatch is occurring within the Phase 2 definitions, Option A is the specific technical reason for the no proposal chosen error shown in the DH_GROUP lines.
Reference: FortiGate Security 7.6 Study Guide (IPsec VPN): "Phase 2 parameters… if Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS) is enabled, a Diffie-Hellman exchange is performed again. Both peers must match the DH Group."
Refer to the exhibit, which shows a partial output of a real-time LDAP debug.
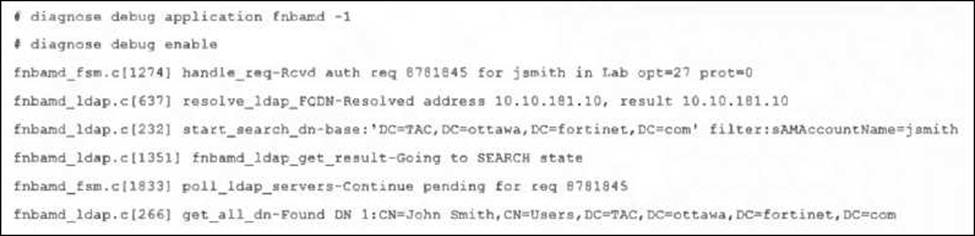
What two conclusions can you draw from the output? (Choose two.)
- A . The user was found in the LDAP tree, whose root is TAC.ottawa.fortinet.com.
- B . FortiOS performs a bind to the LDAP server using the user’s credentials.
- C . FortiOS collects the user group information.
- D . FortiOS is performing the second step (Search Request) in the LDAP authentication process.
Which two observations can you make from the output? (Choose two.)
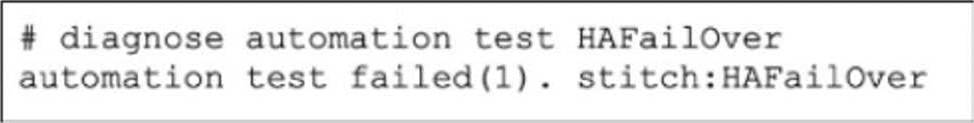
- A . The configuration was backed up
- B . A high availability (HA) failover occurred.
- C . The lest was unsuccessful.
- D . The automation stitch test is not being logged.
C,D
Explanation:
We must analyze the specific CLI output provided in the exhibit to determine the observations.
Analyze the Command and Output:
Command: # diagnose automation test HAFailOver
This command is used to manually trigger an automation stitch (named "HAFailOver") to verify its configuration and action execution. It simulates the trigger event to run the defined actions.
![]()
Output: automation test failed(1). stitch:HAFailOver
The output explicitly states that the test failed. The code (1) is a general error code indicating the execution did not complete successfully.
Evaluate the Options:
What is the correct order of the IKEv2 request-and-response protocol?
- A . Create_Child_SA, IKEAUTH, IKESAJNIT
- B . Create_Child_SA, IKE_SA_INIT. IKE_AUTH
- C . IKE SA INIT, IKE AUTH. Create Child SA OIKE AUTH.
- D . IKE_AUTH_IKE_SA_INIT, Create_Child_SA
C
Explanation:
The Internet Key Exchange version 2 (IKEv2) protocol simplifies the negotiation process compared to IKEv1. It is defined by a specific sequence of message exchanges to establish a secure IPsec tunnel.
The correct chronological order of the IKEv2 exchanges is:
IKE_SA_INIT (Initial Exchange):
This is the first exchange. It negotiates the security parameters for the IKE Security Association (IKE SA), sends nonces, and performs the Diffie-Hellman key exchange. At the end of this exchange, the communication is encrypted, but the peers are not yet authenticated. IKE_AUTH (Authentication Exchange):
This is the second exchange. It authenticates the previous messages, exchanges identities and certificates (if used), and establishes the first Child SA (the actual IPsec Security Association used for data traffic).
CREATE_CHILD_SA (Subsequent Exchanges):
This exchange occurs after the IKE SA and the initial Child SA are established. It is used to create additional Child SAs (for different traffic selectors) or to perform re-keying for the IKE SA or existing Child SAs.
Why other options are incorrect:
A & B: Incorrect because CREATE_CHILD_SA cannot happen before the SA is initialized (IKE_SA_INIT) and authenticated (IKE_AUTH).
D: Incorrect because IKE_AUTH cannot occur before IKE_SA_INIT.
Therefore, the protocol flow is IKE_SA_INIT $rightarrow$ IKE_AUTH $rightarrow$
CREATE_CHILD_SA.
Refer to the exhibit.
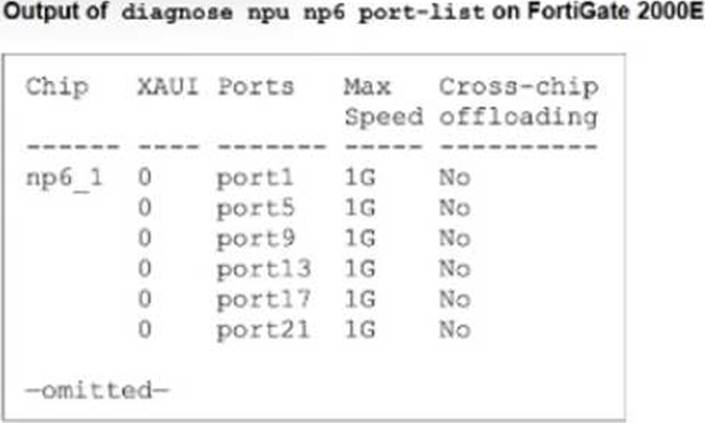
A partial output of diagnose npu up6 port-list on FortiGate 2000E is shown.
An administrator is unable to analyze traffic flowing between port1 and port17 using the diagnose sniffer command.
Which two commands allow the administrator to view the traffic? (Choose two.)
A)
![]()
B)

