Practice Free FCP_FGT_AD-7.6 Exam Online Questions
Refer to the exhibits.
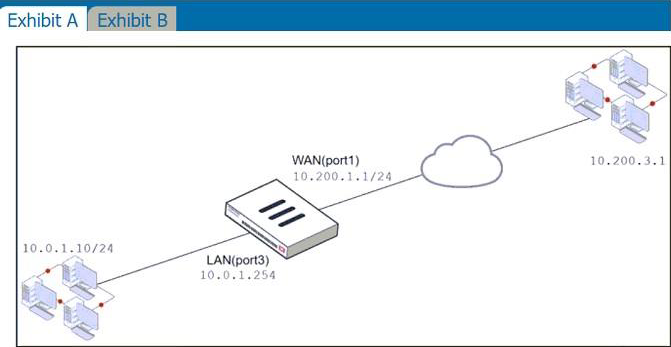
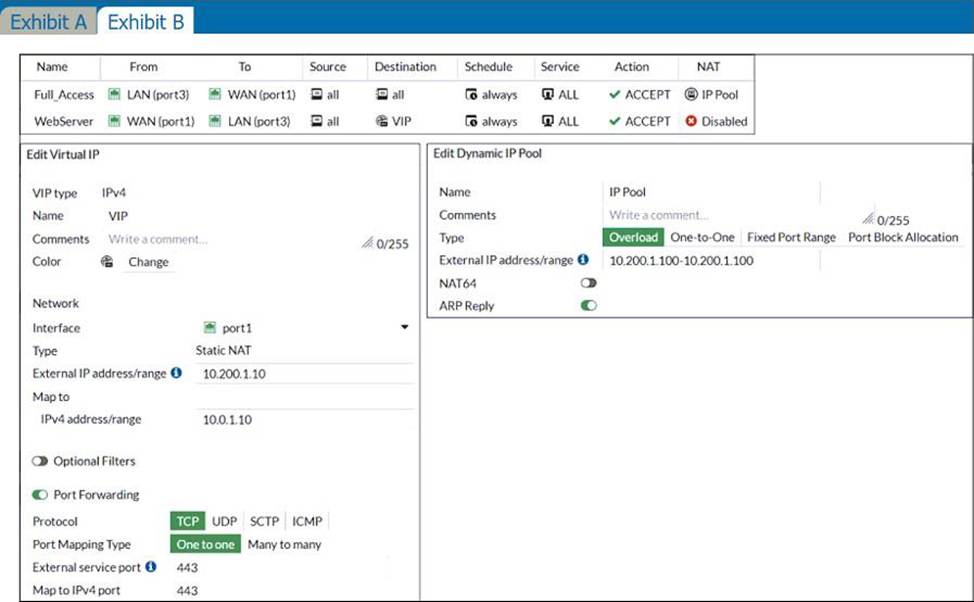
The exhibits contain a network diagram, and virtual IP, IP pool, and firewall policies configuration information.
The WAN (port1) interface has the IP address 10.200.1.1/24.
The LAN (port3) interface has the IP address 10.0.1.254/24.
The first firewall policy has NAT enabled using IP pool.
The second firewall policy is configured with a VIP as the destination address.
Which IP address will be used to source NAT (SNAT) the internet traffic coming from a workstation with the IP address 10.0.1.10?
- A . 10.200.1.1
- B . 10.0.1.254
- C . 10.200.1.10
- D . 10.200.1.100
D
Explanation:
From LAN to WAN, the Source NAT will use the IPPOOL with address configured 10.200.1.100 Destination NAT, from WAN to LAN, will use the VIP
The question says SNAT, so the only correct answer here (looking at the IP Pool) is D.
(Step 2): FortiGate uses as NAT IP the external IP address defined in the VIP when performing SNAT on all egress traffic sourced from the mapped address in the VIP, provided the matching firewall policy has NAT enabled.
Note that you can override the behavior described in step 2 by using an IP pool.
Reference: https://kb.fortinet.com/kb/documentLink.do?externalID=FD44529
Which CLI command allows administrators to troubleshoot Layer 2 issues, such as an IP address conflict?
- A . get system status
- B . diagnose sys top
- C . get system performance status
- D . get system arp
D
Explanation:
D. get system arp
The get system arp command allows administrators to view the ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) table on the FortiGate unit. This table maps IP addresses to MAC addresses and can be used to troubleshoot Layer 2 issues, such as an IP address conflict, by checking for duplicate IP addresses or incorrect MAC address mappings.
If you suspect that there is an IP address conflict, or that an IP has been assigned to the wrong device, you may need to look at the ARP table. The get system arp command is used for that purpose.
Which downstream FortiGate VDOM is used to join the Security Fabric when split-task VDOM is enabled on all FortiGate devices?
- A . FG-traffic VDOM
- B . Root VDOM
- C . Customer VDOM
- D . Global VDOM
B
Explanation:
If you enable split-task VDOM mode on the upstream FGT device, it can allow downstream FGT devices to join the Security Fabric in the root and FG-Traffic VDOMs. If split-task VDOM mode is enabled on the downstream FortiGate, it can only connect to the upstream FortiGate through the downstream FortiGate interface on the root VDOM.
Which two statements about antivirus scanning in a firewall policy set to proxy-based inspection mode, are true? (Choose two.)
- A . A file does not need to be buffered completely before it is moved to the antivirus engine for scanning.
- B . The client must wait for the antivirus scan to finish scanning before it receives the file.
- C . FortiGate sends a reset packet to the client if antivirus reports the file as infected.
- D . If a virus is detected, a block replacement message is displayed immediately.
