Practice Free CAS-005 Exam Online Questions
Which of the following is the main reason quantum computing advancements are leading companies and countries to deploy new encryption algorithms?
- A . Encryption systems based on large prime numbers will be vulnerable to exploitation
- B . Zero Trust security architectures will require homomorphic encryption.
- C . Perfect forward secrecy will prevent deployment of advanced firewall monitoring techniques
- D . Quantum computers will enable malicious actors to capture IP traffic in real time
A
Explanation:
Advancements in quantum computing pose a significant threat to current encryption systems, especially those based on the difficulty of factoring large prime numbers, such as RSA. Quantum
computers have the potential to solve these problems exponentially faster than classical computers, making current cryptographic systems vulnerable.
Why Large Prime Numbers are Vulnerable:
Shor’s Algorithm: Quantum computers can use Shor’s algorithm to factorize large integers efficiently, which undermines the security of RSA encryption.
Cryptographic Breakthrough: The ability to quickly factor large prime numbers means that encrypted data, which relies on the hardness of this mathematical problem, can be decrypted.
Other options, while relevant, do not capture the primary reason for the shift towards new encryption algorithms:
B. Zero Trust security architectures: While important, the shift to homomorphic encryption is not the main driver for new encryption algorithms.
C. Perfect forward secrecy: It enhances security but is not the main reason for new encryption algorithms.
D. Real-time IP traffic capture: Quantum computers pose a more significant threat to the underlying cryptographic algorithms than to the real-time capture of traffic.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX Study Guide
NIST Special Publication 800-208, "Recommendation for Stateful Hash-Based Signature Schemes"
"Quantum Computing and Cryptography," MIT Technology Review
A company designs policies and procedures for hardening containers deployed in the production environment. However, a security assessment reveals that deployed containers are not complying with the security baseline.
Which of the following solutions best addresses this issue throughout early life-cycle stages?
- A . Installing endpoint agents on each container and setting them to report when configurations drift from the baseline
- B . Finding hardened container images and enforcing them as the baseline for new deployments
- C . Creating a pipeline to check the containers through security gates and validating the baseline controls before the final deployment
- D . Running security assessments regularly and checking for the security baseline on containers already in production
C
Explanation:
SecurityX CAS-005 secure DevOps guidance recommends integrating security controls into the CI/CD pipeline. By validating container security baselines at security gates before deployment, noncompliant builds are stopped early, ensuring consistency across environments.
Option B is useful but does not ensure compliance if changes are made after image creation.
Option A detects drift but only after deployment.
Option D is reactive and does not prevent insecure deployments.
A company undergoing digital transformation is reviewing the resiliency of a CSP and is concerned about meeting SLA requirements in the event of a CSP incident.
Which of the following would be best to proceed with the transformation?
- A . An on-premises solution as a backup
- B . A load balancer with a round-robin configuration
- C . A multicloud provider solution
- D . An active-active solution within the same tenant
C
Explanation:
Multicloud provider solutions involve using services from more than one cloud provider to ensure resiliency and redundancy. In the event of a failure or SLA breach by one CSP, another provider can maintain service continuity. An on-premises backup could help, but does not address CSP-specific SLA concerns directly. Round-robin load balancing and active-active within the same tenant still depend on a single provider, thus posing risks if the CSP fails.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX CAS-005, Domain 4.0: Implement redundancy and fault-tolerant strategies, including multicloud deployment for service resiliency.
A company undergoing digital transformation is reviewing the resiliency of a CSP and is concerned about meeting SLA requirements in the event of a CSP incident.
Which of the following would be best to proceed with the transformation?
- A . An on-premises solution as a backup
- B . A load balancer with a round-robin configuration
- C . A multicloud provider solution
- D . An active-active solution within the same tenant
C
Explanation:
Multicloud provider solutions involve using services from more than one cloud provider to ensure resiliency and redundancy. In the event of a failure or SLA breach by one CSP, another provider can maintain service continuity. An on-premises backup could help, but does not address CSP-specific SLA concerns directly. Round-robin load balancing and active-active within the same tenant still depend on a single provider, thus posing risks if the CSP fails.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX CAS-005, Domain 4.0: Implement redundancy and fault-tolerant strategies, including multicloud deployment for service resiliency.
Engineers are unable to control pumps at Site A from Site B when the SCADA controller at Site A experiences an outage. A security analyst must provide a secure solution that ensures Site A pumps can be controlled by a SCADA controller at Site B if a similar outage occurs again.
Which of the following represents the most cost-effective solution?
- A . Procure direct fiber connectivity between Site A and Site B and limit its use to the critical SCADA controller traffic only
- B . Install backup SCADA controllers at each site, isolate them from the OT network, and assign these backup controllers as high-availability pairs.
- C . Isolate the OT environment by providing an air-gapped network segment. Place the SCADA controller for each site in this network segment to minimize outages.
- D . Configure VPN concentrators inside the OT network segments at Site A and Site B and allow the controllers to act as secondary devices for the other site’s pumps across this encrypted tunnel.
D
Explanation:
The most cost-effective and secure solution is to configure VPN concentrators inside the OT networks at both sites (Option D). This setup allows encrypted communications between Site A and Site B, enabling controllers at either site to serve as secondary or failover devices for the other. By leveraging VPN tunnels, the organization avoids the expensive and time-consuming process of laying new fiber infrastructure, while still ensuring secure, authenticated, and encrypted connections across sites.
Option A, direct fiber connectivity, provides high performance but is extremely costly and less flexible than VPN solutions.
Option B, deploying redundant SCADA controllers at each site, increases hardware, licensing, and management costs while still requiring interconnectivity.
Option C, air-gapping the OT network, may improve isolation but would prevent remote failover capabilities, contradicting the requirement for cross-site control.