C)
![]()
D)

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
B,C
Explanation:
The administrator cannot see traffic in the sniffer because it is being offloaded to the NPU (NP6). To view the traffic, offloading must be disabled so packets pass through the CPU.
B. config firewall policy … set auto-asic-offload disable: This is the recommended method to troubleshoot specific traffic. By disabling ASIC offloading in the relevant firewall policies (Policies 5 and 17 in the exhibit), traffic is forced to the CPU and becomes visible to the sniffer.
C. diagnose npu np6 fastpath disable 1: This command temporarily disables the fastpath processing on the specific NP6 processor (ID 1) handling the ports. This forces all traffic handled by that NPU to the CPU, allowing the sniffer to capture it.
Incorrect Options: Option A uses invalid syntax (port-list disable is not a valid command).
Option D (config system npu) is not the standard method for granular troubleshooting.
Refer to the exhibits.
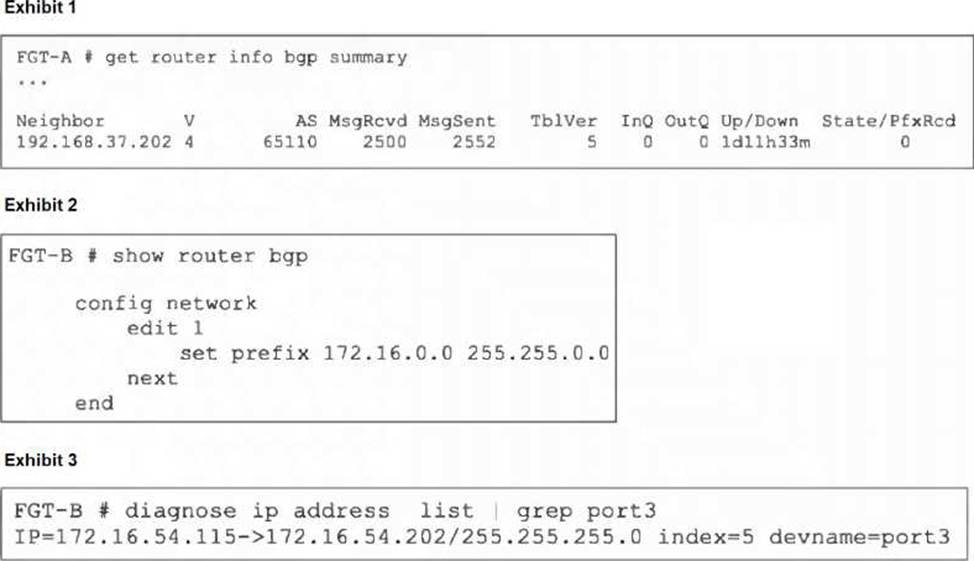
An administrator is attempting to advertise the network configured on port3. However, FGT-A is not receiving the prefix.
Which two actions can the administrator take to fix this problem? (Choose two.)
- A . Modify the prefix using the network command from 172.16.0.0/16 to 172.16.54.0/24.
- B . Manually add the BGP route on FGT-A.
- C . Restart BGP using a soft reset to force both peers to exchange their complete BGP routing tables.
- D . Use the set network-import-check disable command.
Refer to the exhibit.

An IPsec VPN tunnel is dropping, as shown by the debug output.
Analyzing the debug output, what could be causing the tunnel to go down?
- A . Phase 2 drops but Phase 1 is up.
- B . Dead Peer Detection is not receiving its acknowledge packet.
- C . The tunnel drops during rekey negotiation.
- D . The tunnel drops after the timer expires.
Refer to the exhibit.

An IPsec VPN tunnel is dropping, as shown by the debug output.
Analyzing the debug output, what could be causing the tunnel to go down?
- A . Phase 2 drops but Phase 1 is up.
- B . Dead Peer Detection is not receiving its acknowledge packet.
- C . The tunnel drops during rekey negotiation.
- D . The tunnel drops after the timer expires.
