Practice Free FCSS_EFW_AD-7.6 Exam Online Questions
An administrator must standardize the deployment of FortiGate devices across branches with consistent interface roles and policy packages using FortiManager.
What is the recommended best practice for interface assignment in this scenario?
- A . Enable metadata variables to use dynamic configurations in the standard interfaces of FortiManager.
- B . Use the Install On feature in the policy package to automatically assign different interfaces based on the branch.
- C . Create interfaces using device database scripts to use them on the same policy package of FortiGate devices.
- D . Create normalized interface types per-platform to automatically recognize device layer interfaces based on the FortiGate model and interface name.
A
Explanation:
When standardizing the deployment of FortiGate devices across branches using FortiManager, the best practice is to use metadata variables. This allows for dynamic interface configuration while maintaining a single, consistent policy package for all branches.
● Metadata variables in FortiManager enable interface roles and configurations to be dynamically assigned based on the specific FortiGate device.
● This ensures scalability and consistent security policy enforcement across all branches without manually adjusting interface settings for each device.
● When a new branch FortiGate is deployed, metadata variables automatically map to the correct physical interfaces, reducing manual configuration errors.
A company that acquired multiple branches across different countries needs to install new FortiGate devices on each of those branches. However, the IT staff lacks sufficient knowledge to implement the initial configuration on the FortiGate devices.
Which three approaches can the company take to successfully deploy advanced initial configurations on remote branches? (Choose three.)
- A . Use metadata variables to dynamically assign values according to each FortiGate device.
- B . Use provisioning templates and install configuration settings at the device layer.
- C . Use the Global ADOM to deploy global object configurations to each FortiGate device.
- D . Apply Jinja in the FortiManager scripts for large-scale and advanced deployments.
- E . Add FortiGate devices on FortiManager as model devices, and use ZTP or LTP to connect to FortiGate devices.
A, B, E
Explanation:
Use metadata variables to dynamically assign values according to each FortiGate device:
Metadata variables in FortiManager allow device-specific configurations to be dynamically assigned without manually configuring each FortiGate. This is especially useful when deploying multiple devices with similar base configurations.
Use provisioning templates and install configuration settings at the device layer:
Provisioning templates in FortiManager provide a structured way to configure FortiGate devices. These templates can define interfaces, policies, and settings, ensuring that each device is correctly
configured upon deployment.
Add FortiGate devices on FortiManager as model devices, and use ZTP or LTP to connect to FortiGate devices:
Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP) and Local Touch Provisioning (LTP) help automate the deployment of FortiGate devices. By adding devices as model devices in FortiManager, configurations can be pushed automatically when devices connect for the first time, reducing manual effort.
Refer to the exhibit, which shows a hub and spokes deployment.
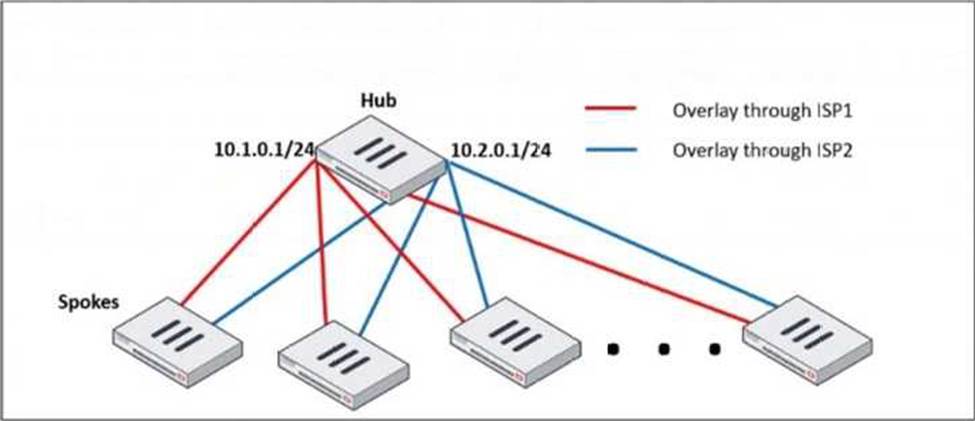
An administrator is deploying several spokes, including the BGP configuration for the spokes to connect to the hub.
Which two commands allow the administrator to minimize the configuration? (Choose two.)
