Practice Free CAS-005 Exam Online Questions
An enterprise is deploying APIs that utilize a private key and a public key to ensure the connection string is protected. To connect to the API, customers must use the private key.
Which of the following would best secure the REST API connection to the database while preventing the use of a hard-coded string in the request string?
- A . Implement a VPN for all APIs
- B . Sign the key with DSA
- C . Deploy MFA for the service accounts
- D . Utilize HMAC for the keys
D
Explanation:
HMAC (Hash-based Message Authentication Code) ensures the integrity and authentication of API requests without exposing static or hard-coded private keys. It uses a secret key and a hash function, preventing replay attacks and tampering. VPNs secure the transport layer, MFA protects user accounts (not API-to-database communications), and DSA is a signature algorithm but does not address hard-coding risk directly.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX CAS-005, Domain 3.0: Implement secure API practices including the
use of HMAC for key protection.
A company’s help desk is experiencing a large number of calls from the finance department slating access issues to www.bank.com.
The security operations center reviewed the following security logs:
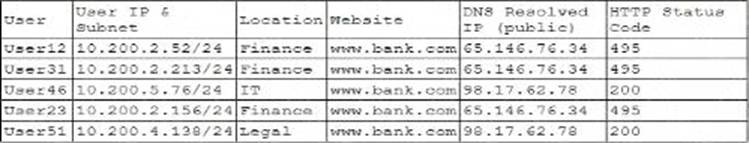
Which of the following is most likely the cause of the issue?
- A . Recursive DNS resolution is failing
- B . The DNS record has been poisoned.
- C . DNS traffic is being sinkholed.
- D . The DNS was set up incorrectly.
C
Explanation:
Sinkholing, or DNS sinkholing, is a method used to redirect malicious traffic to a safe destination. This technique is often employed by security teams to prevent access to malicious domains by substituting a benign destination IP address.
In the given logs, users from the finance department are accessing www.bank.com and receiving HTTP status code 495. This status code is typically indicative of a client certificate error, which can occur if the DNS traffic is being manipulated or redirected incorrectly. The consistency in receiving the same HTTP status code across different users suggests a systematic issue rather than an isolated incident.
Recursive DNS resolution failure (A) would generally lead to inability to resolve DNS at all, not to a specific HTTP error.
DNS poisoning (B) could result in users being directed to malicious sites, but again, would likely result in a different set of errors or unusual activity.
Incorrect DNS setup (D) would likely cause broader resolution issues rather than targeted errors like the one seen here.
By reviewing the provided data, it is evident that the DNS traffic for www.bank.com is being rerouted improperly, resulting in consistent HTTP 495 errors for the finance department users. Hence, the most likely cause is that the DNS traffic is being sinkholed.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX study materials on DNS security mechanisms.
Standard HTTP status codes and their implications.
A company must meet the following security requirements when implementing controls in order to be compliant with government policy:
• Access to the system document repository must be MFA enabled.
• Ongoing risk monitoring must be displayed on a system dashboard.
• Staff must receive email notifications about periodic tasks.
Which of the following best meets all of these requirements?
- A . Implementing a GRC tool
- B . Configuring a privileged access management system
- C . Launching a vulnerability management program
- D . Creating a risk register
A recent security audit identified multiple endpoints have the following vulnerabilities:
• Various unsecured open ports
• Active accounts for terminated personnel
• Endpoint protection software with legacy versions
• Overly permissive access rules
Which of the following would best mitigate these risks? (Select three).
- A . Local drive encryption
- B . Secure boot
- C . Address space layout randomization
- D . Unneeded services disabled
- E . Patching
- F . Logging
- G . Removal of unused accounts
- H . Enabling BIOS password
D,E,G
Explanation:
Disabling unneeded services reduces the attack surface by closing open ports. Patching ensures that endpoint protection software and operating systems are up-to-date, reducing vulnerability exposure. Removing unused accounts eliminates access paths for malicious users exploiting dormant accounts. Secure boot, BIOS passwords, and drive encryption are important, but they address different layers of security than the vulnerabilities listed.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX CAS-005, Domain 2.0: Apply system hardening techniques to endpoint security issues.
An organization determines existing business continuity practices are inadequate to support critical internal process dependencies during a contingency event. A compliance analyst wants the Chief Information Officer (CIO) to identify the level of residual risk that is acceptable to guide remediation activities.
Which of the following does the CIO need to clarify?
- A . Mitigation
- B . Impact
- C . Likelihood
- D . Appetite
D
Explanation:
The CIO needs to clarify the organization’s risk appetite, which defines the level of residual risk the business is willing to accept after all mitigation measures are applied. Risk appetite reflects the balance between operational requirements, security controls, and cost constraints. In business continuity planning, risk appetite helps decision-makers determine which risks must be reduced through additional investments (e.g., redundant systems, faster recovery strategies) and which risks are tolerable based on business priorities.
Mitigation (A) refers to the strategies used to reduce risk but not the threshold of acceptable residual risk. Impact (B) and Likelihood (C) are components of risk assessment―measuring severity and probability―but they do not define acceptance criteria. Risk appetite is the guiding principle that aligns technical controls with executive tolerance for disruption or loss.
By clarifying appetite, the CIO provides the compliance team and IT leadership with a framework for designing remediation activities that ensure continuity of critical internal processes while aligning with the organization’s strategic objectives and regulatory requirements.
A technician is reviewing the logs and notices a large number of files were transferred to remote sites over the course of three months. This activity then stopped. The files were transferred via TLS-protected HTTP sessions from systems that do not normally send traffic to those sites.
The technician will define this threat as:
- A . A decrypting RSA using an obsolete and weakened encryption attack.
- B . A zero-day attack.
- C . An advanced persistent threat.
- D . An on-path attack.
C
Explanation:
The scenario describes a prolonged, stealthy operation where files were exfiltrated over three months via secure channels (TLS-protected HTTP) from unexpected systems, then ceased. This aligns with an Advanced Persistent Threat (APT), characterized by long-term, targeted attacks aimed at data theft or surveillance, often using sophisticated methods to remain undetected.
Option A: Decrypting RSA with weak encryption implies a cryptographic attack, but TLS suggests modern encryption was used, and there’s no evidence of decryption here.
Option B: A zero-day attack exploits unknown vulnerabilities, but the duration and cessation suggest a planned operation, not a single exploit.
Option C: APT fits perfectly―slow, persistent exfiltration from unusual systems indicates a coordinated, stealthy threat actor.
Option D: An on-path (man-in-the-middle) attack intercepts traffic, but there’s no indication of interception; the focus is on unauthorized transfers.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX CAS-005 Domain 1: Risk Management C Threat Identification and Analysis.
During a recent security event, access from the non-production environment to the production environment enabled unauthorized users to install unapproved software and make unplanned configuration changes.
During an investigation, the following findings are identified:
• Several new users were added in bulk by the IAM team.
• Additional firewalls and routers were recently added to the network.
• Vulnerability assessments have been disabled for all devices for more than 30 days.
• The application allow list has not been modified in more than two weeks.
• Logs were unavailable for various types of traffic.
• Endpoints have not been patched in more than ten days.
Which of the following actions would most likely need to be taken to ensure proper monitoring is in place within the organization? (Select two)
- A . Disable bulk user creations by the IAM team.
- B . Extend log retention for all security and network devices for 180 days for all traffic.
- C . Review the application allow list on a daily basis to make sure it is properly configured.
- D . Routinely update all endpoints and network devices as soon as new patches/hot fixes are available.
- E . Ensure all network and security devices are sending relevant data to the SIEM.
- F . Configure rules on all firewalls to only allow traffic from the production environment to the non-production environment.
B,E
Explanation:
The incident highlights gaps in visibility, monitoring, and log management that allowed unauthorized access to persist undetected. The most critical corrective actions are to extend log retention for all devices (B) and to ensure all devices are forwarding relevant logs to the SIEM (E). Together, these steps strengthen monitoring and incident detection capabilities by ensuring that sufficient telemetry is collected, stored, and available for correlation and investigation.
