Practice Free CAS-005 Exam Online Questions
Which of the following are risks associated with vendor lock-in? (Select two).
- A . The client can seamlessly move data.
- B . The vendor can change product offerings.
- C . The client receives a sufficient level of service.
- D . The client experiences decreased quality of service.
- E . The client can leverage a multicloud approach.
- F . The client experiences increased interoperability.
B,D
Explanation:
Vendor lock-in occurs when a client is overly dependent on a vendor, limiting flexibility. Risks include: Option B: Vendors changing offerings (e.g., features, pricing) can disrupt the client, a key lock-in risk.
Option D: Decreased quality of service may result from reliance on a single vendor without alternatives.
Option A: Seamless data movement is a benefit, not a risk.
Option C: Sufficient service is neutral or positive, not a risk.
Option E: Multicloud is hindered by lock-in, not a risk of it.
Option F: Increased interoperability contradicts lock-in’s limitations.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX CAS-005 Domain 1: Risk Management C Vendor Risk Assessment.
Anorganization has noticed an increase in phishing campaigns utilizing typo squatting. A security analyst needs to enrich the data for commonly used domains against the domains used in phishing campaigns. The analyst uses a log forwarder to forward network logs to the SIEM.
Which of the following would allow the security analyst to perform this analysis?
- A . Use a cron job to regularly update and compare domains.
- B . Create a parser that matches domains.
- C . Develop a query that filters out all matching domain names.
- D . Implement a dashboard on the SIEM that shows the percentage of traffic by domain.
D
Explanation:
Enriching data to compare domains requires actionable visibility. Let’s analyze:
A building camera is remotely accessed and disabled from the remote console application during off-hours.
A security analyst reviews the following logs:
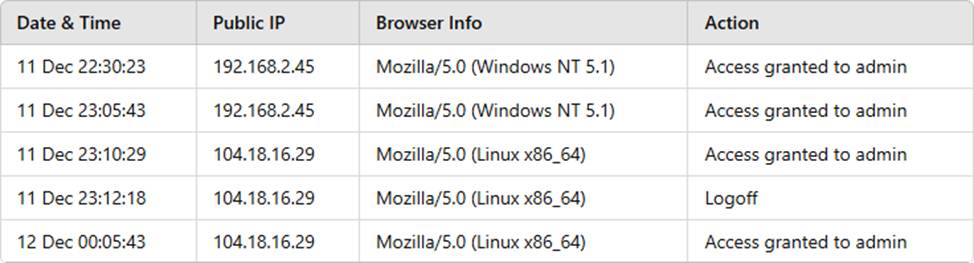
Which of the following actions should the analyst take to best mitigate the threat?
- A . Implement WAF protection for the web application.
- B . Upgrade the firmware on the camera.
- C . Only allow connections from approved IPs.
- D . Block IP 104.18.16.29 on the firewall.
C
Explanation:
The logs indicate unauthorized access from104.18.16.29, an external IP, to the building camera’s administrative console during off-hours. Restricting access only to approved IP sensures that only authorized personnel can remotely control the cameras, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and manipulation.
Implementing WAF protection (A)secures against web application attacks but does not restrict unauthorized administrative access.
Upgrading the firmware (B)is good security hygiene but does not immediately mitigate the active threat.
Blocking IP 104.18.16.29 (D)is a temporary measure, as an attacker can switch to another IP. A better long-term solution is whitelisting trusted IPs.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX (CAS-005) Exam Objectives- Domain 4.0 (Security Operations), Section on Access Control and Network Security
During a gap assessment, an organization notes that OYOD usage is a significant risk. The organization implemented administrative policies prohibiting BYOD usage However, the organization has not implemented technical controls to prevent the unauthorized use of BYOD assets when accessing the organization’s resources.
Which of the following solutions should the organization implement to b»« reduce the risk of OYOD devices? (Select two).
- A . Cloud 1AM to enforce the use of token based MFA
- B . Conditional access, to enforce user-to-device binding
- C . NAC, to enforce device configuration requirements
- D . PAM. to enforce local password policies
- E . SD-WAN. to enforce web content filtering through external proxies
- F . DLP, to enforce data protection capabilities
B,C
Explanation:
To reduce the risk of unauthorized BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) usage, the organization should implement Conditional Access and Network Access Control (NAC).
Why Conditional Access and NAC?
Conditional Access:
User-to-Device Binding: Conditional access policies can enforce that only registered and compliant devices are allowed to access corporate resources.
Context-Aware Security: Enforces access controls based on the context of the access attempt, such as user identity, device compliance, location, and more.
Network Access Control (NAC):
Device Configuration Requirements: NAC ensures that only devices meeting specific security configurations are allowed to connect to the network.
Access Control: Provides granular control over network access, ensuring that BYOD devices comply with security policies before gaining access.
