Practice Free CAS-005 Exam Online Questions
Based on the results of a SAST report on a legacy application, a security engineer is reviewing the following snippet of code flagged as vulnerable:
Which of the following is the vulnerable line of code that must be changed?

- A . Line (02]
- B . Line [04]
- C . Line [07]
- D . Line 108]
- E . Line [10]
E
Explanation:
The vulnerability lies in line [10], where the function strcpy(transmit, input) is used. The strcpy function does not perform boundary checking when copying strings. Since input is defined with a size of 256 characters and transmit only has 20 characters allocated, the strcpy operation will cause a buffer overflow when the contents of input exceed the allocated size of transmit. This creates a significant security vulnerability, as attackers can overwrite adjacent memory, potentially injecting malicious code or altering program execution.
Lines [02], [04], [07], and [08] are not inherently vulnerable by themselves. Line [04] defines the oversized input, but the vulnerability only materializes when combined with the unsafe copy in line [10]. Secure coding practices recommend using safer alternatives like strncpy, which includes a length parameter, or implementing runtime checks to ensure the destination buffer size is not exceeded.
Thus, the vulnerable line that must be changed is line [10], where strcpy is used.
A systems administrator needs to identify new attacks that could be carried out against the environment. The administrator plans to proactively seek out and observe new attacks.
Which of the following is the best way to accomplish this goal?
- A . Configuring an IPS
- B . Implementing sandboxing
- C . Scanning for IoCs
- D . Deploying a honeypot
D
Explanation:
According to SecurityX CAS-005 threat intelligence and testing objectives, a honeypot is a decoy system designed to lure attackers, allowing security teams to observe new tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) in a controlled environment.
An IPS is designed to block known attacks but not discover new ones.
Sandboxing is useful for analyzing suspicious files or malware samples but not for attracting live, unknown attack attempts.
Scanning for IoCs detects known compromise indicators, not new, emerging attacks. A honeypot directly supports proactive attack discovery and analysis.
An organization decides to move to a distributed workforce model. Several legacy systems exist on premises and cannot be migrated because of existing compliance requirements. However, all new systems are required to be cloud-based.
Which of the following would best ensure network access security?
- A . Utilizing a VPN for all users who require legacy system access
- B . Shifting all legacy systems to the existing public cloud infrastructure
- C . Configuring an SDN to block malicious traffic to on-premises networks
- D . Deploying microsegmentation with a firewall acting as the core router
A
Explanation:
For a distributed workforce needing access to compliance-bound on-premises systems, VPN access ensures encrypted, authenticated connectivity while limiting exposure. SecurityX CAS-005 emphasizes using VPNs for secure remote access when direct migration to cloud is not possible.
Moving legacy systems to cloud (B) violates the compliance constraints.
SDN security controls (C) are beneficial but do not inherently provide secure remote connectivity.
Microsegmentation (D) is useful for internal lateral movement control but does not solve remote access needs.
An organization is required to
* Respond to internal and external inquiries in a timely manner
* Provide transparency.
* Comply with regulatory requirements
The organization has not experienced any reportable breaches but wants to be prepared if a breach occurs in the future.
Which of the following is the best way for the organization to prepare?
- A . Outsourcing the handling of necessary regulatory filing to an external consultant
- B . Integrating automated response mechanisms into the data subject access request process
- C . Developing communication templates that have been vetted by internal and external counsel
- D . Conducting lessons-learned activities and integrating observations into the crisis management plan
C
Explanation:
Preparing communication templates that have been vetted by both internal and external counsel ensures that the organization can respond quickly and effectively to internal and external inquiries, comply with regulatory requirements, and provide transparency in the event of a breach.
Why Communication Templates?
Timely Response: Pre-prepared templates ensure that responses are ready to be deployed quickly, reducing response time.
Regulatory Compliance: Templates vetted by counsel ensure that all communications meet legal and regulatory requirements.
Consistent Messaging: Ensures that all responses are consistent, clear, and accurate, maintaining the organization’s credibility.
Crisis Management: Pre-prepared templates are a critical component of a broader crisis management plan, ensuring that all stakeholders are informed appropriately.
Other options, while useful, do not provide the same level of preparedness and compliance:
A web application server that provides services to hybrid modern and legacy financial applications recently underwent a scheduled upgrade to update common libraries, including OpenSSL. Multiple users are now reporting failed connection attempts to the server.
The technician performing initial triage identified the following:
• Client applications more than five years old appear to be the most affected.
• Web server logs show initial connection attempts by affected hosts.
• For the failed connections, logs indicate "cipher unavailable."
Which of the following is most likely to safely remediate this situation?
- A . The server needs to be configured for backward compatibility to SSL 3.0 applications.
- B . The client applications need to be modified to support AES in Galois/Counter Mode or equivalent.
- C . The client TLS configuration must be set to enforce electronic codebook modes of operation.
- D . The server-side digital signature algorithm needs to be modified to support elliptic curve cryptography.
B
Explanation:
The “cipher unavailable” message indicates that the client and server could not agree on a common cipher suite. After the OpenSSL update, the server likely dropped support for older, insecure ciphers (such as RC4 or 3DES) that legacy clients still use. The safest remediation is to update or configure the client applications to support modern, secure ciphers such as AES in Galois/Counter Mode (AES-GCM) or an equivalent strong cipher suite that is supported by the updated OpenSSL server.
