Practice Free FCP_FGT_AD-7.6 Exam Online Questions
Which two statements about SSL VPN between two FortiGate devices are true? (Choose two.)
- A . The client FortiGate requires a client certificate signed by the CA on the server FortiGate.
- B . The client FortiGate requires a manually added route to remote subnets.
- C . The client FortiGate uses the SSL VPN tunnel interface type to connect SSL VPN.
- D . Server FortiGate requires a CA certificate to verify the client FortiGate certificate.
C,D
Explanation:
C. The client FortiGate uses the SSL VPN tunnel interface type to connect SSL VPN.
D. Server FortiGate requires a CA certificate to verify the client FortiGate certificate. Incorrect:
Refer to the exhibit, which contains a radius server configuration.
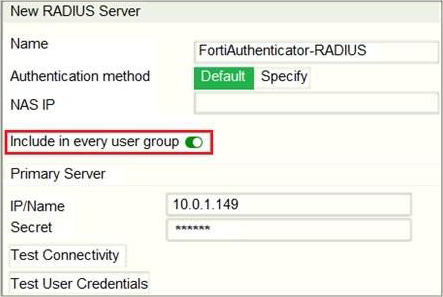
An administrator added a configuration for a new RADIUS server. While configuring, the administrator selected the Include in every user group option.
What will be the impact of using Include in every user group option in a RADIUS configuration?
- A . This option places the RADIUS server, and all users who can authenticate against that server, into every FortiGate user group.
- B . This option places all FortiGate users and groups required to authenticate into the RADIUS server, which, in this case, is FortiAuthenticator.
- C . This option places all users into every RADIUS user group, including groups that are used for the LDAP server on FortiGate.
- D . This option places the RADIUS server, and all users who can authenticate against that server, into
every RADIUS group.
A
Explanation:
The Include in every User Group option adds the RADIUS server and all users that can authenticate against it, to every user group created on FortiGate. So, you should enable this option only in very specific scenarios (for example, when only administrators can authenticate against the RADIUS server and policies are ordered from least restrictive to most restrictive).
An organization requires remote users to send external application data running on their PCs and access FTP resources through an SSUTLS connection.
Which FortiGate configuration can achieve this goal?
- A . SSL VPN quick connection
- B . SSL VPN tunnel
- C . SSL VPN bookmark
- D . Zero trust network access
B
Explanation:
An SSL VPN tunnel allows remote users to securely connect to the organization’s network and transmit all traffic, including external application data and FTP resources, through an encrypted SSL/TLS connection. This ensures secure access to the network while supporting various protocols such as FTP and other application-specific traffic from the user’s PC.
FortiGuard categories can be overridden and defined in different categories. To create a web rating override for the example.com home page, the override must be configured using a specific syntax.
Which two syntaxes are correct to configure a web rating override for the home page? (Choose two.)
- A . www.example.com
- B . www.example.com/index.html
- C . www.example.com:443
- D . example.com
A,D
Explanation:
FortiGate is integrated with FortiAnalyzer and FortiManager.
When a firewall policy is created, which attribute is added to the policy to improve functionality and to support recording logs to FortiAnalyzer or FortiManager?
- A . Log ID
- B . Policy ID
- C . Sequence ID
- D . Universally Unique Identifier
D
Explanation:
When a firewall policy is created in FortiGate integrated with FortiAnalyzer and FortiManager, a Universally Unique Identifier (UUID) is added to the policy to support logging and management.
FortiGate is integrated with FortiAnalyzer and FortiManager.
When a firewall policy is created, which attribute is added to the policy to improve functionality and to support recording logs to FortiAnalyzer or FortiManager?
- A . Log ID
- B . Policy ID
- C . Sequence ID
- D . Universally Unique Identifier
D
Explanation:
When a firewall policy is created in FortiGate integrated with FortiAnalyzer and FortiManager, a Universally Unique Identifier (UUID) is added to the policy to support logging and management.
Refer to the exhibit.
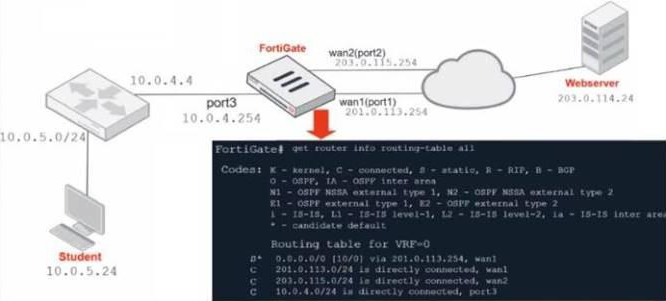
Which contains a network diagram and routing table output. The Student is unable to access Webserver.
What is the cause of the problem and what is the solution for the problem?
- A . The first packet sent from Student failed the RPF check. This issue can be resolved by adding a static route to 10.0.4.0/24 through wan1.