Other options, while useful, do not address the specific need to control and secure BYOD devices effectively:
A company is migrating from a Windows Server to Linux-based servers. A security engineer must deploy a configuration management solution that maintains security software across all the Linux servers.
Which of the following configuration file snippets is the most appropriate to use?
- A . — – name: deployment hosts: linux_servers remote_user: root tasks: – name: Install security software ansible.builtin.apt:
- B . <hosts>linux_servers</hosts> <os_type>Linux 3.1</os_type> <SElinux>true</SElinux> <source>com.canonical.io</source>
- C . {"name":"deployment", "hosts":"linux_servers", "remote_user":"Administrator", "tasks":{"name":"Install security software", "com.microsoft.store.latest"} }
- D . {"task":"install", "hosts":"linux_servers", "remote_user":"root", "se_linux":"false", "application":"AppX"}
A
Explanation:
The correct snippet is Option A, which shows an Ansible YAML playbook designed to deploy and maintain security software on Linux servers. Ansible is a configuration management tool widely used in enterprise environments, and the ansible.builtin.apt module specifically manages package installation on Debian/Ubuntu-based Linux distributions. This ensures consistent security software deployment across multiple servers.
Option B is XML-based and does not represent a valid configuration management script.
Option C incorrectly uses JSON format and Reference Microsoft’s store (com.microsoft.store.latest), which is irrelevant for Linux.
Option D also uses JSON syntax with “AppX,” which applies to Windows applications, not Linux.
CAS-005 emphasizes infrastructure as code (IaC) and automation as best practices for secure system configuration. YAML-based playbooks in Ansible provide repeatability, auditability, and scalability, making Option A the most secure and appropriate solution.
SIMULATION [Identity and Access Management (IAM)]
A product development team has submitted code snippets for review prior to release.
INSTRUCTIONS
Analyze the code snippets, and then select one vulnerability, and one fix for each code snippet.
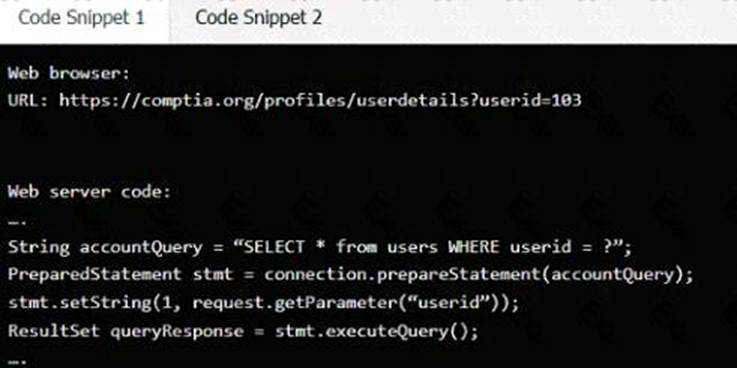
Code Snippet 1
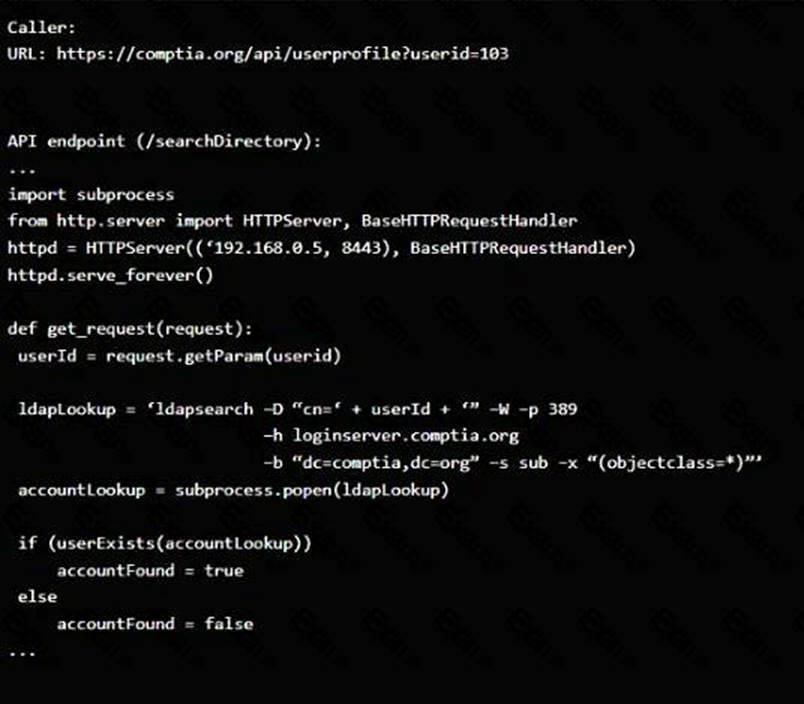
Code Snippet 2
Vulnerability 1:
SQL injection
Cross-site request forgery
Server-side request forgery
Indirect object reference
Cross-site scripting
Fix 1:
Perform input sanitization of the userid field.