Disabling bulk user creation (A) may reduce misuse but does not directly address monitoring gaps. Daily review of the application allow list (C) is operationally impractical and does not provide the breadth of monitoring needed. Routine patching (D) is essential for security hygiene but is separate from monitoring improvements. Configuring firewall rules (F) may reduce traffic flows but does not ensure detection or visibility of unauthorized activity.
By prioritizing comprehensive log collection and ensuring adequate retention, the SOC can correlate anomalies across systems, detect malicious behavior earlier, and conduct forensic investigations effectively. This aligns with CAS-005 best practices for security operations and continuous monitoring in hybrid environments.
During a recent security event, access from the non-production environment to the production environment enabled unauthorized users to install unapproved software and make unplanned configuration changes.
During an investigation, the following findings are identified:
• Several new users were added in bulk by the IAM team.
• Additional firewalls and routers were recently added to the network.
• Vulnerability assessments have been disabled for all devices for more than 30 days.
• The application allow list has not been modified in more than two weeks.
• Logs were unavailable for various types of traffic.
• Endpoints have not been patched in more than ten days.
Which of the following actions would most likely need to be taken to ensure proper monitoring is in place within the organization? (Select two)
- A . Disable bulk user creations by the IAM team.
- B . Extend log retention for all security and network devices for 180 days for all traffic.
- C . Review the application allow list on a daily basis to make sure it is properly configured.
- D . Routinely update all endpoints and network devices as soon as new patches/hot fixes are available.
- E . Ensure all network and security devices are sending relevant data to the SIEM.
- F . Configure rules on all firewalls to only allow traffic from the production environment to the non-production environment.
B,E
Explanation:
The incident highlights gaps in visibility, monitoring, and log management that allowed unauthorized access to persist undetected. The most critical corrective actions are to extend log retention for all devices (B) and to ensure all devices are forwarding relevant logs to the SIEM (E). Together, these steps strengthen monitoring and incident detection capabilities by ensuring that sufficient telemetry is collected, stored, and available for correlation and investigation.
Disabling bulk user creation (A) may reduce misuse but does not directly address monitoring gaps. Daily review of the application allow list (C) is operationally impractical and does not provide the breadth of monitoring needed. Routine patching (D) is essential for security hygiene but is separate from monitoring improvements. Configuring firewall rules (F) may reduce traffic flows but does not ensure detection or visibility of unauthorized activity.
By prioritizing comprehensive log collection and ensuring adequate retention, the SOC can correlate anomalies across systems, detect malicious behavior earlier, and conduct forensic investigations effectively. This aligns with CAS-005 best practices for security operations and continuous monitoring in hybrid environments.
An organization purchased a new manufacturing facility and the security administrator needs to:
• Implement security monitoring.
• Protect any non-traditional device(s)/network(s).
• Ensure no downtime for critical systems.
Which of the following strategies best meets these requirements?
- A . Configuring honeypots in the internal network to capture malicious activity
- B . Analyzing system behavior and responding to any increase in activity
- C . Applying updates and patches soon after they have been released
- D . Observing the environment and proactively addressing any malicious activity
D
Explanation:
For operational technology (OT) and non-traditional devices, downtime must be avoided. CAS-005 recommends passive monitoring and proactive response for environments where active scanning or changes could disrupt operations. Observing the environment continuously and acting on malicious indicators allows security without interrupting critical manufacturing processes.
Honeypots (A) are good for research but don’t provide full facility monitoring.
Behavioral analysis (B) is reactive without proactive measures.
Patching (C) is important but could cause downtime and may be limited in OT environments.
A security engineer reviews an after action report from a previous security breach and notes a long lag time between detection and containment of a compromised account. The engineer suggests using SOAR to address this concern.
Which of the following best explains the engineer’s goal?
- A . To prevent accounts from being compromised
- B . To enable log correlation using machine learning
- C . To orchestrate additional reporting for the security operations center
- D . To prepare runbooks to automate future incident response
