Practice Free AZ-800 Exam Online Questions
HOTSPOT
Your network contains the domains shown in the following exhibit.
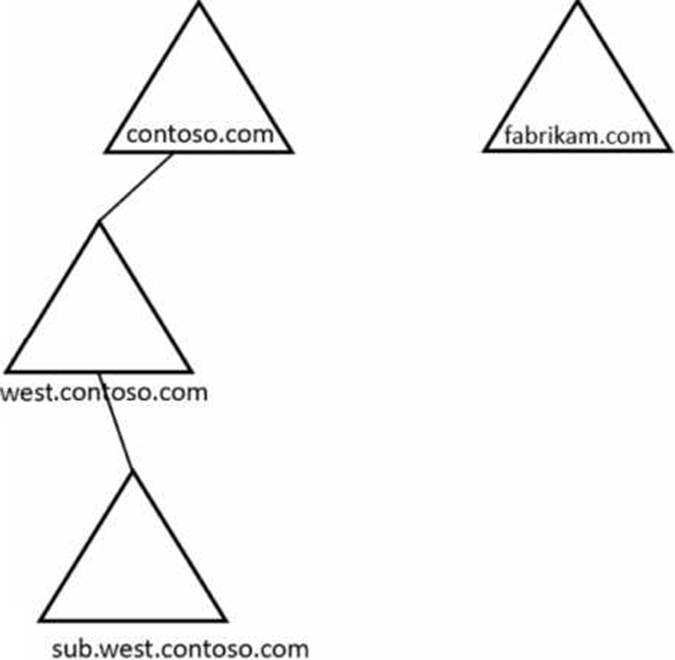
You need to establish trust relationships as shown in the following exhibit.
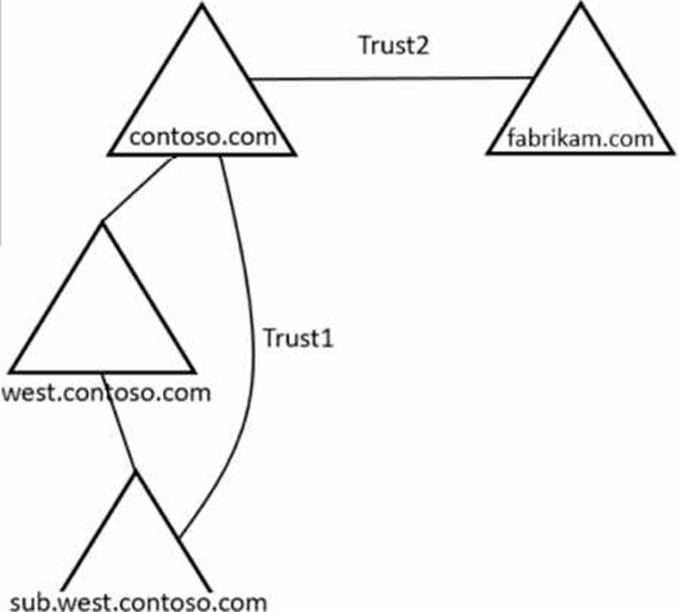
Which type of trust can you use for Trust1 and Trust2? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.


Explanation:
In the Windows Server hybrid core curriculum, trust selection is based on domain/forest boundaries and adjacency. The guidance explains that parent/child domains in the same forest already have implicit, two-way transitive trusts. When authentication frequently crosses nonadjacent domains inside the same forest, you can create a shortcut trust “to optimize name-crack and referral time between domains that otherwise authenticate through multiple hops.” In the scenario, contoso.com (forest root) and sub.west.contoso.com (a grandchild) are nonadjacent domains in the same forest. They already trust through west.contoso.com, so the only additional trust that makes sense―and matches the diagram―is a shortcut trust to shorten the path.
For cross-forest connectivity, the material states that trusts across different forests are not implicit.
To enable authentication between contoso.com and fabrikam.com, you use either:
a Forest trust (created between forest root domains; transitive across the forests and best when ongoing collaboration is required), or an External trust (nontransitive, domain-to-domain; used when a full forest trust is not possible or not desired).
Therefore, Trust1 = Shortcut trust only (intra-forest, nonadjacent domains) and Trust2 = Forest trust or external trust only (inter-forest trust options).
You have a Windows Server container host named Server 1 and a container image named Image1.
You need to start a container from image1. The solution must run the container on a Hyper-V virtual machine.
Which parameter should you specify when you run the docker run command?
- A . –expose
- B . –privileged
- C . –runtime
- D . –entrypoint
- E . –isolation
E
Explanation:
Reference: In Windows Server container scenarios, process isolation shares the host kernel, while Hyper-V isolation runs each container inside a lightweight Hyper-V VM that provides a stronger boundary. The Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure guidance states that when you must run a Windows container with a VM boundary, you start it using Hyper-V isolation. Operationally, this is done at run time with the Docker CLI by specifying the isolation mode: docker run –isolation=hyperv …. Other parameters don’t meet the requirement: –expose only publishes ports, –privileged is a Linux concept not used for Windows security boundaries, –runtime selects the OCI runtime (relevant to Linux), and –entrypoint overrides the default process but does nothing for isolation. Using — isolation=hyperv ensures the container launches on a minimal Hyper-V partition created by the Windows container host, satisfying scenarios that require strict separation, kernel mismatch tolerance, or enhanced defense-in-depth―exactly what the requirement “run the container on a Hyper-V virtual machine” describes. This aligns with the exam’s emphasis on selecting the proper Windows container isolation mode to meet security and compatibility goals during deployment and operations.
Your network contains an Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) domain- The domain contains 10 servers that run Windows Server. The servers have static IP addresses.
You plan to use DHCP to assign IP addresses to the servers.
You need to ensure that each server always receives the same IP address.
Which type of identifier should you use to create a DHCP reservation for each server?
- A . universally unique identifier (UUID)
- B . fully qualified domain name (FQDN)
- C . NetBIOS name
- D . MAC address
D
Explanation:
Reference: In the Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure materials for DHCP, reservations are defined as mappings that “bind a specific hardware (MAC) address to a single, permanent IPv4 address from a scope.” The guide emphasizes that DHCP reservations ensure devices―such as servers using DHCP rather than static addressing―“always receive the same address whenever they request a lease,” and that the required inputs when creating a reservation are the IP address, MAC address (also called hardware address), and a descriptive name. The exam prep further notes that while DHCPv4 supports an optional “Client Identifier,” Windows Server hosts typically use the MAC address by default unless explicitly configured otherwise. Because your 10 Windows Server machines currently use static IPs and you want DHCP to always assign them the same IP, the correct identifier for each reservation is the MAC address. FQDNs and NetBIOS names are not valid unique identifiers for DHCP reservations, and UUIDs are unrelated to DHCP addressing. Therefore, selecting MAC address meets the reservation requirement and aligns with the documented DHCP best practices in the hybrid core infrastructure objectives.
SIMULATION
Task 2
You need to ensure that you can manage SRV1 remotely by using PowerShell
Step 1: Enable PowerShell Remoting on SRV1 On SRV1, run the following command to enable
PowerShell Remoting:
Enable-PSRemoting -Force
This command configures the computer to receive PowerShell remote commands that are sent by using the WS-Management technology.
Step 2: Configure the TrustedHosts List (If Needed) If you’re managing SRV1 from a computer that is not part of the same domain, you’ll need to add the managing computer’s name to the TrustedHosts list on SRV1:
Set-Item wsman:localhostClientTrustedHosts -Value "ManagingComputerName" -Concatenate – Force
Replace “ManagingComputerName” with the name of your managing computer.
Step 3: Start a Remote Session From your managing computer, start a remote session with SRV1 using the Enter-PSSession cmdlet:
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName SRV1 -Credential (Get-Credential)
This command prompts you for credentials and then starts a remote session with SRV1.
Step 4: Run Remote Commands Once the remote session is established, you can run any PowerShell command as if you were directly on SRV1.
For example:
Get-Service
This command gets the status of services on SRV1.