Perform output encoding of queryResponse,
Ensure usex: ia belongs to logged-in user.
Inspect URLS and disallow arbitrary requests.
Implement anti-forgery tokens.
Vulnerability 2
1) Denial of service
2) Command injection
3) SQL injection
4) Authorization bypass
5) Credentials passed via GET
Fix 2
A) Implement prepared statements and bind variables.
B) Remove the serve_forever instruction.
C) Prevent the "authenticated" value from being overridden by a GET parameter.
D) HTTP POST should be used for sensitive parameters.
E) Perform input sanitization of the userid field.
See the solution below in explanation.
Vulnerability 1: SQL injection
SQL injection is a type of attack that exploits a vulnerability in the code that interacts with a database. An attacker can inject malicious SQL commands into the input fields, such as username or password, and execute them on the database server. This can result in data theft, data corruption, or unauthorized access.
Fix 1: Perform input sanitization of the use rid field.
Input sanitization is a technique that prevents SQL injection by validating and filtering the user input values before passing them to the database. The input sanitization should remove any special characters, such as quotes, semicolons, or dashes, that can alter the intended SQL query. Alternatively, the input sanitization can use a whitelist of allowed values and reject any other values.
Code Snippet 2
Vulnerability 2: Cross-site request forgery
Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) is a type of attack that exploits a vulnerability in the code that handles web requests. An attacker can trick a user into sending a malicious web request to a server that performs an action on behalf of the user, such as changing their password, transferring funds, or deleting data. This can result in unauthorized actions, data loss, or account compromise.
Fix 2: Implement anti-forgery tokens.
Anti-forgery tokens are techniques that prevent CSRF by adding a unique and secret value to each web request that is generated by the server and verified by the server before performing the action.
The anti-forgery token should be different for each user and each session, and should not be predictable or reusable by an attacker. This way, only legitimate web requests from the user’s browser can be accepted by the server.
A company developed a new solution that needs to track any changes to the data, and the changes need to be quickly identified.
If any changes are attempted without prior approval, multiple events must be triggered, such as:
Raising alerts
Blocking the unapproved changes
Quickly removing access to the data
Which of the following solutions best meets these requirements?
- A . Tracking all application logs, integrating them to the existing SIEM, flagging any changes, and making them visible on security dashboards
- B . Implementing a file integrity monitoring tool and integrating it via orchestration and automation with other security tools
- C . Introducing more granular access controls and allowing read-only access for non-privileged users
- D . Configuring CASB rules, making access to the data available only to authorized personnel
A company migrated a critical workload from its data center to the cloud. The workload uses a very large data set that requires computational-intensive data processing.
The business unit that uses the workload is projecting the following growth pattern:
• Storage requirements will double every six months.
• Computational requirements will fluctuate throughout the year.
• Average computational requirements will double every year.
Which of the following should the company do to address the business unit’s requirements?
- A . Deploy a cloud-based CDN for storage and a load balancer for compute.
- B . Combine compute and storage in vertically autoscaling mode.
- C . Implement a load balancer for computing and storage resources.
- D . Plan for a horizontally scaling computing and storage infrastructure.
D
Explanation:
SecurityX CAS-005 cloud architecture guidance emphasizes horizontal scaling for workloads that need to handle both predictable and fluctuating growth over time. Horizontal scaling allows the infrastructure to add nodes for both compute and storage dynamically, providing elasticity to meet fluctuating computational demands while accommodating exponential storage growth.
Vertical scaling (B) has hardware limits and is not as flexible for large, sustained growth.
CDN (A) is optimized for content distribution, not intensive compute workloads.
Load balancing (C) distributes workloads but does not address scaling for data growth.
A global organization wants to manage all endpoint and user telemetry. The organization also needs to differentiate this data based on which office it is correlated to.
Which of the following strategies best aligns with this goal?
- A . Sensor placement
- B . Data labeling
- C . Continuous monitoring
- D . Centralized logging
B
Explanation:
Managing telemetry and differentiating it by office requires a way to categorize data. Let’s evaluate:
Operational technology often relies upon aging command, control, and telemetry subsystems that were created with the design assumption of:
- A . operating in an isolated/disconnected system.
- B . communicating over distributed environments
- C . untrustworthy users and systems being present.
- D . an available Etherne VIP network stack for flexibility.
- E . anticipated eavesdropping from malicious actors.
A
Explanation:
Step by Step
Understanding the Scenario: The question focuses on the historical design assumptions behind older operational technology (OT)systems, particularly in the context of command, control, and telemetry.
Analyzing the Answer Choices:
