Practice Free FCSS_EFW_AD-7.6 Exam Online Questions
A user reports that their computer was infected with malware after accessing a secured HTTPS website. However, when the administrator checks the FortiGate logs, they do not see that the website was detected as insecure despite having an SSL certificate and correct profiles applied on the policy.
How can an administrator ensure that FortiGate can analyze encrypted HTTPS traffic on a website?
- A . The administrator must enable reputable websites to allow only SSL/TLS websites rated by FortiGuard web filter.
- B . The administrator must enable URL extraction from SNI on the SSL certificate inspection to ensure the TLS three-way handshake is correctly analyzed by FortiGate.
- C . The administrator must enable DNS over TLS to protect against fake Server Name Indication (SNI) that cannot be analyzed in common DNS requests on HTTPS websites.
- D . The administrator must enable full SSL inspection in the SSL/SSH Inspection Profile to decrypt packets and ensure they are analyzed as expected.
D
Explanation:
FortiGate, like other security appliances, cannot analyze encrypted HTTPS traffic unless it decrypts it first. If only certificate inspection is enabled, FortiGate can see the certificate details (such as the domain and issuer) but cannot inspect the actual web content.
To fully analyze the traffic and detect potential malware threats:
● Full SSL inspection (Deep Packet Inspection) must be enabled in the SSL/SSH Inspection Profile.
● This allows FortiGate to decrypt the HTTPS traffic, inspect the content, and then re-encrypt it before forwarding it to the user.
● Without full SSL inspection, threats embedded in encrypted traffic may go undetected.
Refer to the exhibit, which shows a command output.

FortiGate_A and FortiGate_B are members of an FGSP cluster in an enterprise network.
While testing the cluster using the ping command, the administrator monitors packet loss and found that the session output on FortiGate_B is as shown in the exhibit.
What could be the cause of this output on FortiGate_B?
- A . The session synchronization is encrypted.
- B . session-pickup-connectionless is set to disable on FortiGate_B.
- C . FortiGate_B is configured in passive mode.
- D . FortiGate_A and FortiGate_B have the same standalone-group-id value.
B
Explanation:
The Fortinet FGSP (FortiGate Session Life Support Protocol) cluster allows session synchronization between two FortiGate devices to provide seamless failover. However, ICMP (ping) is a connectionless protocol, and by default, FortiGate does not synchronize connectionless sessions unless explicitly enabled.
In the exhibit:
● The command get system session list | grep icmp on FortiGate_B returns no output, meaning that ICMP sessions are not being synchronized from FortiGate_A.
● If session-pickup-connectionless is disabled, FortiGate_B will not receive ICMP sessions, causing packet loss during failover.
Refer to the exhibit, which shows a command output.

FortiGate_A and FortiGate_B are members of an FGSP cluster in an enterprise network.
While testing the cluster using the ping command, the administrator monitors packet loss and found that the session output on FortiGate_B is as shown in the exhibit.
What could be the cause of this output on FortiGate_B?
- A . The session synchronization is encrypted.
- B . session-pickup-connectionless is set to disable on FortiGate_B.
- C . FortiGate_B is configured in passive mode.
- D . FortiGate_A and FortiGate_B have the same standalone-group-id value.
B
Explanation:
The Fortinet FGSP (FortiGate Session Life Support Protocol) cluster allows session synchronization between two FortiGate devices to provide seamless failover. However, ICMP (ping) is a connectionless protocol, and by default, FortiGate does not synchronize connectionless sessions unless explicitly enabled.
In the exhibit:
● The command get system session list | grep icmp on FortiGate_B returns no output, meaning that ICMP sessions are not being synchronized from FortiGate_A.
● If session-pickup-connectionless is disabled, FortiGate_B will not receive ICMP sessions, causing packet loss during failover.
The IT department discovered during the last network migration that all zero phase selectors in phase 2 IPsec configurations impacted network operations.
What are two valid approaches to prevent this during future migrations? (Choose two.)
