Practice Free CAS-005 Exam Online Questions
A systems engineer is configuring a system baseline for servers that will provide email services. As part of the architecture design, the engineer needs to improve performance of the systems by using an access vector cache, facilitating mandatory access control and protecting against:
• Unauthorized reading and modification of data and programs
• Bypassing application security mechanisms
• Privilege escalation
• interference with other processes
Which of the following is the most appropriate for the engineer to deploy?
- A . SELinux
- B . Privileged access management
- C . Self-encrypting disks
- D . NIPS
A
Explanation:
The most appropriate solution for the systems engineer to deploy is SELinux (Security-Enhanced Linux).
Here’s why:
Mandatory Access Control (MAC): SELinux enforces MAC policies, ensuring that only authorized users and processes can access specific resources. This helps in preventing unauthorized reading and modification of data and programs.
Access Vector Cache: SELinux utilizes an access vector cache (AVC) to improve performance. The AVC caches access decisions, reducing the need for repetitive policy lookups and thus improving system efficiency.
Security Mechanisms: SELinux provides a robust framework to enforce security policies and prevent bypassing of application security mechanisms. It controls access based on defined policies, ensuring that security measures are consistently applied.
Privilege Escalation and Process Interference: SELinux limits the ability of processes to escalate privileges and interfere with each other by enforcing strict access controls. This containment helps in isolating processes and minimizing the risk of privilege escalation attacks.
Reference: CompTIA Security+ SY0-601 Study Guide by Mike Chapple and David Seidl NSA’s Guide to the Secure Configuration of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 (SELinux)
NIST Special Publication 800-53: Security and Privacy Controls for Information Systems and Organizations
A security analyst is reviewing the following authentication logs:
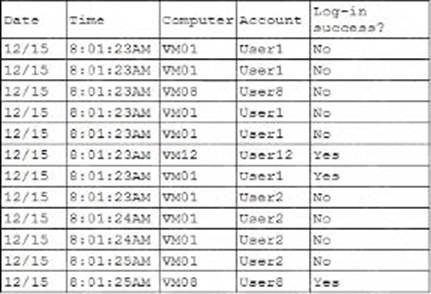
Which of the following should the analyst do first?
- A . Disable User2’s account
- B . Disable User12’s account
- C . Disable User8’s account
- D . Disable User1’s account
D
Explanation:
Based on the provided authentication logs, we observe that User1’s account experienced multiple failed login attempts within a very short time span (at 8:01:23 AM on 12/15). This pattern indicates a potential brute-force attack or an attempt to gain unauthorized access. Here’s a breakdown of why disabling User1’s account is the appropriate first step:
Failed Login Attempts:
The logs show that User1 had four consecutive failed login attempts:
VM01 at 8:01:23 AM
VM08 at 8:01:23 AM
VM01 at 8:01:23 AM
VM08 at 8:01:23 AM
Security Protocols and Best Practices: According to CompTIA Security+ guidelines, multiple failed login attempts within a short timeframe should trigger an immediate response to prevent further potential unauthorized access attempts. This typically involves temporarily disabling the account to stop ongoing brute-force attacks.
Account Lockout Policy: Implementing an account lockout policy is a standard practice to thwart brute-force attacks. Disabling User1’s account will align with these best practices and prevent further failed attempts, which might lead to successful unauthorized access if not addressed.
Reference: CompTIA Security+ SY0-601 Study Guide by Mike Chapple and David Seidl
CompTIA Security+ Certification Exam Objectives
NIST Special Publication 800-63B: Digital Identity Guidelines
By addressing User1’s account first, we effectively mitigate the immediate threat of a brute-force attack, ensuring that further investigation can be conducted without the risk of unauthorized access continuing during the investigation period.
A company wants to use loT devices to manage and monitor thermostats at all facilities The thermostats must receive vendor security updates and limit access to other devices within the organization.
Which of the following best addresses the company’s requirements”
- A . Only allowing Internet access to a set of specific domains
- B . Operating lot devices on a separate network with no access to other devices internally
- C . Only allowing operation for loT devices during a specified time window
- D . Configuring IoT devices to always allow automatic updates
B
Explanation:
The best approach for managing and monitoring IoT devices, such as thermostats, is to operate them on a separate network with no access to other internal devices. This segmentation ensures that the IoT devices are isolated from the main network, reducing the risk of potential security breaches affecting other critical systems. Additionally, this setup allows for secure vendor updates without exposing the broader network to potential vulnerabilities inherent in IoT devices.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX Study Guide: Recommends network segmentation for IoT devices to minimize security risks.
NIST Special Publication 800-183, "Network of Things": Advises on the isolation of IoT devices to enhance security.
"Practical IoT Security" by Brian Russell and Drew Van Duren: Discusses best practices for securing IoT devices, including network segmentation.
A company migrating to a remote work model requires that company-owned devices connect to a VPN before logging in to the device itself. The VPN gateway requires that a specific key extension is deployed to the machine certificates in the internal PKI.
Which of the following best explains this requirement?
- A . The certificate is an additional factor to meet regulatory MFA requirements for VPN access.
- B . The VPN client selected the certificate with the correct key usage without user interaction.
- C . The internal PKI certificate deployment allows for Wi-Fi connectivity before logging in to other systems.
- D . The server connection uses SSL VPN, which uses certificates for secure communication.
B
Explanation:
This scenario describes an enterprise VPN setup that requires machine authentication before a user logs in. The best explanation for this requirement is that the VPN client selects the appropriate certificate automatically based on the key extension in the machine certificate. Understanding the Key Extension Requirement:
PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) issues machine certificates that include specific key usages such as Client Authentication or IPSec IKE Intermediate.
Key usage extensions define how a certificate can be used, ensuring that only valid certificates are
selected by the VPN client.
Why Option B is Correct:
The VPN automatically selects the correct machine certificate with the appropriate key extension. The process occurs without user intervention, ensuring seamless VPN authentication before login.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A (MFA requirement): Certificates used in this scenario are for machine authentication, not user MFA. MFA typically involves user credentials plus a second factor (like OTPs or biometrics), which is not applicable here.
C (Wi-Fi connectivity before login): This refers to pre-logon networking, which is a separate concept where devices authenticate to a Wi-Fi network before login, usually via 802.1X EAP-TLS. However, this question specifically mentions VPN authentication, not Wi-Fi authentication.
D (SSL VPN with certificates): While SSL VPNs do use certificates, this scenario involves machine certificates issued by an internal PKI, which are commonly used in IPSec VPNs, not SSL VPNs.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX CAS-005 Official Study Guide: Section on Machine Certificate Authentication in VPNs
NIST SP 800-53: Guidelines on authentication mechanisms
RFC 5280: Internet X.509 Public Key Infrastructure Certificate and CRL Profile
After a penetration test on the internal network, the following report was generated:
Attack Target Result
Compromised host ADMIN01S.CORP.LOCAL Successful
Hash collected KRBTGT.CORP.LOCAL Successful
Hash collected SQLSV.CORP.LOCAL Successful
Pass the hash SQLSV.CORP.LOCAL Failed
Domain control CORP.LOCAL Successful
Which of the following should be recommended to remediate the attack?
- A . Deleting SQLSV
- B . Reimaging ADMIN01S
- C . Rotating KRBTGT password
- D . Resetting the local domain
C
Explanation:
The attacker gained domain control by collecting the KRBTGT hash (used for Kerberos tickets). Let’s evaluate:
A security administrator needs to review the efficacy of the detection rules configured on the SIEM by employing real-world attacker TTPs.
Which of the following actions should the security administrator take to accomplish this objective?
- A . Perform an internal penetration test.
- B . Use adversary emulation.
- C . Execute an internal vulnerability assessment.
- D . Perform a threat hunt exercise.
- E . Ingest new threat intelligence feeds.
B
Explanation:
The best option is adversary emulation. Adversary emulation involves simulating real-world attacker Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) based on frameworks like MITRE ATT&CK. Unlike penetration tests, which primarily focus on identifying exploitable vulnerabilities, adversary emulation specifically tests the effectiveness of detection and response capabilities against known adversarial behaviors.