- A . neighbor-group
- B . route-reflector-client
- C . neighbor-range
- D . ibgp-enforce-multihop
A, C
Explanation:
neighbor-group:
● This command is used to group multiple BGP neighbors with the same configuration, reducing redundant configuration.
● Instead of defining individual BGP settings for each spoke, the administrator can create a neighbor-group and apply the same policies, reducing manual work.
neighbor-range:
● This command allows the configuration of a range of neighbor IPs dynamically, reducing the need to manually define each spoke neighbor.
● It automatically adds BGP neighbors that match a given prefix, simplifying deployment.
Refer to the exhibit, which shows an enterprise network connected to an internet service provider.
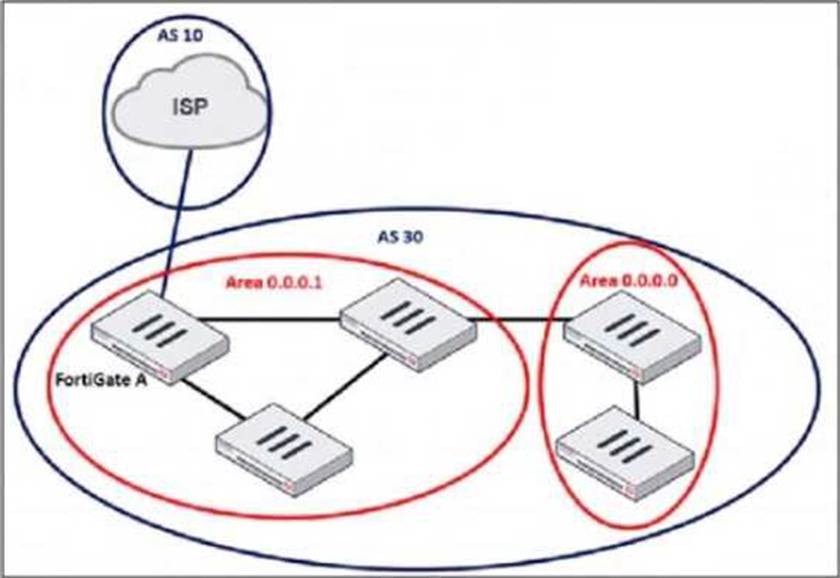
The administrator must configure the BGP section of FortiGate A to give internet access to the enterprise network.
Which command must the administrator use to establish a connection with the internet service provider?
- A . config neighbor
- B . config redistribute bgp
- C . config router route-map
- D . config redistribute ospf
A
Explanation:
In BGP (Border Gateway Protocol), a neighbor (peer) configuration is required to establish a connection between two BGP routers. Since FortiGate A is connecting to the ISP (Autonomous System 10) from AS 30, the administrator must define the ISP’s BGP router as a neighbor.
The config neighbor command is used to:
● Define the ISP’s IP address as a BGP peer
● Specify the remote AS (AS 10 in this case)
● Allow BGP route exchanges between FortiGate A and the ISP
Refer to the exhibit, which shows a partial troubleshooting command output.
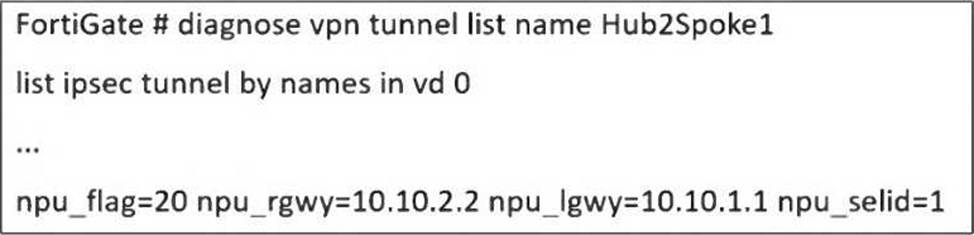
An administrator is extensively using IPsec on FortiGate. Many tunnels show information similar to
the output shown in the exhibit.
What can the administrator conclude?
- A . IPsec SAs cannot be offloaded.
- B . The two IPsec SAs, inbound and outbound, are copied to the NPU.
- C . Only the outbound IPsec SA is copied to the NPU.
- D . Only the inbound IPsec SA is copied to the NPU.
A
Explanation:
Based on the FortiGate Infrastructure 7.6 study guide and the Hardware Acceleration technical documentation, the diagnose vpn tunnel list command provides the status of IPsec tunnel offloading to the Network Processor (NPU).