By implementing VPN concentrators, the organization achieves secure cross-site redundancy, supports operational continuity in case of controller outages, and does so in a cost-effective manner aligned with common OT security practices.
A security architect wants to develop abase line of security configurations These configurations automatically will be utilized machine is created.
Which of the following technologies should the security architect deploy to accomplish this goal?
- A . Short
- B . GASB
- C . Ansible
- D . CMDB
C
Explanation:
To develop a baseline of security configurations that will be automatically utilized when a machine is created, the security architect should deploy Ansible.
Here ’ s why:
Automation: Ansible is an automation tool that allows for the configuration, management, and deployment of applications and systems. It ensures that security configurations are consistently applied across all new machines.
Scalability: Ansible can scale to manage thousands of machines, making it suitable for large enterprises that need to maintain consistent security configurations across their infrastructure.
Compliance: By using Ansible, organizations can enforce compliance with security policies and standards, ensuring that all systems are configured according to best practices.
Reference: CompTIA Security+ SY0-601 Study Guide by Mike Chapple and David Seidl
Ansible Documentation: Best Practices
NIST Special Publication 800-40: Guide to Enterprise Patch Management Technologies
A security review revealed that not all of the client proxy traffic is being captured.
Which of the following architectural changes best enables the capture of traffic for analysis?
- A . Adding an additional proxy server to each segmented VLAN
- B . Setting up a reverse proxy for client logging at the gateway
- C . Configuring a span port on the perimeter firewall to ingest logs
- D . Enabling client device logging and system event auditing
C
Explanation:
Configuring a span port on the perimeter firewall to ingest logs is the best architectural change to ensure that all client proxy traffic is captured for analysis.
Here ’ s why:
Comprehensive Traffic Capture: A span port (or mirror port) on the perimeter firewall can capture all inbound and outbound traffic, including traffic that might bypass the proxy. This ensures that all network traffic is available for analysis.
Centralized Logging: By capturing logs at the perimeter firewall, the organization can centralize logging and analysis, making it easier to detect and investigate anomalies.
Minimal Disruption: Implementing a span port is a non-intrusive method that does not require significant changes to the network architecture, thus minimizing disruption to existing services.
Reference: CompTIA Security+ SY0-601 Study Guide by Mike Chapple and David Seidl NIST Special Publication 800-92: Guide to Computer Security Log Management OWASP Logging Cheat Sheet
A security analyst needs to ensure email domains that send phishing attempts without previous communications are not delivered to mailboxes.
The following email headers are being reviewed

Which of the following is the best action for the security analyst to take?
- A . Block messages from hr-saas.com because it is not a recognized domain.
- B . Reroute all messages with unusual security warning notices to the IT administrator
- C . Quarantine all messages with sales-mail.com in the email header
- D . Block vendor com for repeated attempts to send suspicious messages
D
Explanation:
In reviewing email headers and determining actions to mitigate phishing attempts, the security analyst should focus on patterns of suspicious behavior and the reputation of the sending domains.
Here’s the analysis of the options provided:
A security analyst notices a number of SIEM events that show the following activity:
10/30/2020 – 8:01 UTC – 192.168.1.1 – sc stop HinDctend
10/30/2020 – 8:05 UTC – 192.168.1.2 – c:program filesgamescomptidcasp.exe
10/30/2020 – 8:07 UTC – 192.168.1.1 – c:windowssystem32cmd.exe /c powershell
10/30/2020 – 8:07 UTC – 192.168.1.1 – powershell ―> 40.90.23.154:443
Which of the following response actions should the analyst take first?
- A . Disable powershell.exe on all Microsoft Windows endpoints
- B . Restart Microsoft Windows Defender
- C . Configure the forward proxy to block 40.90.23.154
- D . Disable local administrator privileges on the endpoints
C
Explanation:
The first immediate action in an active incident is containment. Blocking the IP address (40.90.23.154) at the network edge prevents further communication with the malicious external server. Disabling PowerShell or removing local admin privileges are valid hardening steps, but containment by network control is the highest priority during an active compromise to stop data exfiltration or further command and control activity.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX CAS-005, Domain 2.0: Apply incident response techniques focusing on immediate containment actions.
During a recent audit, a company’s systems were assessed.
Given the following information:
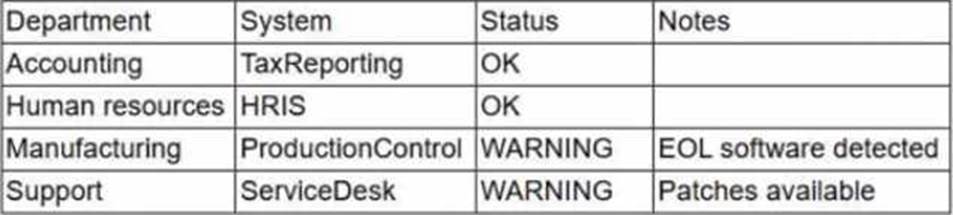
Which of the following is the best way to reduce the attack surface?
- A . Deploying an EDR solution to all impacted machines in manufacturing
- B . Segmenting the manufacturing network with a firewall and placing the rules in monitor mode
- C . Setting up an IDS inline to monitor and detect any threats to the software
- D . Implementing an application-aware firewall and writing strict rules for the application access
D
Explanation:
SecurityX CAS-005 network architecture objectives emphasize limiting exposure of vulnerable systems by using application-aware firewalls with strict rule sets.
This approach directly reduces the attack surface by allowing only approved application traffic to and from the vulnerable systems, mitigating risk until systems are patched or replaced.
EDR (A) enhances detection but doesn’t inherently reduce the exposed services.
Network segmentation in monitor mode (B) doesn’t block threats.
IDS (C) detects activity but does not block it.
