Practice Free AZ-800 Exam Online Questions
You have an on-premises server that runs Windows Server and contains the folders shown in the following table.
You have an Azure subscription.
You plan to implement Azure File Sync
Which folders can be added as Azure File Sync server endpoints?
- A . Folder1 and Folder2 only
- B . Folder1, FoWer2, and FoWet3
- C . Folder1 only
- D . Folder2 and Foldet3 only
- E . Folder3 only
- F . Folder2 only
You have an Azure subscription that contains the virtual networks shown in the following table.
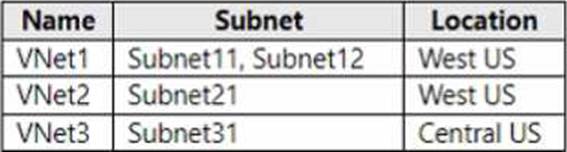
You deploy a virtual machine named VM1 that runs Windows Server. VM1 is connected to Subnet11. You plan to add an additional network interface named NIC1 to VM1.
To which subnets can NIC1 be attached?
- A . Subnet11 only
- B . Subnet12 only
- C . Subnet11 and Subnet12only
- D . Subnet12 and Subnet21 only
- E . Subnet11, Subnet12, Subnet21f and Subnet31
C
Explanation:
In the Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure materials covering Azure IaaS networking and multi-NIC VMs, Microsoft’s guidance clarifies the placement rules for additional network interfaces: all NICs attached to a virtual machine must belong to the same virtual network as the VM’s primary interface, and the VM/NICs must be in the same Azure region. The study guide further explains that, within that virtual network, a NIC may be attached to any subnet of that VNet (including the same subnet as the primary NIC or a different subnet). It is not supported to attach a NIC from a different VNet, even if that VNet resides in the same region or is peered, and NICs cannot span regions.
Applying these rules: VM1 is connected to Subnet11 in VNet1 (West US). An additional NIC (NIC1) can therefore be attached only to subnets that are in VNet1 and in the same region. That includes Subnet11 and Subnet12 (both in VNet1, West US). Subnet21 (in VNet2, West US) is in a different VNet and is not eligible, and Subnet31 (in VNet3, Central US) is both a different VNet and a different region. Consequently, the only valid targets for NIC1 are Subnet11 and Subnet12.
SIMULATION
Task 8
You need to create an Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) site named Site2 that is associated to an IP address range of 192.168.2.0 to 192.168.2.255.
On a domain controller or a computer that has the Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) installed, open Active Directory Sites and Services from the Administrative Tools menu or by typing dssite.msc in the Run box.
In the left pane, right-click on Sites and select New Site.
In the New Object – Site dialog box, enter Site2 as the Name of the new site. Select a site link to associate the new site with, such as DEFAULTIPSITELINK, and click OK. You can also create a new site link if you want to customize the replication frequency and schedule between the sites. For more information on how to create a site link, see Create a Site Link.
In the left pane, right-click on Subnets and select New Subnet.
In the New Object – Subnet dialog box, enter 192.168.2.0/24 as the Prefix of the subnet. This notation represents the IP address range of 192.168.2.0 to 192.168.2.255 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0. Select Site2 as the Site object to associate the subnet with, and click OK.
Wait for the changes to replicate to other domain controllers. You can verify the site and subnet creation by checking the Sites and Subnets containers in Active Directory Sites and Services.
Now, you have created an AD DS site named Site2 that is associated to an IP address range of 192.168.2.0 to 192.168.2.255. You can add domain controllers to the new site and configure the site links and site link bridges to optimize the replication topology.
You have an Azure virtual machine named VM1 that runs Windows Server.
You need to ensure that administrators request access to VM1 before establishing a Remote Desktop connection.
What should you configure?
- A . Azure Front Door
- B . Microsoft Defender for Cloud
- C . Azure AD Privileged Identity Management (PIM)
- D . a network security group (NSG)
B
Explanation:
In the Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure materials, Microsoft emphasizes using Microsoft Defender for Cloud C Just-in-time (JIT) VM access to control administrative access to Azure VMs. The guide explains that JIT “locks down inbound traffic to management ports (for example, RDP 3389) by updating the VM’s NSG/Azure Firewall so they’re blocked by default. When access is needed, an authorized user submits a JIT request in Defender for Cloud specifying the port(s), source IP, and time window. If approved, Defender for Cloud temporarily opens the rule and automatically reverts it when the window expires.” This delivers a request/approval workflow before a Remote Desktop session can be established and minimizes exposure of management ports.
The same objectives note that while Azure AD Privileged Identity Management (PIM) controls role activation/elevation, it does not provide the network gate required to force a request prior to RDP connectivity. Similarly, an NSG by itself can allow/deny traffic but offers no on-demand request workflow. Azure Front Door is for HTTP(S) applications and is not used for RDP. Therefore, to ensure administrators must request access prior to connecting via RDP to VM1, you configure Defender for Cloud JIT VM access, which enforces time-bound, IP-scoped openings of port 3389 and automatically closes them, aligning with the exam guidance for securing Windows Server IaaS VMs.