In the provided exhibit, the specific value npu_flag=20 (which corresponds to 0x20 in hexadecimal) indicates that the IPsec Security Association (SA) cannot be offloaded to the NPU. While the NPU may have visibility of the gateway IPs (npu_rgwy and npu_lgwy), the flag itself serves as a diagnostic indicator that the traffic must be processed by the system CPU rather than the hardware accelerator.
This lack of offloading typically occurs when the tunnel configuration uses a cipher (encryption algorithm) or an HMAC (authentication algorithm) that is not supported by the specific NPU model installed in the FortiGate. For example, if a tunnel is configured with a legacy or highly complex algorithm that the NP6 or NP7 chip is not designed to process in hardware, the FortiOS kernel handles the encryption and decryption, resulting in the npu_flag=20 status. Therefore, despite the presence of NPU-related fields, the specific flag value confirms that hardware acceleration is not active for these SAs.
An administrator must minimize CPU and RAM use on a FortiGate firewall while also enabling essential security features, such as web filtering and application control for HTTPS traffic.
Which SSL inspection setting helps reduce system load while also enabling security features, such as web filtering and application control for encrypted HTTPS traffic?
- A . Use full SSL inspection to thoroughly inspect encrypted payloads.
- B . Disable SSL inspection entirely to conserve resources.
- C . Configure SSL inspection to handle HTTPS traffic efficiently.
- D . Enable SSL certificate inspection mode to perform basic checks without decrypting traffic.
D
Explanation:
To minimize CPU and RAM usage while still enforcing security features like web filtering and application control, SSL certificate inspection mode is the best choice.
● SSL certificate inspection allows FortiGate to inspect only the SSL/TLS handshake, including the Server Name Indication (SNI) and certificate details, without decrypting the full encrypted payload.
● This enables features like web filtering and application control because FortiGate can determine the destination website or application based on SNI and certificate information.
● It significantly reduces system load compared to full SSL inspection, which requires full decryption and re-encryption of traffic.
An administrator must minimize CPU and RAM use on a FortiGate firewall while also enabling essential security features, such as web filtering and application control for HTTPS traffic.
Which SSL inspection setting helps reduce system load while also enabling security features, such as web filtering and application control for encrypted HTTPS traffic?
- A . Use full SSL inspection to thoroughly inspect encrypted payloads.
- B . Disable SSL inspection entirely to conserve resources.
- C . Configure SSL inspection to handle HTTPS traffic efficiently.
- D . Enable SSL certificate inspection mode to perform basic checks without decrypting traffic.
D
Explanation:
To minimize CPU and RAM usage while still enforcing security features like web filtering and application control, SSL certificate inspection mode is the best choice.
● SSL certificate inspection allows FortiGate to inspect only the SSL/TLS handshake, including the Server Name Indication (SNI) and certificate details, without decrypting the full encrypted payload.
● This enables features like web filtering and application control because FortiGate can determine the destination website or application based on SNI and certificate information.
● It significantly reduces system load compared to full SSL inspection, which requires full decryption and re-encryption of traffic.
Refer to the exhibit, which shows a revision history window in the FortiManager device layer.
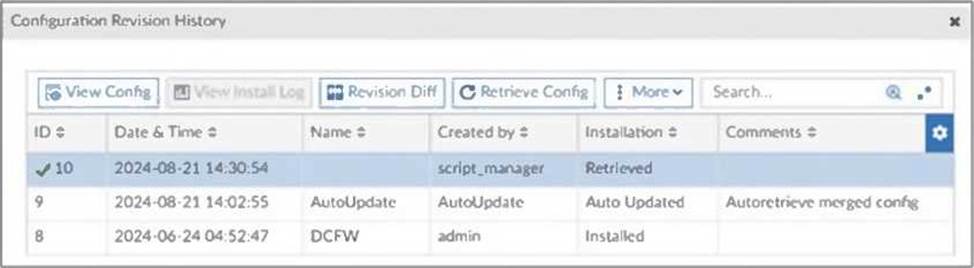
The IT team is trying to identify the administrator responsible for the most recent update in the FortiGate device database.
Which conclusion can you draw about this scenario?
- A . This retrieved process was automatically triggered by a Remote FortiGate Directly (via CLI) script.
- B . The user script_manager is an API user from the Fortinet Developer Network (FDN) retrieving a configuration.
- C . To identify the user who created the event, check it on the Configuration and Installation widget on FortiGate within the FortiManager device layer.