- A . Use routing protocols to specify allowed subnets over the tunnel.
- B . Configure an IPsec-aggregate to create redundancy between each firewall peer.
- C . Clearly indicate to the VPN which segments will be encrypted in the phase two selectors.
- D . Configure an IP address on the IPsec interface of each firewall to establish unique peer connections and avoid impacting network operations.
A, C
Explanation:
Zero phase selectors in IPsec Phase 2 mean that no specific traffic selectors (subnets) are defined, allowing any traffic to be encrypted through the VPN tunnel. This can cause unintended traffic forwarding issues and disrupt network operations.
To prevent this from happening during future migrations:
● Using routing protocols ensures that only specific subnets are advertised over the tunnel. Dynamic routing (such as OSPF or BGP) helps define which networks should use the tunnel, preventing unintended traffic from being encrypted.
● Clearly defining phase 2 selectors avoids the problem of encrypting all traffic by explicitly stating the allowed source and destination subnets. This prevents the tunnel from affecting unrelated network traffic.
A company’s guest internet policy, operating in proxy mode, blocks access to Artificial Intelligence Technology sites using FortiGuard. However, a guest user accessed a page in this category using port 8443.
Which configuration changes are required for FortiGate to analyze HTTPS traffic on nonstandard ports like 8443 when full SSL inspection is active in the guest policy?
- A . Add a URL wildcard domain to the website CA certificate and use it in the SSL/SSH Inspection Profile.
- B . In the Protocol Port Mapping section of the SSL/SSH Inspection Profile, enter 443, 8443 to analyze both standard (443) and non-standard (8443) HTTPS ports.
- C . To analyze nonstandard ports in web filter profiles, use TLSv1.3 in the SSL/SSH Inspection Profile.
- D . Administrators can block traffic on nonstandard ports by enabling the SNI check in the SSL/SSH Inspection Profile.
B
Explanation:
When FortiGate is operating in proxy mode with full SSL inspection enabled, it inspects encrypted HTTPS traffic by default on port 443. However, some websites may use non-standard HTTPS ports (such as 8443), which FortiGate does not inspect unless explicitly configured.
To ensure that FortiGate inspects HTTPS traffic on port 8443, administrators must manually add port 8443 in the Protocol Port Mapping section of the SSL/SSH Inspection Profile. This allows FortiGate to treat HTTPS traffic on port 8443 the same as traffic on port 443, enabling proper inspection and enforcement of FortiGuard category-based web filtering.
A company’s guest internet policy, operating in proxy mode, blocks access to Artificial Intelligence Technology sites using FortiGuard. However, a guest user accessed a page in this category using port 8443.
Which configuration changes are required for FortiGate to analyze HTTPS traffic on nonstandard ports like 8443 when full SSL inspection is active in the guest policy?
- A . Add a URL wildcard domain to the website CA certificate and use it in the SSL/SSH Inspection Profile.
- B . In the Protocol Port Mapping section of the SSL/SSH Inspection Profile, enter 443, 8443 to analyze both standard (443) and non-standard (8443) HTTPS ports.
- C . To analyze nonstandard ports in web filter profiles, use TLSv1.3 in the SSL/SSH Inspection Profile.
- D . Administrators can block traffic on nonstandard ports by enabling the SNI check in the SSL/SSH Inspection Profile.
B
Explanation:
When FortiGate is operating in proxy mode with full SSL inspection enabled, it inspects encrypted HTTPS traffic by default on port 443. However, some websites may use non-standard HTTPS ports (such as 8443), which FortiGate does not inspect unless explicitly configured.
To ensure that FortiGate inspects HTTPS traffic on port 8443, administrators must manually add port 8443 in the Protocol Port Mapping section of the SSL/SSH Inspection Profile. This allows FortiGate to treat HTTPS traffic on port 8443 the same as traffic on port 443, enabling proper inspection and enforcement of FortiGuard category-based web filtering.