B,D
Explanation:
In a firewall policy set to proxy-based inspection mode:
B. The client must wait for the antivirus scan to finish scanning before it receives the file.
In proxy-based inspection, the client may need to wait for the antivirus scan to complete before receiving the file. The file may need to be fully scanned before being delivered to the client, depending on the specific configuration and circumstances.
D. If a virus is detected, a block replacement message is displayed immediately.
If a virus is detected during the antivirus scan in proxy-based inspection mode, FortiGate can generate a block replacement message immediately, informing the user that the file is infected. So, both statements B and D are valid in the context of proxy-based inspection mode.
Which type of logs on FortiGate record information about traffic directly to and from the FortiGate management IP addresses?
- A . Local traffic logs
- B . Forward traffic logs
- C . System event logs
- D . Security logs
A
Explanation:
The type of logs on FortiGate that record information about traffic directly to and from the FortiGate management IP addresses is:
A network administrator wants to set up redundant IPsec VPN tunnels on FortiGate by using two IPsec VPN tunnels and static routes.
All traffic must be routed through the primary tunnel when both tunnels are up. The secondary tunnel must be used only if the primary tunnel goes down. In addition, FortiGate should be able to detect a dead tunnel to speed up tunnel failover.
Which two key configuration changes must the administrator make on FortiGate to meet the requirements? (Choose two.)
- A . Configure a higher distance on the static route for the primary tunnel, and a lower distance on the static route for the secondary tunnel.
- B . Configure a lower distance on the static route for the primary tunnel, and a higher distance on the
static route for the secondary tunnel. - C . Enable Auto-negotiate and Autokey Keep Alive on the phase 2 configuration of both tunnels.
- D . Enable Dead Peer Detection.
B,D
Explanation:
To set up redundant IPsec VPN tunnels on FortiGate and meet the specified requirements, the administrator should make the following key configuration changes:
B. Configure a lower distance on the static route for the primary tunnel, and a higher distance on the static route for the secondary tunnel.
By configuring a lower administrative distance for the static route of the primary tunnel, the FortiGate will prefer this route when both tunnels are up. If the primary tunnel goes down, the higher administrative distance on the static route for the secondary tunnel will cause the FortiGate to use the secondary tunnel.
D. Enable Dead Peer Detection.
Dead Peer Detection (DPD) should be enabled to detect the status of the VPN tunnels. If the FortiGate detects that the primary tunnel is no longer responsive (dead), it can trigger the failover to the secondary tunnel, ensuring a faster tunnel failover.
So, the correct choices are B and D.
When browsing to an internal web server using a web-mode SSL VPN bookmark, which IP address is used as the source of the HTTP request?
- A . remote user’s public IP address
- B . The public IP address of the FortiGate device.
- C . The remote user’s virtual IP address.
- D . The internal IP address of the FortiGate device.
D
Explanation:
The internal IP address of the FortiGate device.
The SSL VPN portal enables remote users to access internal network resources through a secure channel using a web browser. The portal, bookmarks are used as links to internal network resources. Source IP seen by the remote resources is FortiGate’s internal IP address and not the user’s IP address.
Reference: https://kb.fortinet.com/kb/documentLink.do?externalID=FD36530
Refer to the exhibit, which contains a session diagnostic output.
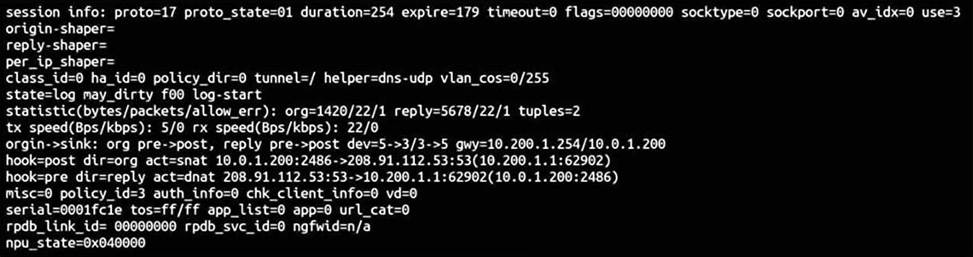
Which statement is true about the session diagnostic output?
- A . The session is in TCP ESTABLISHED state.
- B . The session is a bidirectional UDP connection.
- C . The session is a UDP unidirectional state.
- D . The session is a bidirectional TCP connection.
B
Explanation:
The session is a bidirectional UDP connection.
B. Protocol 17 means UDP and proto_state=1 is bidirectional (proto_state=0 is unidirectional) proto=17 -> UDP proto_state=01 -> UDP Reply seen
A is wrong
An administrator is configuring an Ipsec between site A and site B. The Remotes Gateway setting in both sites has been configured as Static IP Address. For site A, the local quick mode selector is 192.16.1.0/24 and the remote quick mode selector is 192.16.2.0/24.
How must the administrator configure the local quick mode selector for site B?
- A . 192.16.3.0/24
- B . 192.16.2.0/24
- C . 192.16.1.0/24
- D . 192.16.0.0/8
B
Explanation:
The local quick mode selector for site B should be configured to match the remote quick mode selector of site
Which two statements about SSL VPN between two FortiGate devices are true? (Choose two.)
- A . The client FortiGate requires a client certificate signed by the CA on the server FortiGate.
- B . The client FortiGate requires a manually added route to remote subnets.
- C . The client FortiGate uses the SSL VPN tunnel interface type to connect SSL VPN.
- D . Server FortiGate requires a CA certificate to verify the client FortiGate certificate.
C,D
Explanation:
C. The client FortiGate uses the SSL VPN tunnel interface type to connect SSL VPN.
D. Server FortiGate requires a CA certificate to verify the client FortiGate certificate. Incorrect:
