Practice Free FCP_FGT_AD-7.6 Exam Online Questions
Refer to the exhibits.
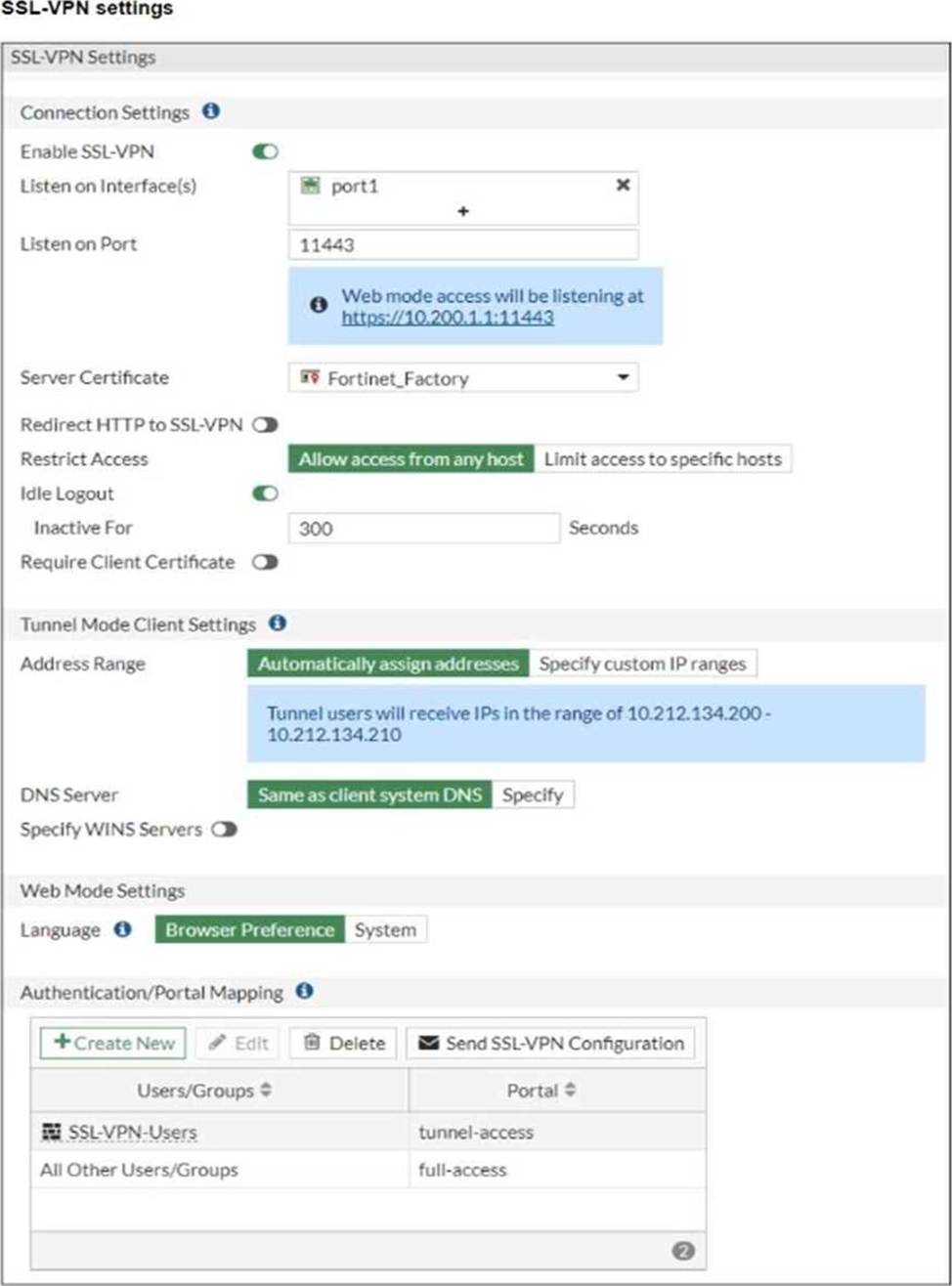
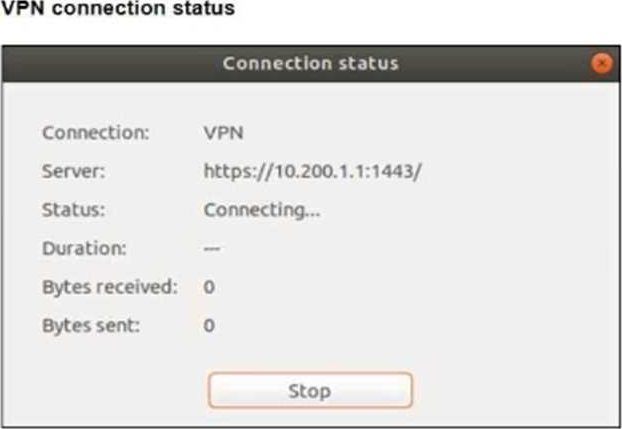
The SSL VPN connection fails when a user attempts to connect to it.