- D . Find the user in the FortiManager system logs and use the type=script command to find the administrator user in the user field.
D
Explanation:
The Configuration Revision History window in FortiManager shows that the most recent configuration change (ID 10) was created by script_manager with the action Retrieved.
Since script_manager is a system-level script execution user, the IT team needs to find who actually triggered this script. This can be done by:
● Checking the FortiManager system logs for script execution events.
● Using the type=script filter to locate the administrator associated with the script execution.
An administrator configured the FortiGate devices in an enterprise network to join the Fortinet Security Fabric. The administrator has a list of IP addresses that must be blocked by the data center firewall. This list is updated daily.
How can the administrator automate a firewall policy with the daily updated list?
- A . With FortiNAC
- B . With FortiAnalyzer
- C . With a Security Fabric automation
- D . With an external connector from Threat Feeds
D
Explanation:
The best way to automate a firewall policy using a daily updated list of IP addresses is by using an external connector from Threat Feeds. This allows FortiGate to dynamically retrieve real-time threat intelligence from external sources and apply it directly to security policies.
By configuring Threat Feeds, the administrator can:
● Automatically update firewall policies with the latest malicious IPs daily.
● Block traffic from those IPs in real-time without manual intervention.
● Integrate with FortiGuard, third-party threat intelligence sources, or custom feeds (CSV,
STIX/TAXII, etc.).
Refer to the exhibit, which shows the ADVPN IPsec interface representing the VPN IPsec phase 1 from Hub A to Spoke 1 and Spoke 2, and from Hub В to Spoke 3 and Spoke 4.
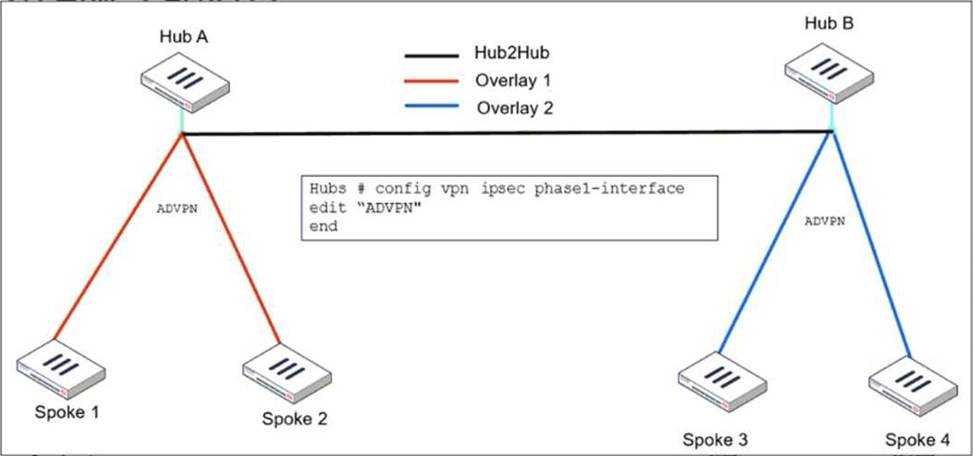
An administrator must configure an ADVPN using IBGP and EBGP to connect overlay network 1 with 2.
What must the administrator configure in the phase 1 VPN IPsec configuration of the ADVPN tunnels?
- A . set auto-discovery-sender enable and set network-id x
- B . set auto-discovery-forwarder enable and set remote-as x
- C . set auto-discovery-crossover enable and set enforce-multihop enable
- D . set auto-discovery-receiver enable and set npu-offload enable
C
Explanation:
When configuring ADVPN (Auto-Discovery VPN) to connect overlay networks across different hubs using IBGP and EBGP, special configurations are required to allow spokes from different overlay networks to dynamically establish tunnels.
● set auto-discovery-crossover enable
● This allows cross-hub tunnel discovery in an ADVPN deployment where multiple hubs are used.
● Since Hub A and Hub B belong to different overlays, enabling crossover discovery ensures that spokes from one overlay can dynamically create direct tunnels to spokes in the other overlay when needed.
● set enforce-multihop enable
● This setting ensures that BGP peers using loopback interfaces can establish connectivity even if they are not directly connected.
● Multihop BGP sessions are required when using loopback addresses as BGP peer sources because the connection might need to traverse multiple routers before reaching the BGP neighbor.
● This is especially useful in ADVPN deployments with multiple hubs, where routes might need to cross from one hub to another.
