Practice Free AZ-104 Exam Online Questions
DRAG DROP
You have an Azure subscription that contains virtual machine named VM1.
You need to back up VM. The solution must ensure that backups are stored across three availability zones in the primary region.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Explanation:
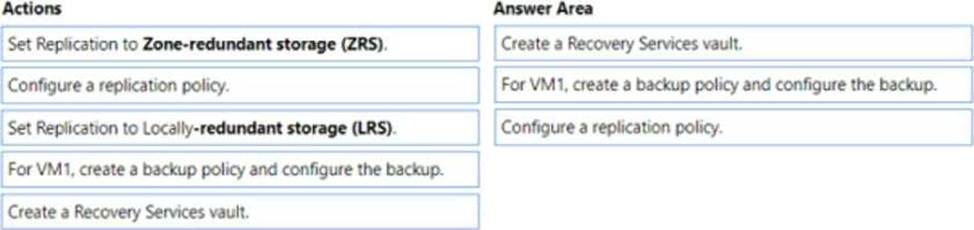
According to 1, Availability Zones are unique physical locations within an Azure region that provide high availability and disaster recovery for your virtual machines. To back up your VM across three availability zones in the primary region, you need to perform the following actions in sequence: Create a Recovery Services vault2 that will store your backups and enable geo-redundancy for cross-region protection.
For VM1, create a backup policy and configure the backup2 to use the Recovery Services vault as the backup destination.
Configure a replication policy1 that will replicate your VM1 to another availability zone in the same region.
HOTSPOT
You have an Azure virtual machine named VM1 and a Recovery Services vault named Vault1.
You create a backup Policy1 as shown in the exhibit. (Click the Exhibit tab.)
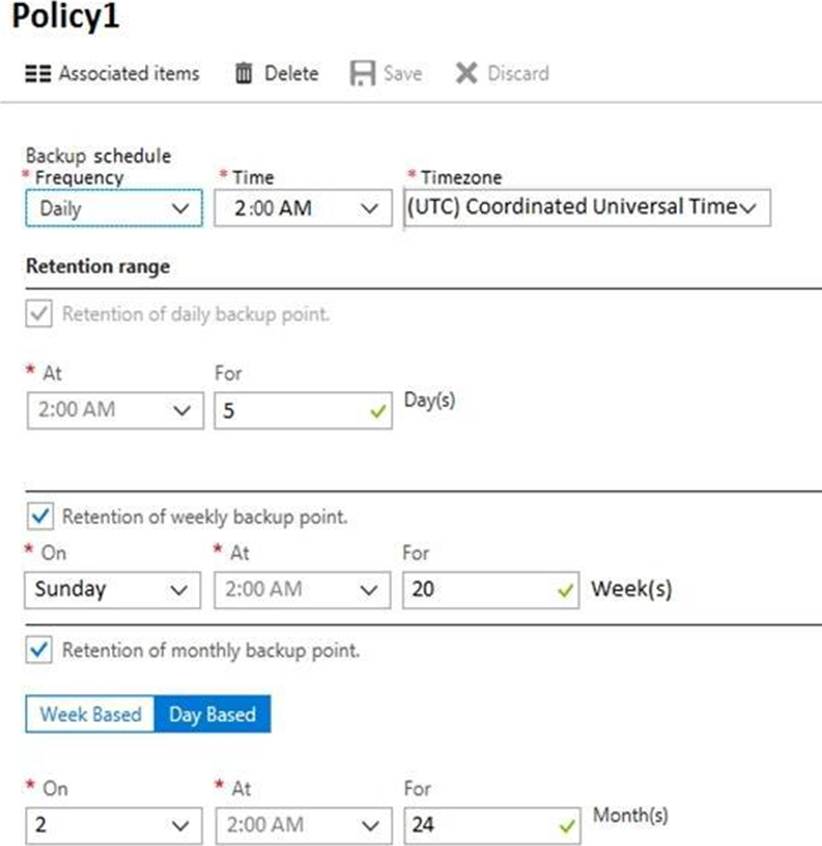
You configure the backup of VM1 to use Policy1 on Thursday, January 1.
You need to identify the number of available recovery points for VM1.
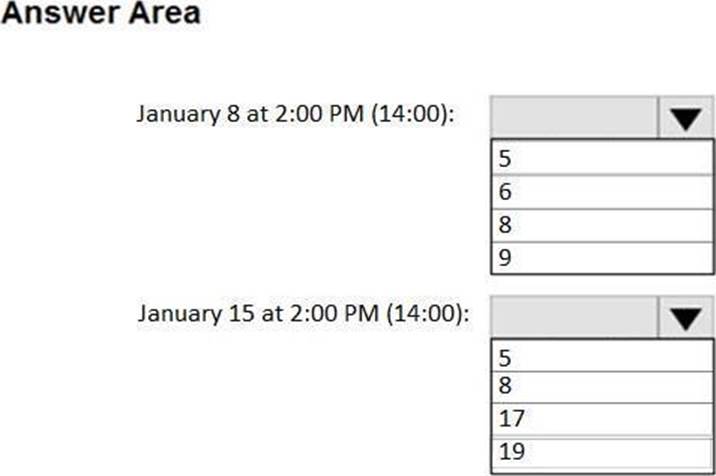
How many recovery points are available on January 8 and on January 15? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Explanation:
Box 1: 6
4 daily + 1 weekly + monthly
Box 2: 8
4 daily + 2 weekly + monthly + yearly
You have an Azure subscription that contains a virtual machine named VM1.
You have an on-premises datacenter that contains a domain controller named DC1. ExpressRoute is used to connect the on-premises datacenter to Azure.
You need to use Connection Monitor to identify network latency between VM1 and DC1.
What should you install on DC1?
- A . the Log Analytics agent
- B . the Azure Network Watcher Agent virtual machine extension
- C . an Azure Monitor agent extension
- D . the Azure Connected Machine agent for Azure Arc-enabled servers
HOTSPOT
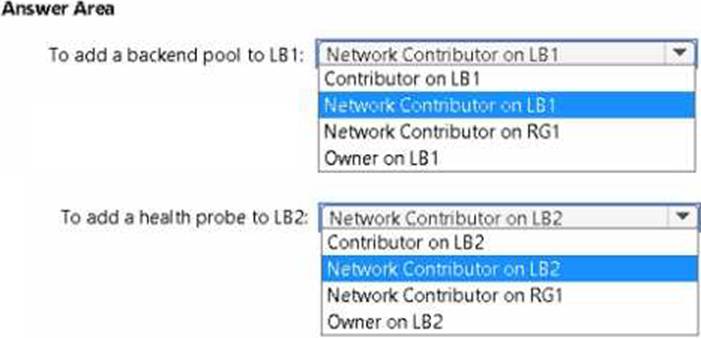
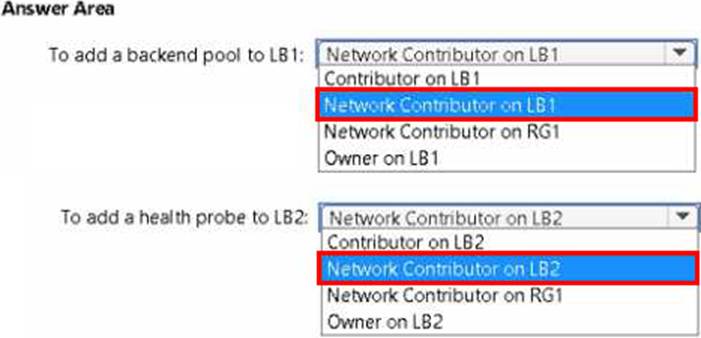
You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that contains a resource group named RG1. In RG1, you create an internal load balancer named LB1 and a public load balancer named LB2. You need to ensure that an administrator named Admin1 can manage LB1 and LB2. The solution must follow the principle of least privilege.
Which role should you assign to Admin1 for each task? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
HOTSPOT
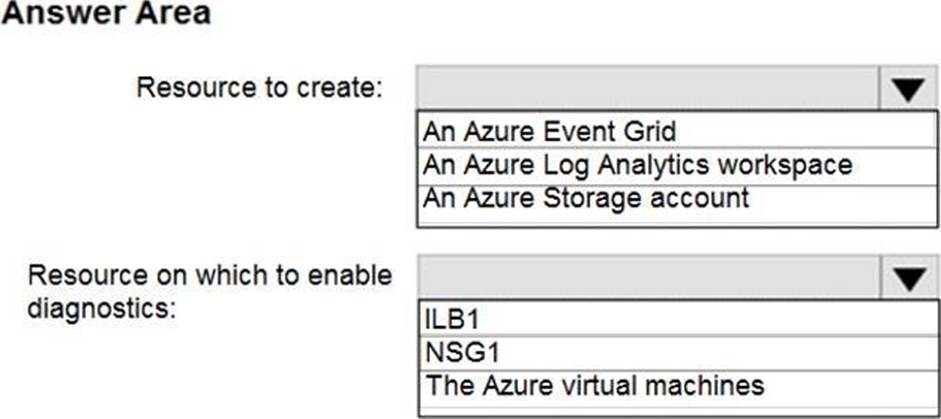
You have an Azure virtual network named VNet1 that connects to your on-premises network by using a site-to-site VPN. VMet1 contains one subnet named Subnet1.
Subnet1 is associated to a network security group (NSG) named NSG1. Subnet1 contains a basic internal load balancer named ILB1. ILB1 has three Azure virtual machines in the backend pool. You need to collect data about the IP addresses that connects to ILB1. You must be able to run interactive queries from the Azure portal against the collected data.