- B . The first reply packet for Student failed the RPF check. This issue can be resolved by adding a static route to 10.0.4.0/24 through wan1.
- C . The first reply packet for Student failed the RPF check. This issue can be resolved by adding a static route to 203.0.114.24/32 through port3.
- D . The first packet sent from Student failed the RPF check. This issue can be resolved by adding a static route to 203.0.114.24/32 through port3.
C
Explanation:
The first reply packet for Student failed the RPF check. This issue can be resolved by adding a static route to 203.0.114.24/32 through port3.
Option C is the correct answer based on the provided information, let’s analyze it:
Option C states: "The first reply packet for Student failed the RPF check. This issue can be resolved by adding a static route to 203.0.114.24/32 through port3."
The issue is related to the first reply packet from the Student failing the Reverse Path Forwarding (RPF) check and that adding a static route to 203.0.114.24/32 through "port3" will resolve the problem, then you can go ahead with this solution.
In a typical RPF check scenario, it ensures that the incoming packet is arriving on the expected interface based on the routing table. Adding a static route to 203.0.114.24/32 through "port3" may indeed resolve the RPF issue if the routing is misconfigured.
Option C is the correct solution based on your network setup and further analysis, you can proceed with implementing that static route to see if it resolves the issue. Additionally, it’s a good practice to monitor the network to ensure that the problem is indeed resolved after making the change.
Which engine handles application control traffic on the next-generation firewall (NGFW) FortiGate?
- A . Internet Service Database (ISDB) engine
- B . Intrusion prevention system engine
- C . Antivirus engine
- D . Application control engine
B
Explanation:
The application control engine on a FortiGate next-generation firewall is responsible for identifying and managing application traffic. It allows administrators to set policies based on application types, regardless of the port or protocol being used.
Refer to the exhibit.
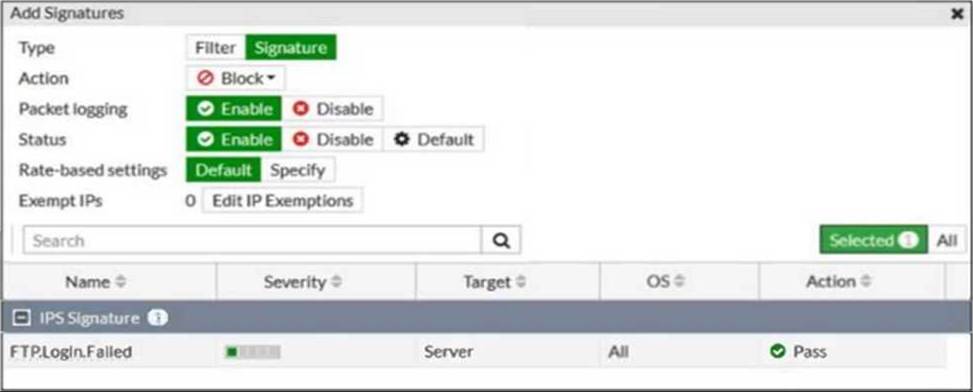
Review the intrusion prevention system (IPS) profile signature settings shown in the exhibit.
What do you conclude when adding the FTP.Login.Failed signature to the IPS sensor profile?
- A . Traffic matching the signature will be allowed and logged.
- B . The signature setting uses a custom rating threshold.
- C . The signature setting includes a group of other signatures.
- D . Traffic matching the signature will be silently dropped and logged.
D
Explanation:
The exhibit shows that the "FTP.Login.Failed" IPS signature is set with the action "Pass" and packet logging enabled. This means that any traffic matching this signature will be allowed through the FortiGate, and the traffic details will be logged for monitoring and analysis purposes.
Reference: FortiOS 7.4.1 Administration Guide: IPS Signature Actions
In which two ways can RPF checking be disabled? (Choose two.)
- A . Enable anti-replay in firewall policy.
- B . Enable asymmetric routing.
- C . Disable strict-src-check under system settings.
- D . Disable the RPF check at the FortiGate interface level for the source check.
B,D
Explanation:
B. Disabling the RPF check at the FortiGate interface level means that the FortiGate device won’t perform RPF checks for the specified interface, allowing traffic with source addresses that do not conform to RPF checks.
D. Enabling asymmetric routing means that the network allows different paths for incoming and outgoing traffic, and this can lead to situations where RPF checks may fail.
Option A is incorrect because enabling anti-replay in a firewall policy is not a method for disabling RPF checking. Anti-replay is a feature that helps prevent the insertion of malicious or duplicate packets into the network.
Option C is incorrect because disabling strict-src-check under system settings is not a valid option for
disabling RPF checking. Strict source checking is typically related to RPF checks, but disabling it might
not disable RPF checks entirely.
Reference: https://kb.fortinet.com/kb/documentLink.do?externalID=FD51279
https://community.fortinet.com/t5/FortiGate/Technical-Tip-How-to-disable-Reverse-Path-Forwarding-RPF -per/ta-p/193338
