Practice Free CAS-005 Exam Online Questions
A software development team requires valid data for internal tests. Company regulations, however do not allow the use of this data in cleartext.
Which of the following solutions best meet these requirements?
- A . Configuring data hashing
- B . Deploying tokenization
- C . Replacing data with null record
- D . Implementing data obfuscation
B
Explanation:
Tokenization replaces sensitive data elements with non-sensitive equivalents, called tokens, that can be used within the internal tests. The original data is stored securely and can be retrieved if necessary. This approach allows the software development team to work with data that appears realistic and valid without exposing the actual sensitive information.
Configuring data hashing (Option A) is not suitable for test data as it transforms the data into a fixed-length value that is not usable in the same way as the original data. Replacing data with null records (Option C) is not useful as it does not provide valid data for testing. Data obfuscation (Option D) could be an alternative but might not meet the regulatory requirements as effectively as tokenization.
Reference: CompTIA Security+ Study Guide
NIST SP 800-57 Part 1 Rev. 5, "Recommendation for Key Management"
PCI DSS Tokenization Guidelines
A global organization is reviewing potential vendors to outsource a critical payroll function. Each vendor’s plan includes using local resources in multiple regions to ensure compliance with all regulations. The organization’s Chief Information Security Officer is conducting a risk assessment on the potential outsourcing vendors’ sub processors.
Which of the following best explains the need for this risk assessment?
- A . Risk mitigations must be more comprehensive than the existing payroll provider.
- B . Due care must be exercised during all procurement activities.
- C . The responsibility of protecting PII remains with the organization.
- D . Specific regulatory requirements must be met in each jurisdiction.
C
Explanation:
Per SecurityX CAS-005 GRC principles, outsourcing a function does not transfer accountability for protecting personally identifiable information (PII). While sub processors handle data, the originating organization remains responsible under most data protection laws and frameworks (e.g., GDPR, CCPA).
Due care in procurement (option B) is important, but it is a supporting concept, not the primary driver in this context.
Jurisdictional compliance (option D) is a requirement, but the underlying reason for risk assessment is that accountability for PII protection remains with the organization.
A company recently experienced a ransomware attack. Although the company performs systems and data backup on a schedule that aligns with its RPO (Recovery Point Objective) requirements, the backup administrator could not recover critical systems and data from its offline backups to meet the RPO. Eventually, the systems and data were restored with information that was six months outside of RPO requirements.
Which of the following actions should the company take to reduce the risk of a similar attack?
- A . Encrypt and label the backup tapes with the appropriate retention schedule before they are sent to the off-site location.
- B . Implement a business continuity process that includes reverting manual business processes.
- C . Perform regular disaster recovery testing of IT and non-IT systems and processes.
- D . Carry out a tabletop exercise to update and verify the RACI matrix with IT and critical business functions.
C
Explanation:
Understanding the Ransomware Issue:
The key issue here is that backups were not recoverable within the required RPO timeframe.
This means the organization did not properly test its backup and disaster recovery (DR) processes.
To prevent this from happening again, regular disaster recovery testing is essential.
Why Option C is Correct:
Disaster recovery testing ensures that backups are functional and can meet business continuity needs.
Frequent DR testing allows organizations to identify and fix gaps in recovery strategies.
Regular testing ensures that recovery meets the RPO & RTO (Recovery Time Objective) requirements.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A (Encrypt & label backup tapes): While encryption is important, it does not address the failure to meet RPO requirements.
B (Reverting to manual business processes): While a manual continuity plan is good for resilience, it does not resolve the backup and recovery failure.
D (Tabletop exercise & RACI matrix): A tabletop exercise is a planning activity, but it does not involve
actual recovery testing.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX CAS-005 Official Study Guide: Disaster Recovery & Business Continuity Planning
NIST SP 800-34: Contingency Planning Guide for Information Systems
ISO 22301: Business Continuity Management Standards
A company recently experienced a ransomware attack. Although the company performs systems and data backup on a schedule that aligns with its RPO (Recovery Point Objective) requirements, the backup administrator could not recover critical systems and data from its offline backups to meet the RPO. Eventually, the systems and data were restored with information that was six months outside of RPO requirements.
Which of the following actions should the company take to reduce the risk of a similar attack?
- A . Encrypt and label the backup tapes with the appropriate retention schedule before they are sent to the off-site location.
- B . Implement a business continuity process that includes reverting manual business processes.
- C . Perform regular disaster recovery testing of IT and non-IT systems and processes.
- D . Carry out a tabletop exercise to update and verify the RACI matrix with IT and critical business functions.