You have an Azure subscription that contains the following resources:
• An Azure Log Analytics workspace
• An Azure Automation account
• Azure Arc.
You have an on-premises server named Server1 that is onboaraed to Azure Arc
You need to manage Microsoft updates on Server! by using Azure Arc
Which two actions should you perform? Each correct answer presents part of the solution. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point
- A . Add Microsoft Sentinel to the Log Analytics workspace
- B . On Server1, install the Azure Monitor agent
- C . From the Automation account, enable Update Management for Server1.
- D . From the Virtual machines data source of the Log Analytics workspace, connect Server1.
BC
Explanation:
To manage Microsoft updates on an on-premises server via Azure Arc, you must leverage the Azure Update Management solution. According to official Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure study guides, Azure Arc-enabled servers allow you to manage your non-Azure Windows and Linux machines as if they were native Azure resources. To facilitate update management, the infrastructure relies on a connection between the machine, an Azure Automation account, and a Log Analytics workspace.
First, you must install the Azure Monitor agent (or the Legacy Log Analytics agent, though AMA is the current standard) on Server1. This agent is responsible for collecting inventory data and the status of available updates, then sending that metadata to the Log Analytics workspace. Azure Arc simplifies this deployment by allowing the agent to be installed as an extension directly from the Azure portal.
Second, you must enable Update Management from the Automation account. The Update Management solution uses the data collected by the agent to assess the update status of the server. Once enabled, you can create update deployments to schedule the installation of updates during defined maintenance windows. This integrated approach ensures that hybrid servers―those residing on-premises but managed via Azure Arc―receive the same governance and patching consistency as cloud-native virtual machines.
Option A is incorrect as Sentinel is for security orchestration, and Option D is incorrect because Arc-enabled servers are not connected through the "Virtual machines" data source used for native Azure VMs.
HOTSPOT
You have an Azure subscription that contains a virtual network named VNet1. Vnet1 contains three subnets named Subnet1, Subnet2, and Subnet3.
You deploy a virtual machine that has the following settings:
• Name:VM1
• Subnet: Subnet2
• Network interface name: NIC1
• Operating system: Windows Server 2022
You need to ensure that VM1 can route traffic between Subnet1 and Subnet3. The solution must minimize administrative effort.
What should you do? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.


Explanation:
From the Azure portal: Enable IP forwarding for NIC1.
On VM1: Install and configure Routing and Remote Access
In Azure VNets, layer-3 routing between subnets is provided by the platform, but if you want a VM to act as a router (NVA) and forward traffic between subnets, two things are required: the NIC must be allowed to pass traffic not destined to itself, and the guest OS must be configured to perform IP forwarding/routing. The Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure guidance for “Manage and maintain Windows Server IaaS virtual machines” and “Implement on-premises and hybrid networking” explains that Azure requires IP forwarding to be enabled on the NIC for any VM acting as a router or load balancer so that the fabric will deliver transit packets to the VM instead of dropping them. The Windows Server role that provides routing is Routing and Remote Access (RRAS); enabling the LAN routing feature configures the TCP/IP stack to forward packets between interfaces (including forwarding back out the same interface when used with Azure’s virtual switch). The same material notes that adding extra NICs is not mandatory for simple transit scenarios, and that user-defined routes can be used when you need to steer traffic through the router; however, to enable the VM itself to route, the minimal administrative steps are: turn on IP forwarding for the NIC in Azure and install/configure RRAS in the guest. This combination allows VM1 to route traffic between Subnet1 and Subnet3 with the least effort.
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in
the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You are planning the deployment of DNS to a new network.
You have three internal DNS servers as shown in the following table.
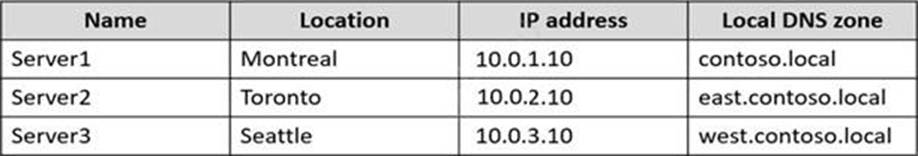
The contoso.local zone contains zone delegations for east.contoso.local and west.contoso.local. All the DNS servers use root hints.
You need to ensure that all the DNS servers can resolve the names of all the internal namespaces and internet hosts.
Solution: You configure Server2 and Server3 to forward DNS requests to 10.0.1.10.
Does this meet the goal?
- A . Yes
- B . No
A
Explanation:
In the Windows Server DNS planning guidance from Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure, forwarders can be used to centralize name resolution through a designated DNS server. The guide states that a DNS server can be configured to “forward queries it cannot resolve to one or more upstream DNS servers” and that this is often used to “centralize Internet and internal namespace resolution through an authoritative hub server.” In this scenario, Server1 hosts the contoso.local parent zone and already contains delegations to east.contoso.local and west.contoso.local. If Server2 and Server3 are set to forward unresolved queries to 10.0.1.10 (Server1), they will resolve:
• Internal names―Server1 is authoritative for the parent and, through delegations, can refer requests to the appropriate child-zone servers.
• Internet names―Server1 uses root hints and can resolve external hosts, with Server2/Server3 receiving the answers via forwarding.
The study materials emphasize: “Delegations enable a parent zone to direct queries to child zones,” and “forwarders do not break authority―authoritative data is answered locally; only unresolved names are forwarded.” Thus, configuring Server2 and Server3 to forward to Server1 satisfies the requirement that all DNS servers resolve all internal namespaces and Internet hosts, while keeping the design simple and consistent with DNS best practices.
DRAG DROP
You deploy a single-domain Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) forest named contoso.com.
You deploy five servers to the domain. You add the servers to a group named iTFarmHosts.
You plan to configure a Network Load Balancing (NIB) cluster named NLBCluster.contoso.com that will contain the five servers.
You need to ensure that the NLB service on the nodes of the cluster can use a group managed service account (gMSA) to authenticate.
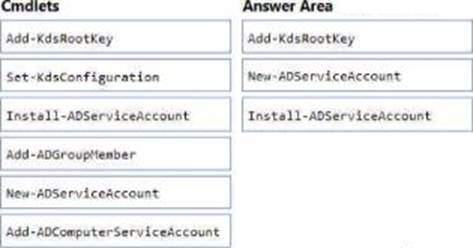
Which three PowerShell cmdlets should you run in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate cmdiets from the list of cmdlets to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Explanation:
The AZ-800 materials explain that group Managed Service Accounts (gMSAs) rely on the KDS (Key Distribution Service) to generate and rotate passwords. Therefore, in a new forest you must first create a KDS root key:
“Before creating your first gMSA, run Add-KdsRootKey to seed the KDS” (the key may need propagation time).
Next, you create the gMSA and scope which computers can retrieve its managed password:
Use New-ADServiceAccount with -PrincipalsAllowedToRetrieveManagedPassword set to the security group that contains the NLB nodes (here, ITFarmHosts), and specify the DNS host name as needed for the service (e.g., NLBCluster.contoso.com).
Finally, on each cluster node you install (register) the gMSA locally so services can run under it:
Run Install-ADServiceAccount on each server in ITFarmHosts.
Cmdlets like Add-ADComputerServiceAccount are used for standalone MSAs (sMSAs), not gMSAs, and Set-ADForestConfiguration isn’t required. This sequence enables the NLB service on all five nodes to authenticate using the gMSA with automatic password management.
SIMULATION
Task 5
You need to ensure that a DHCP scope named scope! on SRV1 can service client requests.
On SRV1, open DNS Manager from the Administrative Tools menu or by typing dnsmgmt.msc in the Run box.
In the left pane, expand your DHCP server and click on IPv4.
In the right pane, right-click on the scope that you want to activate, such as scope1, and select Activate.
Wait for the scope to be activated. You can verify the activation status by checking the icon next to the scope name. A green arrow indicates that the scope is active, while a red arrow indicates that the scope is inactive.
Now, the DHCP scope named scope1 on SRV1 can service client requests and lease IP addresses to DHCP clients. You can test the DHCP service by using the ipconfig /renew command on a DHCP client computer that is connected to the same subnet as the scope.
HOTSPOT
Your network contains an Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) forest. The forest contains two domains named contoso.com and east.contoso.com. Contoso.com contains two users named CONTOSO User1 and EASTUser2.
You need to ensure that the users can perform the following tasks:
• User1 must deploy an additional domain controller to eastcontoso.com.
• User2 must deploy a new domain controller that will host a domain named west.contoso.com.
The solution must follow the principle of least privilege.
To which group should you add each user? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

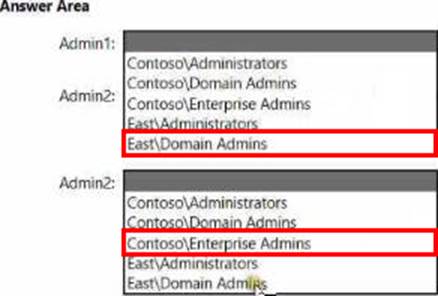
Explanation:
The Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure guidance for AD DS promotion and forest operations states that adding a new domain controller to an existing domain requires credentials that “are a member of Domain Admins in the target domain (or equivalent delegated rights).” This is the minimum built-in role permitted to run AD DS installation and write to the domain’s configuration containers for DC promotion. Therefore, to add an additional DC in east.contoso.com, the least-privilege group for User1 is EASTDomain Admins.
For creating a new domain (child domain or new tree) in an existing forest, the exam materials specify that this is a forest-wide operation handled by the Domain Naming Master and requires enterprise-level permissions: “to create or remove domains in a forest, you must use an account that is a member of the Enterprise Admins group.” Domain Admins in a single domain are insufficient because the task modifies forest-level naming contexts. Thus, to deploy the first DC for west.contoso.com, the least-privilege role that satisfies the requirement for User2 is CONTOSOEnterprise Admins.
These selections follow the principle of least privilege: User1 is scoped to the child domain’s administration only, while User2 receives the forest-level rights necessary to add a new domain.