What should the user do to successfully connect to the SSL VPN?
- A . Change the SSL VPN portal to the tunnel.
- B . Change the idle timeout.
- C . Change the server IP address.
- D . Change the SSL VPN port on the client.
D
Explanation:
The SSL VPN is configured to listen on port 11443 on the FortiGate device, as shown in the SSL VPN settings in the exhibit. However, the user is attempting to connect to the server using port 1443, as displayed in the VPN connection status. The mismatch between the ports is causing the connection failure. To resolve this, the user should change the client configuration to use port 11443 to match the FortiGate SSL VPN configuration.
Which three security features require the intrusion prevention system (IPS) engine to function? (Choose three.)
- A . Web filter in flow-based inspection
- B . Antivirus in flow-based inspection
- C . DNS filter
- D . Web application firewall
- E . Application control
A,B,E
Explanation:
Refer to the exhibit to view the application control profile.
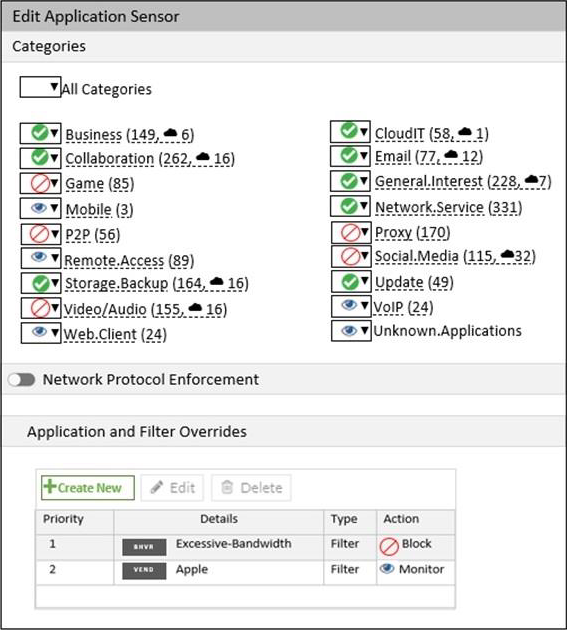
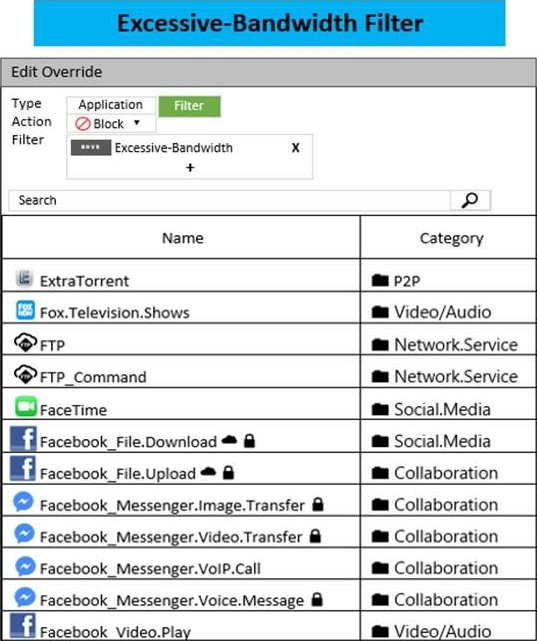
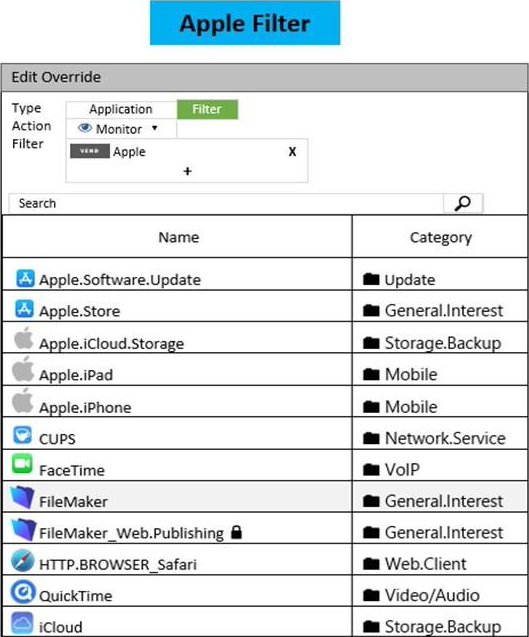

Based on the configuration, what will happen to Apple FaceTime?