To secure your enterprise network traffic, which step does FortiGate perform first, when handling the first packets of a session? (Choose one answer)
- A . Installation of the session key in the network processor (NP)
- B . Decryption
- C . A reverse path forwarding (RPF) check
- D . IP integrity header checking
D
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed 150 to 200 words of Explanation From Exact Extract of Enterprise Firewall 7.6 Administrator documents:
Based on the FortiOS 7.6 Administration Guide and the Life of a Packet documentation (Parallel Path Processing), the FortiGate follows a specific, hardcoded sequence when processing the first packet of a new session. This process is divided into several stages: Ingress, Kernel, and Egress.
The very first stage is Ingress, where all packets accepted by a network interface are processed by the TCP/IP stack. Immediately following this, the packet must pass through IP integrity header checking. This step involves reading the packet headers to verify that the packet is a valid protocol (TCP, UDP, ICMP, etc.) and that the header length is correct. This sanity check is performed before any other security functions, such as decryption (which occurs later in the Ingress stage) or the Reverse Path Forwarding (RPF) check (which occurs even later during the Routing step in the Kernel stage).
Installation of the session key (Option A) only occurs after the packet has matched a firewall policy and the session has been fully established and offloaded to the NPU. Therefore, IP integrity header checking is the absolute first security-related validation performed on an incoming packet.
Refer to the exhibit.
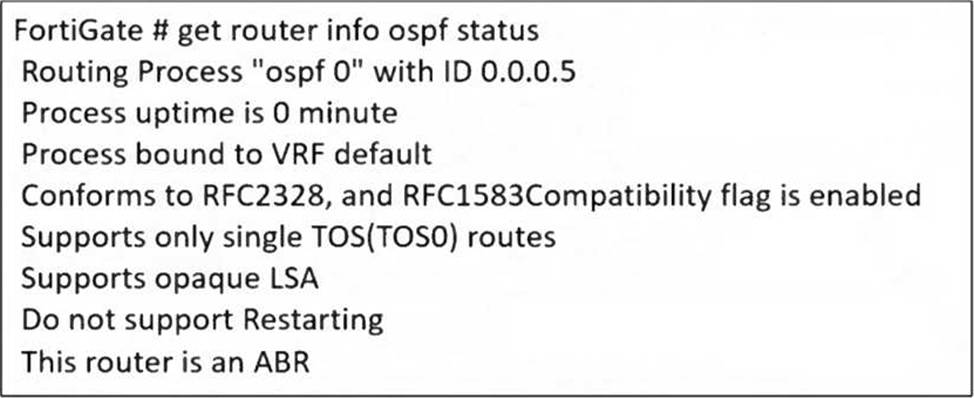
The partial output of an OSPF command is shown. While checking the OSPF status of FortiGate, you receive the output shown in the exhibit.
Based on the output, which two statements about FortiGate are correct? (Choose two answers)
- A . FortiGate has OSPF ECMP enabled.
- B . FortiGate is a backup designated router.
- C . FortiGate injects external routing information.
- D . FortiGate is connected to multiple areas.
A, D
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed 150 to 200 words of Explanation From Exact Extract of Enterprise Firewall 7.6 Administrator documents:
Based on the FortiOS 7.6 Infrastructure study guide and official documentation regarding OSPF monitoring, the command output get router info ospf status provides critical details about the OSPF process.
Multiple Areas (Option D): The last line of the exhibit explicitly states, "This router is an ABR" (Area Border Router). By definition in the OSPF protocol, an ABR is a router that is connected to multiple OSPF areas, typically Area 0 (the backbone) and at least one other non-backbone area.
OSPF ECMP (Option A): The output indicates that the OSPF process "Conforms to RFC2328". RFC 2328 is the standard for OSPFv2, which includes the capability for Equal-Cost Multi-Path (ECMP). In FortiOS, when OSPF is enabled and multiple routes to the same destination have the same cost, ECMP is supported by default unless specifically limited by the maximum-paths configuration. The mention of this RFC compliance in the status output confirms the engine’s capability and support for multi-path routing.
Option C is incorrect because the output does not label the device as an ASBR (Autonomous System Boundary Router), which would be required to inject external routing information.
Option B is incorrect because "ABR" refers to area hierarchy, not the election status (DR/BDR) on a specific network segment.
A FortiGate device with UTM profiles is reaching the resource limits, and the administrator expects the traffic in the enterprise network to increase.
The administrator has received an additional FortiGate of the same model.
Which two protocols should the administrator use to integrate the additional FortiGate device into this enterprise network? (Choose two.)
- A . FGSP with external load balancers
- B . FGCP in active-active mode and with switches
- C . FGCP in active-passive mode and with VDOM disabled
- D . VRRP with switches
A, B
Explanation:
When adding an additional FortiGate to an enterprise network that is already reaching its resource limits, the goal is to distribute traffic efficiently and ensure high availability.
FGSP (FortiGate Session Life Support Protocol) with external load balancers
– FGSP allows session-aware load balancing between multiple FortiGate units without requiring them to be in an HA (High Availability) cluster.
– With external load balancers, incoming traffic is evenly distributed across multiple FortiGate devices.
– This approach is useful for scaling out traffic handling capacity while ensuring that sessions remain synchronized between firewalls.
– FGSP is effective when stateful failover is required but without the constraints of traditional HA.
FGCP (FortiGate Clustering Protocol) in active-active mode and with switches
– FGCP active-active mode enables multiple FortiGate devices to share traffic loads, increasing throughput and efficiency.
– Active-active mode is suitable for balancing UTM processing across multiple FortiGates, making it ideal when resource limits are a concern.
– Using switches ensures redundancy and avoids single points of failure in the network.
– This mode is commonly used in enterprise networks where both scalability and redundancy are required.
Refer to the exhibits.
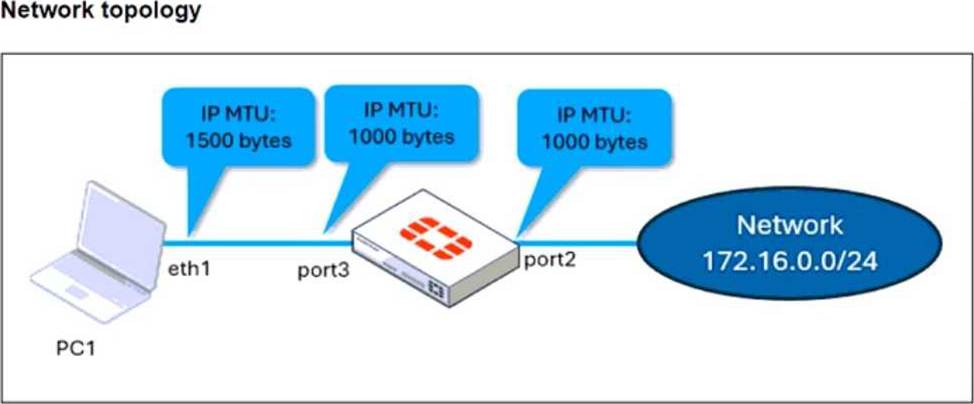
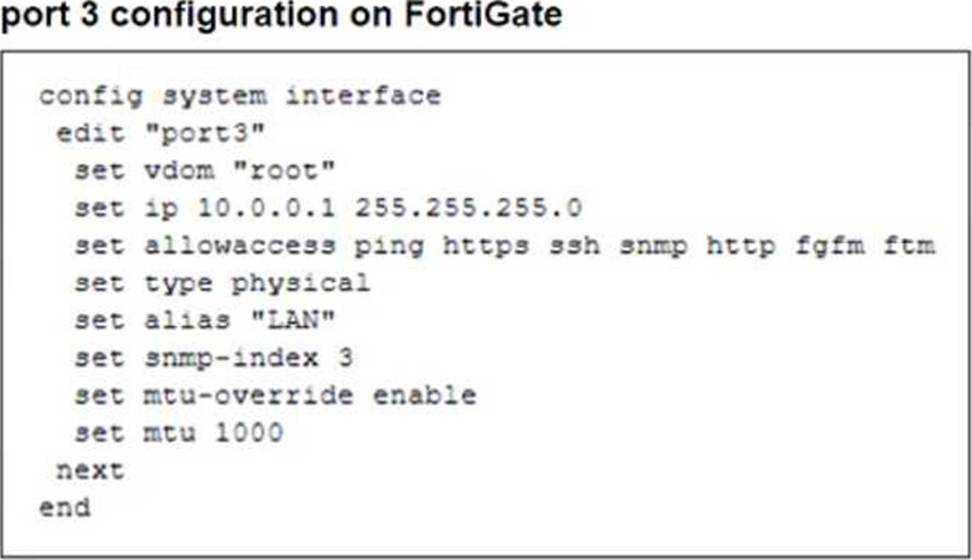
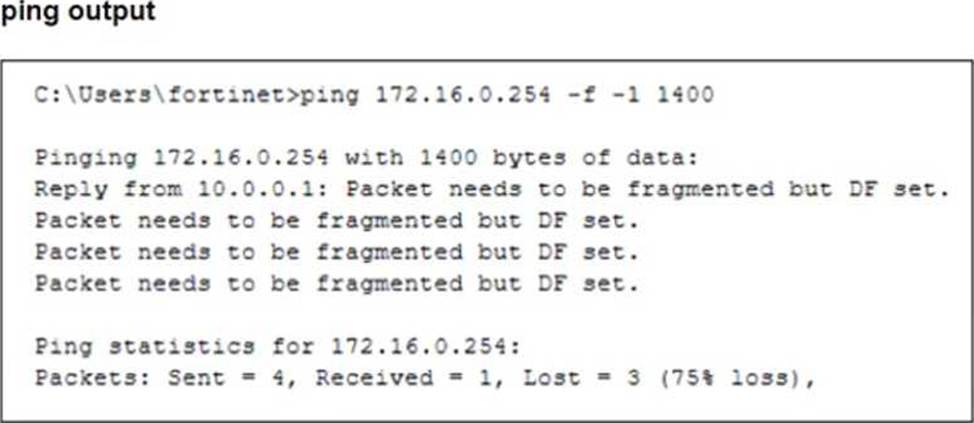
The configuration of a user’s Windows PC, which has a default MTU of 1500 bytes, along with FortiGate interfaces set to an MTU of 1000 bytes, and the results of PC1 pinging server 172.16.0.254 are shown.
Why is the user in Windows PC1 unable to ping server 172.16.0.254 and is seeing the message:
Packet needs to be fragmented but DF set?
- A . Option ip.flags.mf must be set to enable on FortiGate. The user has to adjust the ping MTU to 1000 to succeed.
- B . Fragmented packets must be encrypted. To connect any application successfully, the user must install the Fortinet_CA certificate in the Microsoft Management Console.
- C . FortiGate honors the do not fragment bit and the packets are dropped. The user has to adjust the ping MTU to 972 to succeed.
- D . The user must trigger different traffic because path MTU discovery techniques do not recognize ICMP payloads.
C
Explanation:
The issue occurs because FortiGate enforces the "do not fragment" (DF) bit in the packet, and the packet size exceeds the MTU of the network path. When the Windows PC1 (with an MTU of 1500 bytes) attempts to send a 1400-byte packet, the FortiGate interface (with an MTU of 1000 bytes) needs to fragment it. However, since the DF bit is set, FortiGate drops the packet instead of fragmenting it.
To resolve this, the user should adjust the ping packet size to fit within the path MTU. In this case, reducing the packet size to 972 bytes (1000 bytes MTU minus 28 bytes for the IP and ICMP headers) should allow successful transmission.