Option A (penetration testing) provides value but may not align test cases with SIEM detection rules.
Option C (vulnerability assessment) identifies weaknesses but does not test detection rules.
Option D (threat hunting) is proactive analysis but does not validate existing SIEM rule coverage in a structured manner.
Option E (threat feeds) enrich SIEM data but do not test its efficacy.
CAS-005 identifies adversary emulation as a key strategy for validating detection and response coverage. It provides measurable results about what alerts are triggered and where detection gaps exist, enabling organizations to tune SIEM rules for improved efficacy.
An organization mat performs real-time financial processing is implementing a new backup solution Given the following business requirements?
* The backup solution must reduce the risk for potential backup compromise
* The backup solution must be resilient to a ransomware attack.
* The time to restore from backups is less important than the backup data integrity
* Multiple copies of production data must be maintained
Which of the following backup strategies best meets these requirement?
- A . Creating a secondary, immutable storage array and updating it with live data on a continuous basis
- B . Utilizing two connected storage arrays and ensuring the arrays constantly sync
- C . Enabling remote journaling on the databases to ensure real-time transactions are mirrored
- D . Setting up antitempering on the databases to ensure data cannot be changed unintentionally
A
Explanation:
A user submits a help desk ticket stating then account does not authenticate sometimes. An analyst reviews the following logs for the user:
Which of the following best explains the reason the user’s access is being denied?
- A . incorrectly typed password
- B . Time-based access restrictions
- C . Account compromise
- D . Invalid user-to-device bindings
B
Explanation:
The logs reviewed for the user indicate that access is being denied due to time-based access restrictions. These restrictions are commonly implemented to limit access to systems during specific hours to enhance security. If a user attempts to authenticate outside of the allowed time window, access will be denied. This measure helps prevent unauthorized access during non-business hours, reducing the risk of security incidents.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX Study Guide: Covers various access control methods, including time-based restrictions, as a means of enhancing security.
NIST Special Publication 800-53, "Security and Privacy Controls for Information Systems and Organizations": Recommends the use of time-based access restrictions as part of access control policies.
"Access Control and Identity Management" by Mike Chapple and Aaron French: Discusses the implementation and benefits of time-based access restrictions.
A systems administrator works with engineers to process and address vulnerabilities as a result of continuous scanning activities. The primary challenge faced by the administrator is differentiating between valid and invalid findings.
Which of the following would the systems administrator most likely verify is properly configured?
- A . Report retention time
- B . Scanning credentials
- C . Exploit definitions
- D . Testing cadence
B
Explanation:
When differentiating between valid and invalid findings from vulnerability scans, the systems administrator should verify that the scanning credentials are properly configured. Valid credentials ensure that the scanner can authenticate and access the systems being evaluated, providing accurate and comprehensive results. Without proper credentials, scans may miss vulnerabilities or generate false positives, making it difficult to prioritize and address the findings effectively.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX Study Guide: Highlights the importance of using valid credentials for accurate vulnerability scanning.
"Vulnerability Management" by Park Foreman: Discusses the role of scanning credentials in obtaining accurate scan results and minimizing false positives.
"The Art of Network Security Monitoring" by Richard Bejtlich: Covers best practices for configuring and using vulnerability scanning tools, including the need for valid credentials.
A company implemented a NIDS and a NIPS on the most critical environments. Since this implementation, the company has been experiencing network connectivity issues.
Which of the following should the security architect recommend for a new NIDS/NIPS implementation?
- A . Implementing the NIDS with a port mirror in the core switch and the NIPS in the main firewall
- B . Implementing the NIDS and the NIPS together with the main firewall
- C . Implementing a NIDS without a NIPS to increase the detection capability
- D . Implementing the NIDS in the bastion host and the NIPS in the branch network router
A
Explanation:
Best practice in CAS-005 network security design is to deploy:
NIDS passively via a port mirror (SPAN port) to avoid introducing latency or failure points.
NIPS inline in a strategic point, such as integrated with the main firewall, to actively block threats. This combination provides both visibility and active protection without overloading network paths.