Option A (SSL 3.0) is unsafe because SSL 3.0 is deprecated and vulnerable to multiple attacks (e.g., POODLE).
Option C (ECB mode) is insecure due to pattern leakage and should never be enforced.
Option D (ECC signatures) relates to key exchange and signatures, not to the “cipher unavailable” issue directly.
This approach aligns with SecurityX CAS-005 cryptographic interoperability guidance―modernize clients rather than reintroduce insecure protocols.
After discovering that an employee is using a personal laptop to access highly confidential data, a systems administrator must secure the company’s data.
Which of the following capabilities best addresses this situation?
- A . OCSP stapling
- B . CASB
- C . SOAR
- D . Conditional access
- E . Package monitoring
D
Explanation:
The best solution is Conditional Access (D). Conditional access policies enforce access requirements based on contextual signals such as device compliance, user identity, location, or risk profile. In this case, the administrator can configure conditional access to ensure that only managed, corporate-approved devices are allowed to access confidential data. If an employee attempts to use a personal laptop, the access request will be blocked or redirected to a secure process (e.g., virtual desktop).
Option A (OCSP stapling) relates to certificate revocation checking and does not control device access.
Option B (CASB) provides cloud access visibility and control but is broader and less precise than enforcing direct device-level conditional policies.
Option C (SOAR) orchestrates responses but is not primarily designed for access enforcement.
Option E (package monitoring) detects software changes but does not prevent unauthorized device usage.
Conditional access is a core principle in Zero Trust and modern IAM, making it the best solution for ensuring that sensitive data can only be accessed from trusted devices.
A company SIEM collects information about the log sources.
Given the following report information:
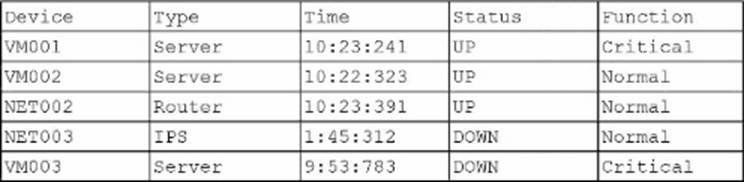
Which of the following actions should a security engineer take to enhance the security monitoring posture?
- A . Calibrate the timing on the log sources to enhance event correlation.
- B . Implement a centralized use case library to get alerts based on the type of log sources.
- C . Perform a non-reporting device assessment to collect missing log sources.
- D . Create a resiliency plan to prevent losing event logs from log sources.
C
Explanation:
The SIEM report shows that some devices, such as VM003 (Critical server) and NET003 (IPS), are DOWN and therefore not reporting logs. In security monitoring, the absence of log data from critical systems creates dangerous blind spots. If logs are missing, attacks can proceed undetected, or investigations may lack the data needed for incident response.
The most effective action is to perform a non-reporting device assessment (C). This means identifying and correcting issues where devices fail to send logs, whether due to outages, misconfigurations, or integration gaps. Ensuring all critical devices, especially servers and intrusion prevention systems, consistently send logs to the SIEM strengthens overall visibility and monitoring posture.
Option A (time calibration) is important for correlation accuracy but does not address missing log feeds.
Option B (centralized use case library) enhances detection but only works if the SIEM is receiving complete data.
Option D (resiliency plan) helps protect log retention but is irrelevant if logs are never received in the first place.
Therefore, fixing non-reporting log sources is the highest priority to improve monitoring effectiveness.
An organization wants to implement a secure cloud architecture across all instances.
Given the following requirements:
• Establish a standard network template.
• Deployments must be consistent.
• Security policies must be able to be changed at scale.
Which of the following technologies meets these requirements?
- A . Serverless deployment model
- B . Container orchestration
- C . Infrastructure as code
- D . CLI cloud administration
- E . API gateway
Employees use their badges to track the number of hours they work. The badge readers cannot be upgraded due to facility constraints. The software for the badge readers uses a legacy platform and requires connectivity to the enterprise resource planning solution.
Which of the following is the best to ensure the security of the badge readers?
- A . Segmentation
- B . Vulnerability scans
- C . Anti-malware
A
Explanation:
Segmentation is the best option to ensure the security of legacy badge readers that cannot be upgraded. Segmentation isolates the legacy devices on a separate network segment to minimize their exposure to potential threats. This approach reduces the attack surface by preventing unauthorized access from other parts of the network while still allowing necessary connectivity to the enterprise resource planning (ERP) system.
Vulnerability scans (B)are useful for identifying weaknesses but do not actively protect the badge readers.
Anti-malware (C)is ineffective since the badge readers use a legacy platform that likely does not support modern endpoint protection solutions.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX (CAS-005) Exam Objectives- Domain 2.0 (Security Architecture), Section on Network Segmentation & Attack Surface Management
Users are experiencing a variety of issues when trying to access corporate resources examples include
• Connectivity issues between local computers and file servers within branch offices
• Inability to download corporate applications on mobile endpoints wtiilc working remotely
• Certificate errors when accessing internal web applications
Which of the following actions are the most relevant when troubleshooting the reported issues? (Select two).
- A . Review VPN throughput
- B . Check IPS rules
- C . Restore static content on lite CDN.
- D . Enable secure authentication using NAC
- E . Implement advanced WAF rules.
- F . Validate MDM asset compliance
A,F
Explanation:
The reported issues suggest problems related to network connectivity, remote access, and certificate management:
