Practice Free FCP_FMG_AD-7.6 Exam Online Questions
A service provider administrator has assigned a global policy package to a managed customer ADOM named My_ADOM. The customer administrator has access only to My_ADOM.
How can the customer administrator edit the global header policy of the global policy package?
- A . The customer administrator can edit the header policy by using workspace mode on the global ADOM.
- B . The customer administrator can edit the header policy by using workflow mode on the global ADOM and My_ADOM.
- C . The service provider administrator can unlock the global policy from the global ADOM to authorize changes to the customer administrator.
- D . The customer administrator cannot edit the global header policy; only the service provider administrator can make changes from the global ADOM.
D
Explanation:
The global policy package is managed only from the global ADOM by the service provider administrator. Customer administrators with access solely to their ADOM (My_ADOM) cannot edit the global header policy; such changes must be made by the service provider administrator in the global ADOM.
Refer to the exhibit.

What are two results from the configuration shown in the exhibit? (Choose two.)
- A . Ungraceful closed sessions will keep the ADOM in a locked state until the administrator session times out.
- B . The administrator can lock policy blocks and FortiManager global ADOM.
- C . The same administrator can lock more than one ADOM at the same time.
- D . The administrator must have access to the ADOM to approve changes.
A, B
Explanation:
In normal workspace mode, ungraceful session closures will keep the ADOM locked until the session times out, preventing other administrators from editing.
Normal workspace mode allows administrators to lock policy blocks and the global ADOM, providing granular locking control.
Refer to the exhibit.
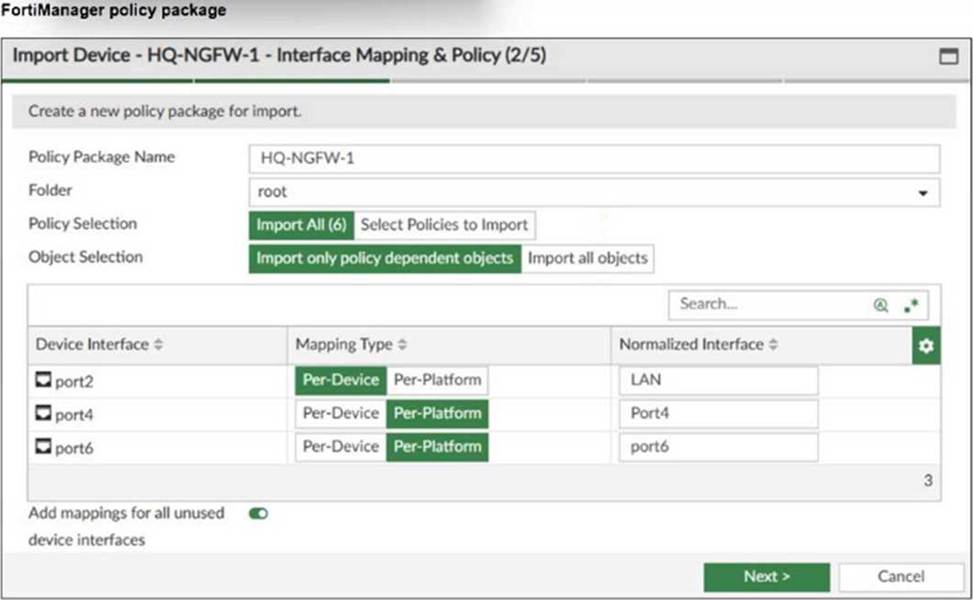
An administrator added a FortiGate device to FortiManager with the default object settings at the ADOM layer.
What can you conclude from the import policy package process of the HQ-NGFW- 1 device?
- A . The administrator must select Per Platform for all interfaces to correctly detect all interfaces from HQ-NGFW-1.
- B . The administrator must manually create the port4 interface on the ADOM layer to avoid import policy errors.
- C . FortiManager will create LAN, port4, and port6 as normalized interfaces at the ADOM layer.
- D . FortiGate may not work as expected when the administrator does not import all objects.
C
Explanation:
The import process shows that FortiManager will create normalized interfaces named LAN, port4, and port6 at the ADOM layer, mapping them to the corresponding device interfaces based on the import settings.
Refer to the exhibit.
