Practice Free CAS-005 Exam Online Questions
An organization would like to increase the effectiveness of its incident response process across its multiplatform environment. A security engineer needs to implement the improvements using the organization’s existing incident response tools.
Which of the following should the security engineer use?
- A . Playbooks
- B . Event collectors
- C . Centralized logging
- D . Endpoint detection
A
Explanation:
The correct answer is Playbooks (A). In incident response, playbooks are structured workflows that define step-by-step actions for specific incident types (e.g., ransomware, phishing, insider threats). They allow SOC analysts to standardize responses across multiple platforms and tools, ensuring consistency and faster mitigation. By leveraging playbooks, organizations integrate existing incident response tools into automated or semi-automated processes, improving efficiency and reducing human error.
Option B (event collectors) consolidate logs but do not directly improve response processes.
Option C (centralized logging) enhances visibility but does not provide a framework for action.
Option D (endpoint detection) expands detection capabilities but does not enhance the process effectiveness of incident response.
CAS-005 emphasizes structured response through automation and orchestration. Playbooks, often implemented via SOAR platforms, allow integration of detection, triage, and remediation steps, making them the most effective way to increase incident response maturity.
A global company with a remote workforce implemented a new VPN solution. After deploying the VPN solution to several hundred users, the help desk starts receiving reports of slow access to both internally and externally available applications. A security analyst reviews the following:
VPN client routing: 0.0.0.0/0 → eth1
Which of the following solutions should the analyst use to fix this issue?
- A . Move the servers to a screened subnet.
- B . Enable split tunneling.
- C . Configure an NAC solution.
- D . Implement DNS over HTTPS.
B
Explanation:
The routing entry 0.0.0.0/0 forces all traffic from remote clients―including traffic destined for the public internet―through the VPN tunnel. This is called full-tunnel VPN routing. While it ensures strong security by forcing all traffic to pass through corporate controls, it can also overload VPN gateways and cause slow access to both internal and external applications, as seen in this scenario.
The correct fix is to enable split tunneling (B). Split tunneling allows only corporate traffic (e.g., private IP ranges or internal applications) to flow through the VPN, while internet-bound traffic routes directly to the internet. This reduces congestion on VPN concentrators, improves performance for remote users, and ensures efficient use of bandwidth.
Moving servers to a screened subnet (A) relates to internal segmentation but does not fix the VPN bottleneck. NAC (C) enforces device compliance but does not address routing inefficiencies. DNS over HTTPS (D) secures name resolution but is unrelated to network congestion.
Thus, enabling split tunneling balances security and performance for remote workers.
An organization recently implemented a purchasing freeze that has impacted endpoint life-cycle management efforts.
Which of the following should a security manager do to reduce risk without replacing the endpoints?
- A . Remove unneeded services
- B . Deploy EDR
- C . Dispose of end-of-support devices
- D . Reimage the system
A
Explanation:
Removing unnecessary services from existing endpoints reduces the attack surface by minimizing the number of potential vulnerabilities attackers could exploit. This is a cost-effective method to harden devices without requiring new purchases, aligning perfectly with a purchasing freeze. Deploying new EDR solutions or disposing of devices would likely conflict with the resource freeze, and reimaging systems does not address minimizing services proactively.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX CAS-005, Domain 3.0: Implement endpoint security controls and hardening techniques.
A security analyst is reviewing the following log:
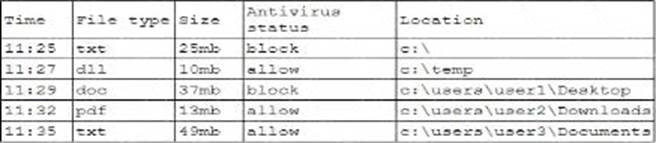
Which of the following possible events should the security analyst investigate further?
- A . A macro that was prevented from running
- B . A text file containing passwords that were leaked
- C . A malicious file that was run in this environment
- D . A PDF that exposed sensitive information improperly
B
Explanation:
Based on the log provided, the most concerning event that should be investigated further is the presence of a text file containing passwords that were leaked.
Here’s why:
Sensitive Information Exposure: A text file containing passwords represents a significant security risk, as it indicates that sensitive credentials have been exposed in plain text, potentially leading to unauthorized access.
Immediate Threat: Password leaks can lead to immediate exploitation by attackers, compromising user accounts and sensitive data. This requires urgent investing
A security engineer receives an alert from the threat intelligence platform with the following information:
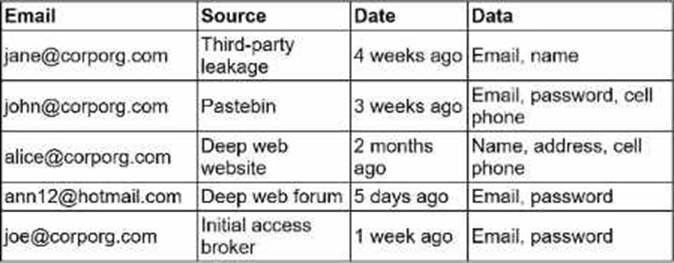
Which of the following actions should the security engineer do first?
- A . Reset John’s and Joe’s access.
- B . Contact John. Ann. and Joe to inform them about the incident and schedule a password reset.
- C . Reset John’s, Ann’s, and Joe’s passwords and disconnect all users* active sessions
- D . Reset John’s and Joe’s passwords and inform authorities about the leakage.
A
Explanation:
The first action should be to reset access for John and Joe, who are corporate accounts belonging to the organization. Their credentials were exposed in recent leaks, including one from an initial access broker (Joe), which indicates an active exploitation risk. Immediate password resets and session invalidations prevent adversaries from using the compromised credentials to gain access.
Ann’s account (@hotmail.com) is personal and not under corporate management, so while her exposure is concerning, it does not pose a direct risk to organizational systems. Contacting her can follow later steps but should not delay urgent remediation for John and Joe.
Option B delays remediation.
Option C overreaches by including Ann in corporate resets.
Option D includes contacting authorities prematurely, which is important but secondary to immediate containment.
CAS-005 emphasizes rapid containment of credential leaks affecting corporate identities, making access resets for John and Joe the first step.
A news organization wants to implement workflows that allow users to request that untruthful data be retraced and scrubbed from online publications to comply with the right to be forgotten.
Which of the following regulations is the organization most likely trying to address’
- A . GDPR
- B . COPPA
- C . CCPA
- D . DORA
A
Explanation:
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is the regulation most likely being addressed by the news organization. GDPR includes provisions for the "right to be forgotten," which allows individuals to request the deletion of personal data that is no longer necessary for the purposes for which it was collected. This regulation aims to protect the privacy and personal data of individuals within the European Union.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX Study Guide: Covers GDPR and its requirements, including the right to be forgotten.
GDPR official documentation: Details the rights of individuals, including data erasure and the right to be forgotten.
"GDPR: A Practical Guide to the General Data Protection Regulation" by IT Governance Privacy Team: Provides a comprehensive overview of GDPR compliance, including workflows for data deletion requests.
Which of the following are the best ways to mitigate the threats that are the highest priority? (Select two).
- A . Isolate network systems using Zero Trust architecture with microsegmentation and SD-WAN
- B . Scan all systems and source code with access to sensitive data for vulnerabilities.
- C . Implement a cloud access security broker and place it in blocking mode to prevent information exfiltration.
- D . Apply data labeling to all sensitive information within the environment with special attention to payroll information.
- E . Institute a technical approval process that requires multiple parties to sign off on mass payroll changes.
An organization is developing a disaster recovery plan that requires data to be backed up and available at a moment’s notice.
Which of the following should the organization consider first to address this requirement?
- A . Implement a change management plan to ensure systems are using the appropriate versions.
- B . Hire additional on-call staff to be deployed if an event occurs.
- C . Design an appropriate warm site for business continuity.
- D . Identify critical business processes and determine associated software and hardware requirements.
D
Explanation:
For a disaster recovery (DR) plan requiring immediate data availability, the first step is understanding what needs to be protected and recovered. Identifying critical business processes and their associated software and hardware requirements establishes the foundation for the DR plan. This ensures that backups and recovery mechanisms align with business priorities, meeting the "moment’s notice" requirement.
Option A: A change management plan is important for system consistency but doesn’t directly address immediate data availability in a DR context.
Option B: Hiring staff supports execution but doesn’t define what needs to be recovered or how. It’s a later step.
Option C: A warm site (a partially operational backup site) is a good DR solution, but designing it comes after identifying critical processes and resources.
Option D: This is the first step in any DR planning process―knowing what’s critical ensures the plan meets availability goals efficiently.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX CAS-005 Domain 4: Cybersecurity Operations C Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity Planning.
Acompany must build and deploy security standards for all servers in its on-premises and cloud environments based on hardening guidelines.
Which of the following solutions most likely meets the requirements?
- A . Develop a security baseline to integrate with the vulnerability scanning platform to alert about any server not aligned with the new security standards.
- B . Create baseline images for each OS in use, following security standards, and integrate the images into the patching and deployment solution.
- C . Build all new images from scratch, installing only needed applications and modules in accordance with the new security standards.
- D . Run a script during server deployment to remove all the unnecessary applications as part of provisioning.
B
Explanation:
Creating secure baseline images ensures consistent, repeatable deployment aligned with hardening standards. These images can be used across on-premises and cloud environments, ensuring compliance and reducing misconfigurations.
Vulnerability alerts (A) are reactive, not preventive.
Building images from scratch (C) is time-consuming and unnecessary if baselines exist. Scripts for cleanup (D) are useful but do not prevent initial insecure configurations.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX (CAS-005) Exam Objectives – Domain 3.0 (Security Engineering), Section on System Hardening & Configuration Management
A Chief Information Security Officer requests an action plan to remediate vulnerabilities. A security analyst reviews the output from a recent vulnerability scan and notices hundreds of unique vulnerabilities. The output includes the CVSS score, IP address, hostname, and the list of vulnerabilities. The analyst determines more information is needed in order to decide which vulnerabilities should be fixed immediately.
Which of the following is the best source for this information?
- A . Third-party risk review
- B . Business impact analysis
- C . Incident response playbook
- D . Crisis management plan
B
Explanation:
The correct source is the Business Impact Analysis (BIA). A BIA provides context about which systems and applications are most critical to business operations, regulatory compliance, and customer obligations. While CVSS scores indicate severity in technical terms, they do not reflect the business impact of exploitation. For example, a medium-severity vulnerability on a critical payment system may pose more business risk than a high-severity vulnerability on a test server.
Option A (third-party risk review) focuses on vendor security posture, not internal remediation priorities.
Option C (incident response playbook) guides response during active incidents, not vulnerability prioritization.
Option D (crisis management plan) addresses executive-level communications during crises, not technical risk assessment.
By combining vulnerability scan data with BIA context, security teams can prioritize remediation efforts based on business-critical systems, ensuring the highest-risk vulnerabilities are remediated first. This aligns with CAS-005’s guidance on risk-based prioritization of remediation efforts.