Step 5: Exit the Remote Session When you’re finished, exit the remote session:
Exit-PSSession
Note: Ensure that both the managing computer and SRV1 are properly configured to communicate over the network, and that any firewalls allow for the necessary ports (default is 5985 for HTTP and 5986 for HTTPS) to be open for WS-Management traffic12.
By following these steps, you should be able to manage SRV1 remotely using PowerShell. Make sure you have the appropriate administrative privileges to perform these actions.
DRAG DROP
You have a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server and has the Active Directory Federation Services role installed.
You plan to deploy Web Application Proxy to a server named Server2.
You export the Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) certificate from Server1.
Which actions should you perform on Server2 in sequence? To answer, drag the appropriate actions to the correct order. Each action may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
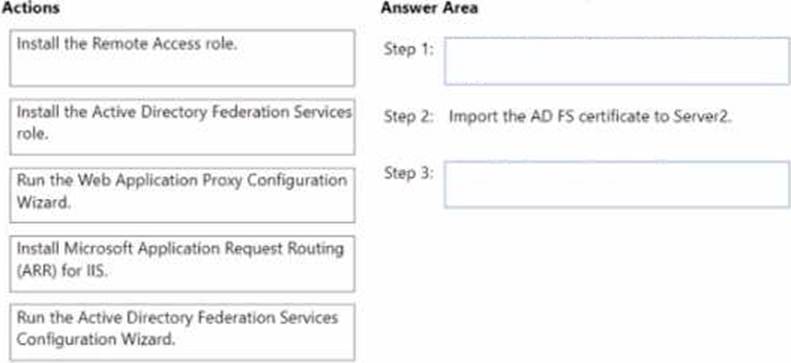

Explanation:
Step 1: Install the Remote Access role.
Step 2: Import the AD FS certificate to Server2.
Step 3: Run the Web Application Proxy Configuration Wizard.
In Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure, the Web Application Proxy (WAP) component is documented as a role service of the Remote Access role and is deployed on an edge or perimeter server to publish AD FS and other web apps. The guide states that before configuring WAP, you must install the Remote Access role with the Web Application Proxy role service on the proxy server. It further explains that WAP must establish trust with the existing AD FS farm by using the AD FS service communications certificate: “Import the federation service SSL certificate (with private key) on the proxy server and place it in the local computer’s personal store.” After the certificate is present, you run the Web Application Proxy Configuration Wizard to “specify the Federation Service name, provide AD FS credentials, and complete the trust and configuration.” The materials also clarify that you do not install the AD FS role on the proxy and Microsoft Application Request Routing (ARR) is not required for WAP. The AD FS Configuration Wizard applies to federation servers, not proxies. Therefore, the minimal and correct sequence on Server2 is: Install Remote Access (WAP) → Import the AD FS cert → Run the Web Application Proxy Configuration Wizard, which configures the trust and enables publishing of the AD FS endpoint.
You have an Azure subscription that contains the storage accounts shown in the following table.
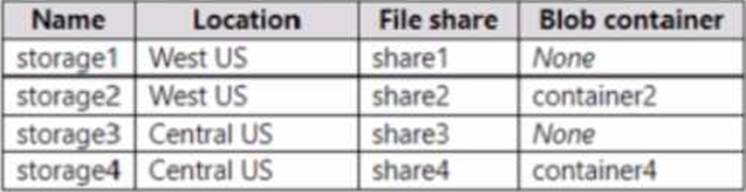
In the West US Azure region, you create a storage sync service named SyncA.
You plan to create a sync group named GroupA.
What is the maximum number of cloud endpoints you can use with GroupA?
- A . 1
- B . 2
- C . 3
- D . 4
A
Explanation:
The Azure File Sync section of the Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure materials states that a sync group defines the topology for synchronization and “contains one cloud endpoint and one or more server endpoints.” A cloud endpoint is an Azure file share associated with a Storage Sync Service. The guidance also notes that “the Storage Sync Service and the storage account (file share) must reside in the same Azure region” and that “a single Azure file share can be the cloud endpoint for only one sync group.” In the scenario, SyncA is in West US, so only file shares in West US (for example, storage1share1 or storage2share2) are eligible. However, regardless of how many eligible shares exist, the exam guide is explicit: each sync group supports a maximum of one cloud endpoint. Additional endpoints in the group must be server endpoints on Windows Server volumes. Therefore, the maximum number of cloud endpoints you can use with GroupA is 1, which directly reflects the product’s architecture and the documented exam objective requirements.
