Practice Free CBAP Exam Online Questions
A major manufacturer of popular beverages has appointed a local distributor to serve a specific territory. The demand for the beverages has a pronounced seasonal pattern. The distributor performs well overall, but is repeatedly unable to keep up with fulfilling many customer orders during peak demand periods. The distributor’s current delivery capability is stretched to deliver 60 tons of merchandise per day whereas the season’s peak demand periods need a daily delivery capability of up to 100 tons.
The distributor is under pressure to fully meet the year-round market demand in order to stay in business. The distributor’s management wants to identify and consider more cost-effective options as resorting to adding more trucks and drivers would not be economically feasible.
A business analyst (BA) has spent several days observing and measuring the warehouse activities to understand the situation and to gain insights into possible solutions. The delivery workflow is a four-step process: (1) picking the orders and assembling them on trays, (2) bringing the trays to the loading bay, (3) loading the orders into trucks, and (4) delivering the orders to customers. As the following table illustrates, overall performance depends is dependent on five major resources: (1) the workers who pick the orders and load them into trucks, (2) the tallyers who check the orders, (3) the drivers, (4) the trucks, and (5) eight loading bays (LBs).
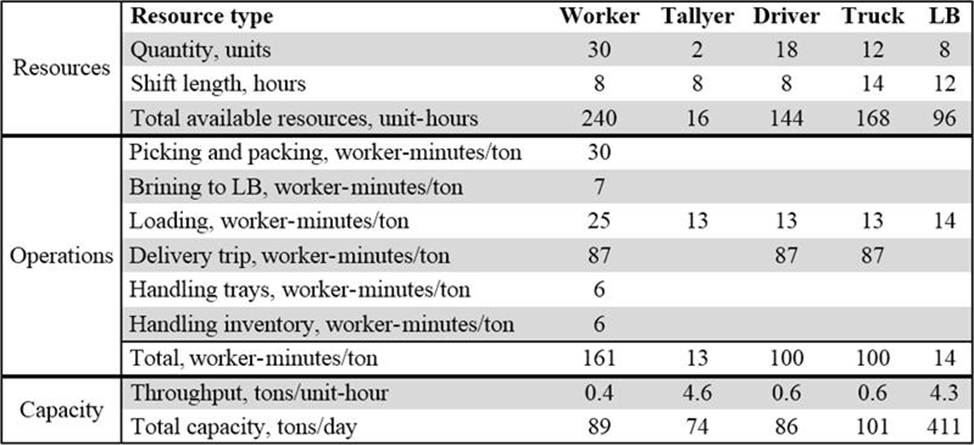
Preparing a customer order for loading takes about one hour. Upon the BA’s observation, only 30% of trips have their orders available for loading when a truck arrives. This causes a waste of both the truck’s and the driver’s time.
What should the BA recommend to eliminate such waste?
- A . Elicit requirements for a system to coordinate in advance order processing activities with all trips
- B . Begin assembling orders for the next trip immediately following the truck’s departure
- C . Hire more warehouse staff (workers) so that order assembly is done faster and less waiting occurs
- D . Ask the drivers to call the operations team member if they are going to be late
You are the business analyst for your organization and are with another business analyst, Steve, on the requirements elicitation for a new solution. You warn Steve that you’ll need to be tracing the requirements in an effort to prevent scope creep.
What is scope creep?
- A . The scope grows slightly larger as more requirements, often unneeded, are added to the scope
- B . The scope slips on the schedule which in turn delays the project delivery date
- C . Gold plating
- D . The scope shifts from the original intent of the business case
Management comes to you and asks you to complete some specifications and models about the current state of the organization. Management wants you to complete this business analysis activity as soon as possible and report back to them with your findings.
What is the primary purpose of the specify and model requirements process?
- A . To analyze the processes of an organization to determine what processes can be improved, removed, or added.
- B . To analyze the utility function within the organization to determine how risk tolerance may allow for new opportunities.
- C . To analyze the roles and responsibilities of users within the organization to determine how the processes may be improved.
- D . To analyze the functioning of an organization and to provide an insight into opportunities for improvement.
A utility company found mat its current billing system charges customers ‘or tie r usage, but does so incorrectly when the system estimates reads on meters rather than performs actual reads. Company stakeholders would i*e to improve this aspect of the system but are hesitant to make changes because they are otherwise pleased with the system A business analyst (BA) has completed a current state diagram and would like to start discussions on what the future state may look like .
What information can the BA determine by having a current slate diagram?
- A . The needs for the future state solution
- B . The cost/benefit measures for the new system
- C . The strengths and weaknesses of the current system
- D . The change management plan for implementation
Which one of the following diagrams visualize the result of the root cause analysis study?
- A . Activity diagrams
- B . State diagrams
- C . Tornado diagrams
- D . Cause-and effect diagrams
Which one of the following diagrams visualize the result of the root cause analysis study?
- A . Activity diagrams
- B . State diagrams
- C . Tornado diagrams
- D . Cause-and effect diagrams
The BA is working on the design options for the future state at the martial arts organization. There are several design elements that need to be considered for the future state .
Which of the following design elements does the Activity Diagram address?
- A . People who operate and maintain the solution
- B . Operational business decisions to be made
- C . Business processes to be performed and managed
- D . Business policies and business rules
A business analyst (BA) conducts a Business rules analysts exercise to identity the organizational rules constraining the project in addition to existing regulations and contracts.
What else does the BA check?
- A . Backlogs
- B . Policies
- C . Business case
- D . Permissions matrix
Gary is the business analyst for his organization and he is preparing a presentation about the requirements for a large software development project.
Before Gary makes the presentation what should he do as part of his preparation for the presentation?
- A . Determine an appropriate format for the presentation.
- B . Confirm that he has the authority to host the presentation.
- C . Confirm that the stakeholders have signed off on the requirements.
- D . Hire a scribe to keep the minutes of the meeting.
What does the T in SWOT analysis mean?
- A . Trial
- B . Threats
- C . Test
- D . Time