- A . Apple FaceTime will be allowed, based on the Apple filter configuration.
- B . Apple FaceTime will be allowed, based on the Categories configuration.
- C . Apple FaceTime will be blocked, based on the Excessive-Bandwidth filter configuration.
- D . Apple FaceTime will be allowed only if the filter in Application and Filter Overrides is set to Learn.
C
Explanation:
Apple facetime will be blocked according to the "Excessive Bandwidth" filter.
Facetime belongs to VoIP category which is monitored here and therefore should be allowed, however, because of the behavior of the facetime "Excessive-Bandwidth", the custom filter Excessive-Bandwidth will block Facetime and the lookup won’t continue to the second filter.
The excessive bandwidth filter contains facetime and is referenced by the application sensor with the action to block. There is no reference to a bandwidth threshold at which point the filter is applied so the number of calls is irrelevant.
Examine the IPS sensor and DoS policy configuration shown in the exhibit, then answer the question below.
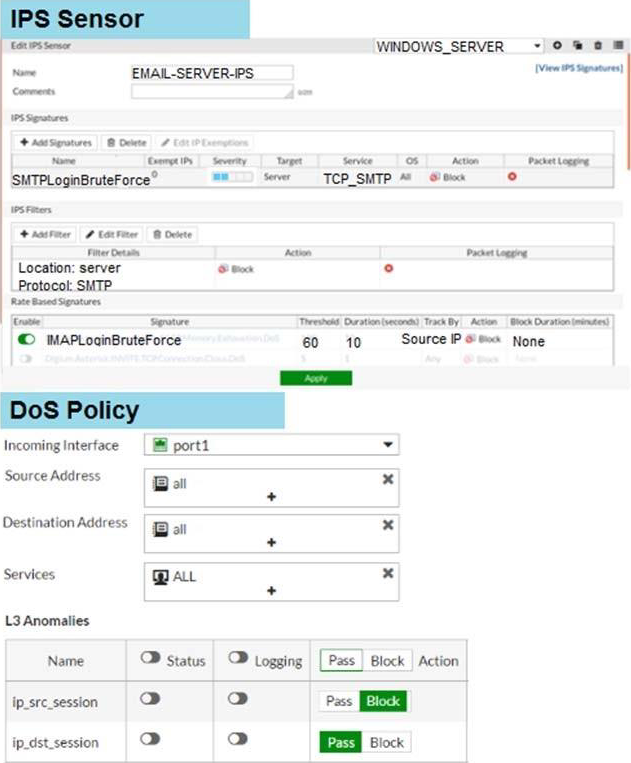
When detecting attacks, which anomaly, signature, or filter will FortiGate evaluate first?
- A . SMTP.Login.Brute.Force
- B . IMAP.Login.brute.Force
- C . ip_src_session
- D . Location: server Protocol: SMTP
B
Explanation:
IMAP.Login.brute.Force
Anomalies can be zero-day or denial of service attack
Are Detected by behaivoral analysis:
Rate Based IPS Signatures.
DoS Policies.
Protocol Constraint Inspections.
DoS policy disabled in this scenario.
Refer to the exhibits.
Exhibit A.
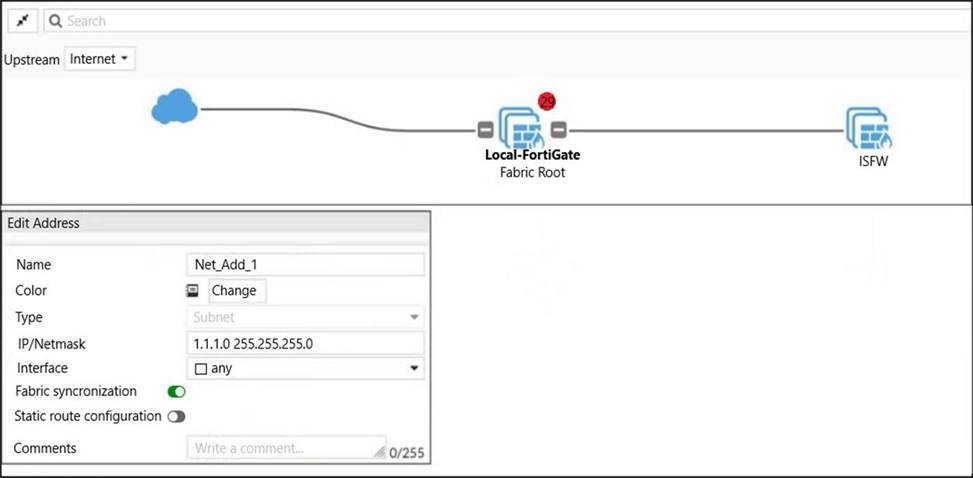
Exhibit B.
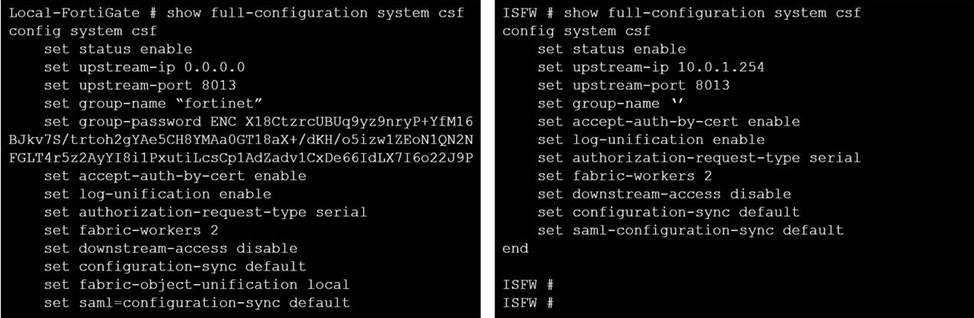
An administrator creates a new address object on the root FortiGate (Local-FortiGate) in the security fabric. After synchronization, this object is not available on the downstream FortiGate (ISFW).
What must the administrator do to synchronize the address object?
- A . Change the csf setting on Local-FortiGate (root) to set configuration-sync local.
- B . Change the csf setting on ISFW (downstream) to set configuration-sync local.
- C . Change the csf setting on Local-FortiGate (root) to set fabric-object-unification default.
- D . Change the csf setting on ISFW (downstream) to set fabric-object-unification default.
C
Explanation:
Change the csf setting on Local-FortiGate (root) to set fabric-object-unification default.
The CLI command set fabric-object-unification is only available on the root FortiGate. When set to local, global objects will not be synchronized to downstream devices in the Security Fabric. The default value is default.
Option A will not synchronise global fabric objects downstream.
Which security fabric feature causes an event trigger to monitor the network when a threat is detected?