C
Explanation:
Understanding the Ransomware Issue:
The key issue here is that backups were not recoverable within the required RPO timeframe.
This means the organization did not properly test its backup and disaster recovery (DR) processes.
To prevent this from happening again, regular disaster recovery testing is essential.
Why Option C is Correct:
Disaster recovery testing ensures that backups are functional and can meet business continuity needs.
Frequent DR testing allows organizations to identify and fix gaps in recovery strategies.
Regular testing ensures that recovery meets the RPO & RTO (Recovery Time Objective) requirements.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A (Encrypt & label backup tapes): While encryption is important, it does not address the failure to meet RPO requirements.
B (Reverting to manual business processes): While a manual continuity plan is good for resilience, it does not resolve the backup and recovery failure.
D (Tabletop exercise & RACI matrix): A tabletop exercise is a planning activity, but it does not involve
actual recovery testing.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX CAS-005 Official Study Guide: Disaster Recovery & Business Continuity Planning
NIST SP 800-34: Contingency Planning Guide for Information Systems
ISO 22301: Business Continuity Management Standards
A company plans to implement a research facility with Intellectual property data that should be protected.
The following is the security diagram proposed by the security architect
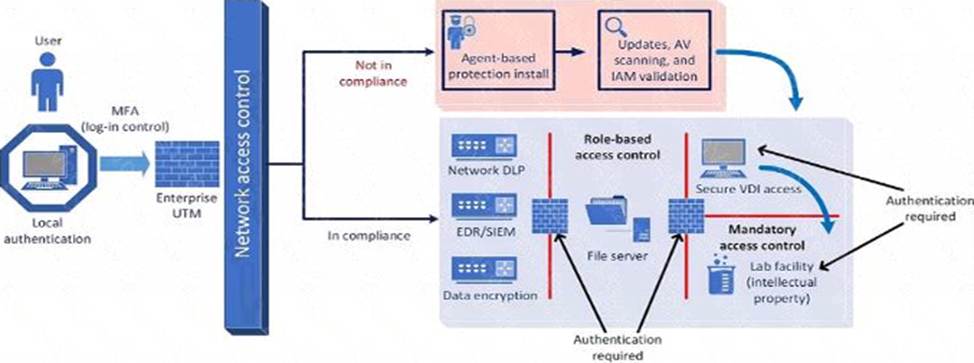
Which of the following security architect models is illustrated by the diagram?
- A . Identity and access management model
- B . Agent based security model
- C . Perimeter protection security model
- D . Zero Trust security model
D
Explanation:
The security diagram proposed by the security architect depicts a Zero Trust security model. Zero Trust is a security framework that assumes all entities, both inside and outside the network, cannot be trusted and must be verified before gaining access to resources.
Key Characteristics of Zero Trust in the Diagram:
Role-based Access Control: Ensures that users have access only to the resources necessary for their role.
Mandatory Access Control: Additional layer of security requiring authentication for access to sensitive areas.
Network Access Control: Ensures that devices meet security standards before accessing the network.
Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): Enhances security by requiring multiple forms of verification.
This model aligns with the Zero Trust principles of never trusting and always verifying access requests, regardless of their origin.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX Study Guide
NIST Special Publication 800-207, "Zero Trust Architecture"
"Implementing a Zero Trust Architecture," Forrester Research
An engineering team determines the cost to mitigate certain risks is higher than the asset values The team must ensure the risks are prioritized appropriately.
Which of the following is the best way to address the issue?
- A . Data labeling
- B . Branch protection
- C . Vulnerability assessments
- D . Purchasing insurance
D
Explanation:
When the cost to mitigate certain risks is higher than the asset values, the best approach is to purchase insurance. This method allows the company to transfer the risk to an insurance provider, ensuring that financial losses are covered in the event of an incident. This approach is cost-effective and ensures that risks are prioritized appropriately without overspending on mitigation efforts.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX Study Guide: Discusses risk management strategies, including risk transfer through insurance.
NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF): Highlights the use of insurance as a risk mitigation strategy.
"Information Security Risk Assessment Toolkit" by Mark Talabis and Jason Martin: Covers risk management practices, including the benefits of purchasing insurance.
During a security assessment using an CDR solution, a security engineer generates the following report about the assets in me system:
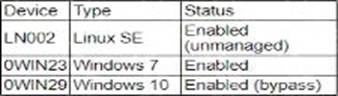
After five days, the EDR console reports an infection on the host 0WIN23 by a remote access Trojan.
Which of the following is the most probable cause of the infection?