HOTSPOT
You need to configure Azure File Sync to meet the file sharing requirements.
What should you do? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE Each correct selection is worth one point.


Explanation:
In Azure File Sync architecture (covered in Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure under “Implement and manage storage solutions”), the fundamental design points are:
Sync group C “A sync group defines a sync topology. Each sync group contains exactly one cloud endpoint (an Azure file share) and one or more server endpoints.” A server endpoint is a folder on a registered Windows Server. A server can participate in multiple sync groups so long as the server endpoints are different paths.
Storage Sync Service C “The Storage Sync Service is the top-level resource that maintains server registrations and houses your sync groups.” A Windows Server registers to one Storage Sync Service at a time, and that service can contain many sync groups and many servers.
FS1 must sync with newyorkfiles and companyfiles; FS2 must sync with seattlefiles and companyfiles. Since one Storage Sync Service can host multiple sync groups and multiple servers, and a server must be registered to a single service, the most efficient design is a single Storage Sync Service containing all three sync groups and both servers.
HOTSPOT
You plan to deploy an Azure virtual machine that will run Windows Server.
You need to ensure that an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) user [email protected] can connect 10 the virtual machine by using the Azure Serial Console.
What should you do? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
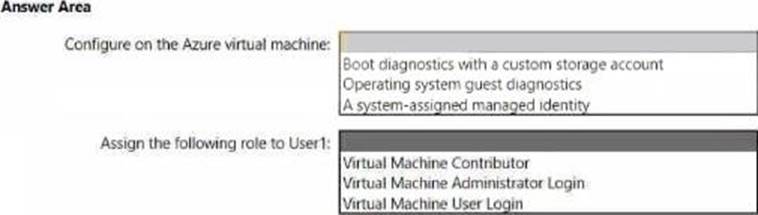
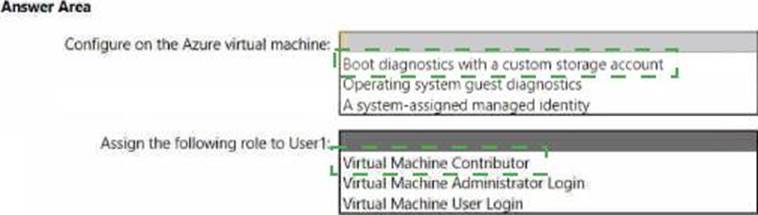
Explanation:
In the AZ-800 materials on “Manage and maintain Windows Server IaaS virtual machines,” the Serial Console requirement is called out clearly: the VM must have Boot diagnostics enabled so Azure can capture the console and provide an interactive text console during boot and runtime. The guidance explains that enabling Boot diagnostics (either managed or with a storage account) stores the console output and screen shots that the Serial Console relies on. Guest-level diagnostics or a managed identity are not prerequisites for Serial Console access.
Access control to the Serial Console is governed by Azure RBAC. The study guidance states that users must be granted either Virtual Machine Contributor (broad rights) or the minimal login roles; for secure, least-privilege access to a console session with administrative rights, assign Virtual Machine Administrator Login to the user. This role allows interactive sign-in to the VM (RDP/SSH/Serial Console) without granting configuration permissions on the VM.
Therefore, to let [email protected] use the Serial Console while meeting least-privilege objectives, enable Boot diagnostics on the VM (here, with a custom storage account, which satisfies the boot diagnostics requirement) and assign the Virtual Machine Administrator Login role to User1.
You have a Windows Server container host named Server! that has a single disk.
On Server1, you plan to start the containers shown in the following table.