- A . Security rating
- B . Optimization
- C . Automation stiches
- D . Fabric connectors
C
Explanation:
Automation stitches
In the context of the Fortinet Security Fabric, automation stitches are responsible for orchestrating responses to security events. When a threat is detected, automation stitches can trigger events to monitor the network, coordinate responses, and ensure a synchronized defense across the entire security fabric. Therefore, option C is the correct answer.
Each automation stitch pairs an event trigger and one or more actions, it allows you to monitor your network and take appropiate action when SecFabric detects a threat.
Which three settings and protocols can be used to provide secure and restrictive administrative access to FortiGate? (Choose three.)
- A . SSH
- B . FortiTelemetry
- C . Trusted host
- D . HTTPS
- E . Trusted authentication
A,C,D
Explanation:
To provide secure and restrictive administrative access to FortiGate, the following three settings and protocols can be used:
Which security feature does FortiGate provide to protect servers located in the internal networks from attacks such as SQL injections?
- A . Denial of Service
- B . Web application firewall
- C . Antivirus
- D . Application control
B
Explanation:
Some FortiGate features are meant to protect clients, not servers. For example, FortiGuard web filtering blocks requests based on the category of the server’s web pages. Antivirus prevents clients from accidentally downloading spyware and worms. Neither protects a server (which doesn’t send requests―it receives them) from malicious scripts or SQL injections. Protecting web servers requires a different approach because they are subject to other kinds of attacks. This is where WAF applies. The WAF feature is available only in proxy inspection mode.
Web Application Firewall (WAF) is a security feature that protects web applications from a variety of attacks, including SQL injections. It analyzes and filters HTTP traffic between a web application and the internet to block malicious attempts to exploit vulnerabilities in the application. By monitoring and filtering HTTP traffic, WAF helps prevent attacks such as SQL injections, cross-site scripting (XSS), and other web application vulnerabilities.
Which three CLI commands, can you use to troubleshoot Layer 3 issues if the issue is in neither the physical layer nor the link layer? (Choose three.)
- A . execute ping
- B . execute traceroute
- C . diagnose sys top
- D . get system arp
- E . diagnose sniffer packet any
A, B, E
Explanation:
execute ping
This command helps test network connectivity by sending ICMP echo requests to a specified IP address to check if the device is reachable.
execute traceroute
This command traces the route packets take to a destination, which is useful for identifying network
hops and potential delays or routing issues.
get system arp
This command shows the ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) table, which is used to map IP addresses to MAC addresses. It’s useful for verifying IP-to-MAC address resolution on the network.
Refer to the exhibit.
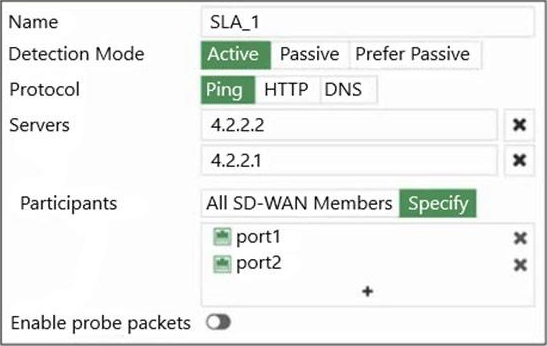
An administrator has configured a performance SLA on FortiGate, which failed to generate any traffic.
Why is FortiGate not sending probes to 4.2.2.2 and 4.2.2.1 servers? (Choose two.)
- A . The Detection Mode setting is not set to Passive.
- B . Administrator didn’t configure a gateway for the SD-WAN members, or configured gateway is not valid.
- C . The configured participants are not SD-WAN members.
- D . The Enable probe packets setting is not enabled.
B,D
Explanation:
The correct answers are:
B. Administrator didn’t configure a gateway for the SD-WAN members, or configured gateway is not valid.
D. The Enable probe packets setting is not enabled.
For option B, if the gateway for the SD-WAN members is not configured or is not valid, the FortiGate will not be able to send traffic through the SD-WAN members to reach the servers.
For option D, if the "Enable probe packets" setting is not enabled, the FortiGate will not send probe packets to the specified servers to check the health of the SD-WAN members.