- A . OW1N23 uses a legacy version of Windows that is not supported by the EDR
- B . LN002 was not supported by the EDR solution and propagates the RAT
- C . The EDR has an unknown vulnerability that was exploited by the attacker.
- D . 0W1N29 spreads the malware through other hosts in the network
A
Explanation:
OWIN23 is running Windows 7, which is a legacy operating system. Many EDR solutions no longer provide full support for outdated operating systems like Windows 7, which has reached its end of life and is no longer receiving security updates from Microsoft. This makes such systems more vulnerable to infections and attacks, including remote access Trojans (RATs).
During a recent security event, access from the non-production environment to the production environment enabled unauthorized users to:
Install unapproved software
Make unplanned configuration changes
During the investigation, the following findings were identified:
Several new users were added in bulk by the IAM team
Additional firewalls and routers were recently added
Vulnerability assessments have been disabled for more than 30 days
The application allow list has not been modified in two weeks
Logs were unavailable for various types of traffic
Endpoints have not been patched in over ten days
Which of the following actions would most likely need to be taken to ensure proper monitoring? (Select two)
- A . Disable bulk user creations by the IAM team
- B . Extend log retention for all security and network devices to 180 days for all traffic
- C . Review the application allow list daily
- D . Routinely update all endpoints and network devices as soon as new patches/hot fixes are available
- E . Ensure all network and security devices are sending relevant data to the SIEM
- F . Configure firewall rules to only allow production-to-non-production traffic
A,D,E
Explanation:
Understanding the Security Event:
Unauthorized users gained access from non-production to production.
IAM policies were weak, allowing bulk user creation.
Vulnerability assessments were disabled, and patching was delayed.
Logs were unavailable, making incident response difficult.
Why Options A, D, and E are Correct:
A (Disable bulk user creation by IAM team) → Prevents unauthorized mass user account creation, which could be exploited by attackers.
D (Routine updates for endpoints & network devices) → Patch management ensures vulnerabilities are not left open for attackers.
E (Ensure all security/network devices send logs to SIEM) → Helps with real-time monitoring and
detection of unauthorized activities.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
B (180-day log retention) → While log retention is good, real-time monitoring is the priority.
C (Review application allow list daily) → Reviewing it daily is impractical. Regular audits are better.
F (Restrict production-to-non-production traffic) → The issue is unauthorized access, not traffic routing.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX CAS-005 Official Study Guide: IAM, Patch Management & SIEM Logging Best Practices
NIST 800-53 (AC-2, AU-12): Audit Logging & Access Control
An organization is implementing advanced security controls associated with the execution of software applications on corporate endpoints. The organization must implement a deny-all, permit-by-exception approach to software authorization for all systems regardless of OS.
Which of the following should be implemented to meet these requirements?
- A . SELinux
- B . MDM
- C . XDR
- D . Block list
- E . Atomic execution
D
Explanation:
Step by Step
Understanding the Scenario: The organization wants a strict application control policy: deny all software execution by default and only allow specifically authorized applications. This must be enforced across all operating systems. It is implied that they mean an Allow list, but Block List is the only reasonable answer.
Analyzing the Answer Choices:
A security engineer must resolve a vulnerability in a deprecated version of Python for a custom-developed flight simulation application that is monitored and controlled remotely. The source code is proprietary and built with Python functions running on the Ubuntu operating system. Version control is not enabled for the application in development or production. However, the application must remain online in the production environment using built-in features.
Which of the following solutions best reduces the attack surface of these issues and meets the outlined requirements?
- A . Configure code-signing within the CI/CD pipeline, update Python with aptitude, and update modules with pip in a test environment. Deploy the solution to production.
- B . Enable branch protection in the GitHub repository. Update Python with aptitude, and update modules with pip in a test environment. Deploy the solution to production.
- C . Use an NFS network share. Update Python with aptitude, and update modules with pip in a test environment. Deploy the solution to production.
- D . Configure version designation within the Python interpreter. Update Python with aptitude, and update modules with pip in a test environment. Deploy the solution to production.
A
Explanation:
Code-signing within the CI/CD pipeline ensures that only verified and signed code is deployed, mitigating the risk of supply chain attacks. Updating Python with aptitude and updating modules with pip ensures vulnerabilities are patched. Deploying the solution to production after testing maintains application availability while securing the development lifecycle.
Branch protection (B) applies only to version-controlled environments, which is not the case here.
NFS network share (C) does not address the deprecated Python vulnerability.
Version designation (D) does not eliminate security risks from outdated dependencies.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX (CAS-005) Exam Objectives – Domain 3.0 (Security Engineering), Section on Software Assurance and Secure Development