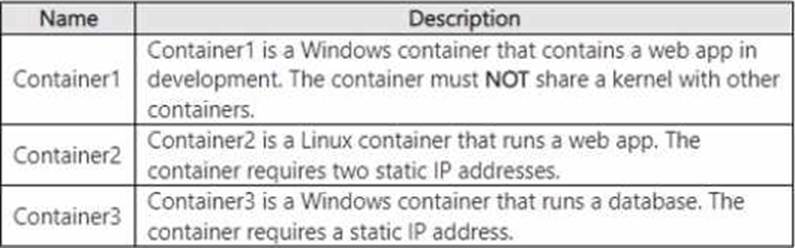
Which isolation mode can you use for each container? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Your network contains an Active Directory Domains Services (AD DS) domain named contoso.com.
You implement a central store.
You create a new Group Policy Object (GPO) named GP01.
When you attempt to edit GP01, you see the settings shown in the exhibit. (Click the Exhibit tab.)
You need to ensure that all settings are available.
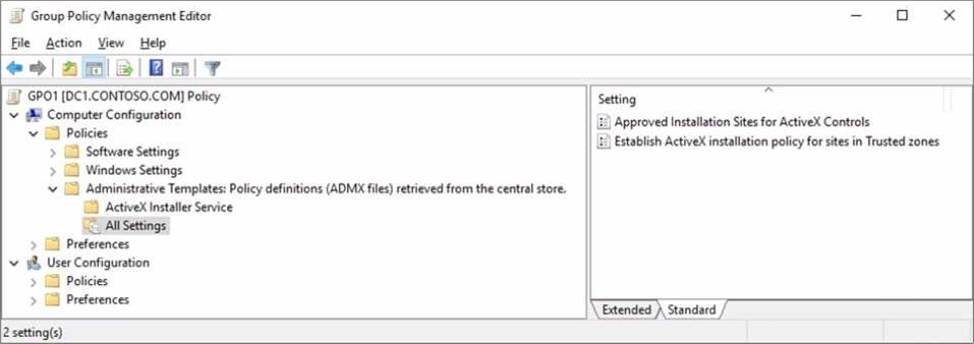
Solution: You delete the \contoso.comSYSVOLcontoso.comPoliciesPolicyDefinitions folder.
Does this meet the goal?
- A . Yes
- B . No
HOTSPOT
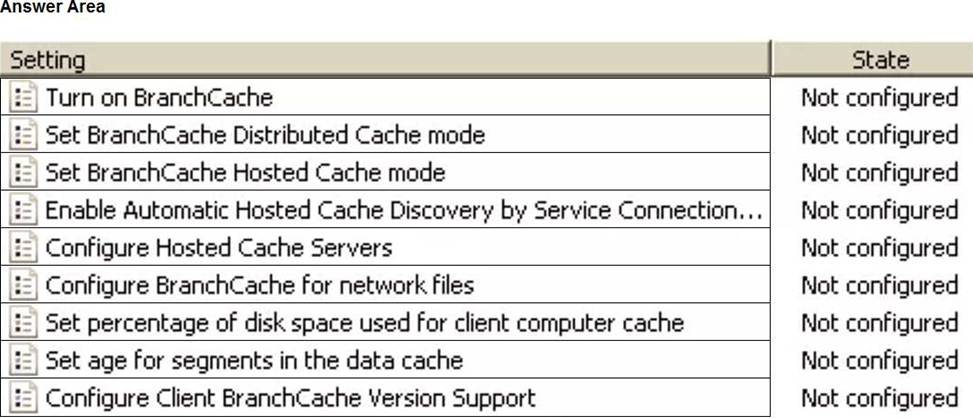
Your company has a main office and 10 branch offices that are connected by using WAN links. The network contains an Active Directory domain.
All users have laptops and regularly travel between offices.
You plan to implement BranchCache in the branch offices.
In each branch office, you install a server that runs Windows Server and the BranchCache feature.
You register the servers in Active Directory.
You need to configure the laptops to use the local BranchCache server automatically. The solution must minimize administrative effort.
Which two Group Policy settings should you configure? To answer, select the settings in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
–> Enable Automatic Hosted Cache Discovery by Service Connection …