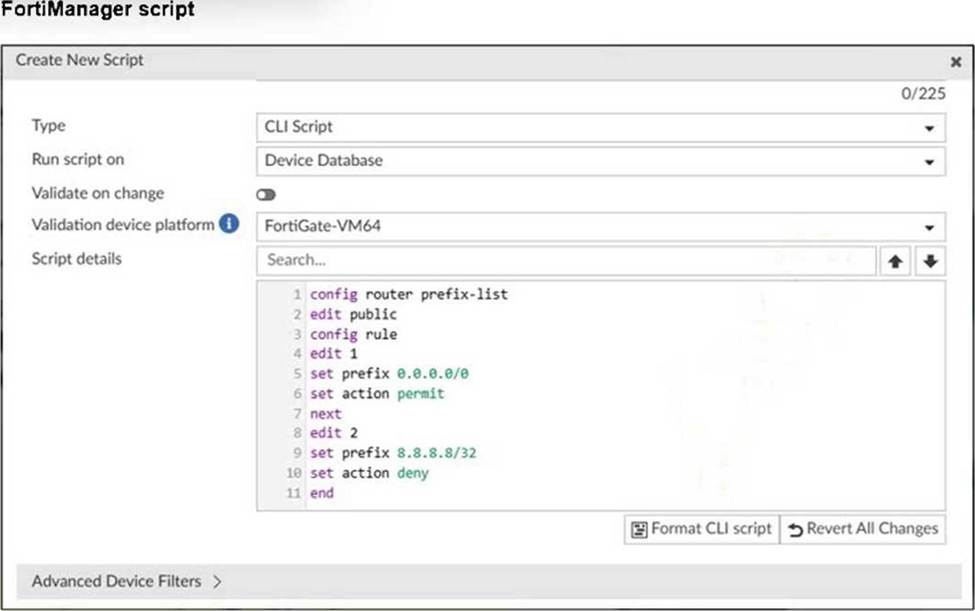
Which two results occur if you run the script using the Device Database option? (Choose two.)
- A . The device Config Status is tagged as Modified.
- B . The script history shows the successful installation of the script on the remote FortiGate.
- C . The successful execution of a script on the Device Database creates a new revision history.
- D . The administrator must install these changes on a managed device using the Install Wizard.
A, D
Explanation:
Running a script on the Device Database marks the configuration as modified but does not immediately apply changes to the device.
The administrator must use the Install Wizard to push and install these changes from the Device Database onto the managed device.
The administrator uses FortiManager to push a CLI script using the Remote FortiGate Directly (via CLI) option to configure an IPsec VPN.
However, when running the script, the administrator receives the following error:
config vpn ipsec phase2-interface [parameter(s) invalid. detail: object mismatch]
What must the administrator do to resolve the script error and successfully apply the IPsec configuration?
- A . Add the end command after finishing the IPsec phase 1-interface configuration block.
- B . Use IPsec templates to deploy provisioning templates.
- C . Add a second config vpn ipsec phase2-interface block without linking it to phase1.
- D . Run the script using the policy package or ADOM database method.
D
Explanation:
Running the script through the policy package or ADOM database method allows FortiManager to properly interpret object relationships and dependencies in the IPsec configuration, preventing object mismatch errors when pushing complex VPN settings directly via CLI.
What is the purpose of ADOM revisions?
- A . ADOM revisions find unused, duplicate, and unnecessary firewall policies and objects.
- B . ADOM revisions show specific changes in a policy package when it is installed.
- C . ADOM revisions compare previous snapshots of the Policy Package and ADOM-level objects with the device-level database.
- D . ADOM revisions save the current state of all policy packages and objects for an ADOM.
D
Explanation:
ADOM revisions save the current state of all policy packages and objects within an ADOM, allowing administrators to track changes over time and revert to previous configurations if needed.
Which two conditions trigger FortiManager to create a new revision history? (Choose two.)
- A . When FortiManager installs device-level changes on a managed device
- B . When changes to the device-level database are made on FortiManager
- C . When FortiManager is auto-updated with configuration changes made directly on a managed device
- D . When a provisioning template is assigned to a managed device on the device-level database
B, C
Explanation:
FortiManager creates a new revision history entry whenever changes are made to the device-level database on FortiManager.
FortiManager also creates a new revision when it auto-updates its database with configuration changes detected directly on a managed device.
Company policy dictates that any time a change is made to a policy package on FortiManager an ADOM revision is created before the change installed, and that revision is held for a minimum of 90 days.
Over the past three months, each installed change has resulted in several unused policies and duplicate objects.
The FortiManager administrator plans to upgrade the FortiGate devices and then upgrade the FortiManager ADOM from version 7.4 to 7.6.
Which action can the administrator take to avoid slow ADOM upgrades?
- A . Check and repair the global configuration database before upgrading.
- B . Export firewall policies to Excel, delete them on the ADOM. then reimport them after upgrading the ADOM.
- C . Find unused firmware templates, then delete them before upgrading.
- D . Limit ADOM revisions before upgrading.
D
Explanation:
Limiting ADOM revisions reduces the number of stored historical configurations, which helps avoid performance degradation and slow ADOM upgrades caused by a large volume of revisions.
Refer to the exhibit.
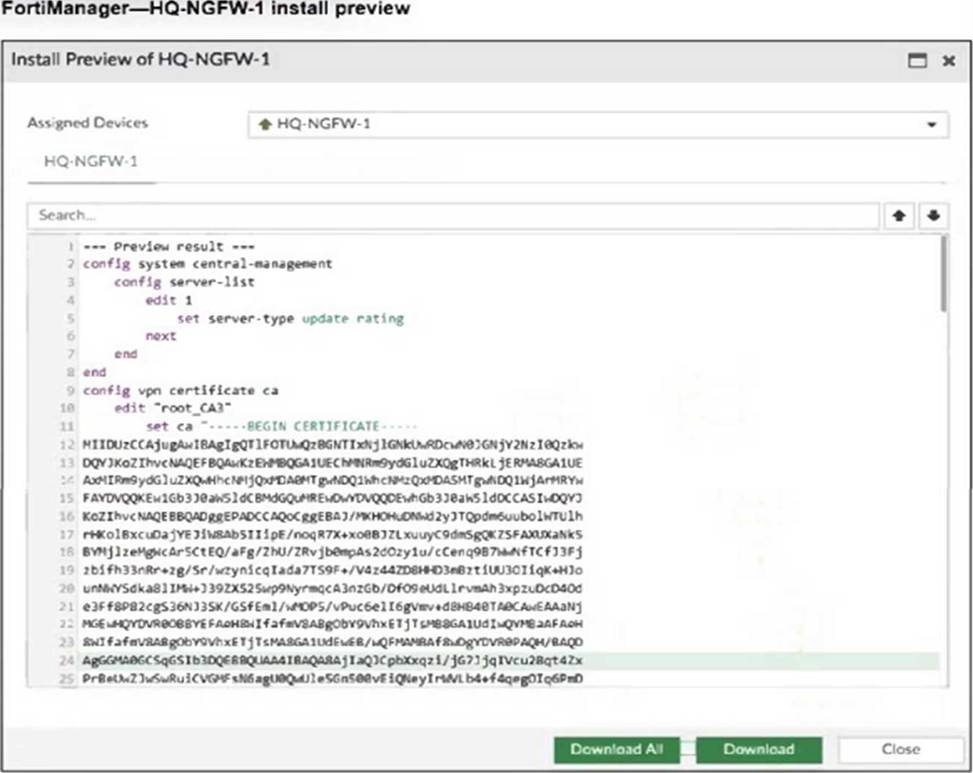
An administrator assigned a new policy package to FortiGate HQ-NGFW-1. In the installation preview, they noticed some settings they did not modify and are unsure about the changes.
Based on the exhibit, which two things will happen if they continue with the installation? (Choose two.)
- A . FortiGate HQ-NGFW-1 can use FortiManager firmware templates to upgrade firmware and ratings.
- B . FortiGate HQ-NGFW-1 can contact the FortiManager acting as FortiGuard Distribution Server (FDS) to download FortiGuard updates.
- C . FortiGate HQ-NGFW-1 will use the root_CA3 certificate in firewall address objects or policies.
- D . FortiManager will install the CA certificate named root_CA3 to authenticate FortiGate-to-FortiManager communication protocol (FGFM) tunnel connections with FortiGate HQ- NGFW-1.
B, D
Explanation:
The configuration includes a server-list with server-type set to "update rating," which enables FortiGate HQ-NGFW-1 to contact FortiManager as a FortiGuard Distribution Server (FDS) for FortiGuard updates.
The installation includes a root_CA3 certificate, which FortiManager will install on FortiGate HQ-NGFW-1 to authenticate FGFM tunnel connections between the devices.
An administrator is copying a system template profile between ADOMs by running the following command:
execute fmprofile export-profile ADOM 3547 /tmp/Backup_File output dump to file: [/tmp/Backup_File]
Where does this command export the system template profile from?
- A . FortiManager /tmp/Backup_File folder
- B . FortiManager ADOM policy database
- C . ADOM device database
- D . FortiManager configuration backup file
B
Explanation:
The command exports the system template profile from the FortiManager ADOM policy database, which stores the configuration templates for devices within that ADOM.