What should you do? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Explanation:
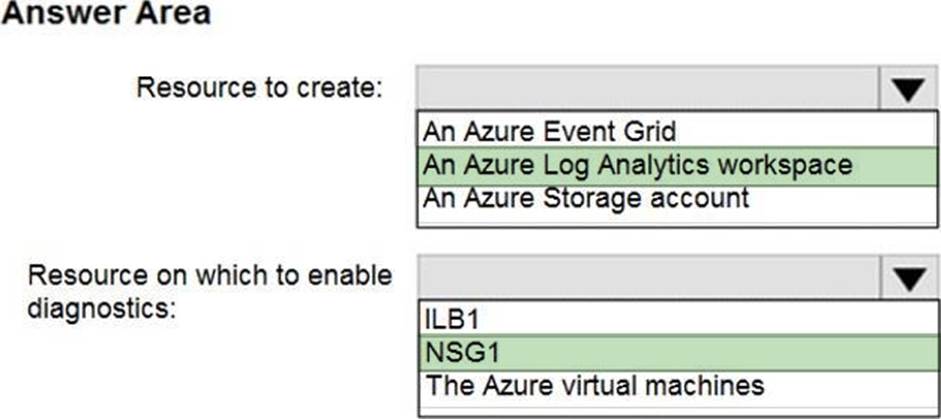
Box 1: An Azure Log Analytics workspace
In the Azure portal you can set up a Log Analytics workspace, which is a unique Log Analytics environment with its own data repository, data sources, and solutions.
Box 2: NSG1
NSG flow logs allow viewing information about ingress and egress IP traffic through a Network security group. Through this, the IP addresses that connect to the ILB can be monitored when the diagnostics are enabled on a Network Security Group.
We cannot enable diagnostics on an internal load balancer to check for the IP addresses.
As for Internal LB, it is basic one. Basic can only connect to storage account. Also, Basic LB has only activity logs, which doesn’t include the connectivity workflow. So, we need to use NSG to meet the mentioned requirements.
HOTSPOT
You plan to use Azure Network Watcher to perform the following tasks:
Task1: Identify a security rule that prevents a network packet from reaching an Azure virtual machine
Task2: Validate outbound connectivity from an Azure virtual machine to an external host
Which feature should you use for each task? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
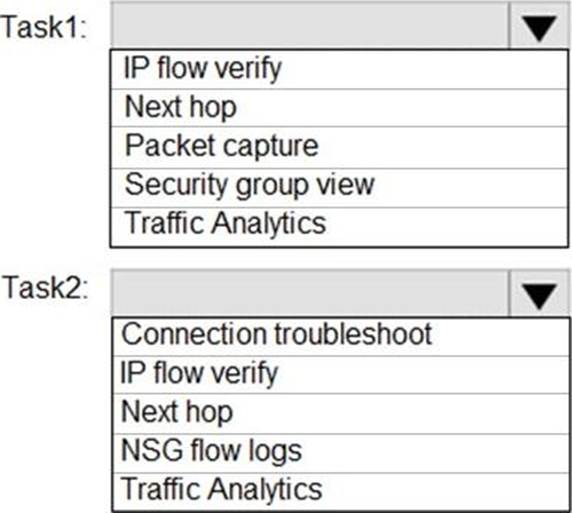

Explanation:
Task 1: IP flow verify
The IP flow verify capability enables you to specify a source and destination IPv4 address, port, protocol (TCP or UDP), and traffic direction (inbound or outbound). IP flow verify then tests the communication and informs you if the connection succeeds or fails. If the connection fails, IP flow verify tells you which security rule allowed or denied the communication, so that you can resolve the problem.
Task 2: Connection troubleshoot
The connection troubleshoot capability enables you to test a connection between a VM and another VM, an FQDN, a URI, or an IPv4 address. The test returns similar information returned when using the connection monitor capability, but tests the connection at a point in time, rather than monitoring it over time.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/network-watcher/network-watcher-monitoring-overview
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/network-watcher/network-watcher-ip-flow-verify-overview
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/network-watcher/network-watcher-connectivity-overview
You need to prepare the environment to meet the authentication requirements.
Which two actions should you perform? Each correct answer presents part of the solution. NOTE Each correct selection is worth one point.
- A . Azure Active Directory (AD) Identity Protection and an Azure policy
- B . a Recovery Services vault and a backup policy
- C . an Azure Key Vault and an access policy
- D . an Azure Storage account and an access policy
C
Explanation:
D: Seamless SSO works with any method of cloud authentication – Password Hash Synchronization or Pass-through Authentication, and can be enabled via Azure AD Connect.
B: You can gradually roll out Seamless SSO to your users. You start by adding the following Azure AD URL to all or selected users’ Intranet zone settings by using Group Policy in Active Directory: https://autologon.microsoftazuread-sso.com
You need to prepare the environment to meet the authentication requirements.
Which two actions should you perform? Each correct answer presents part of the solution. NOTE Each correct selection is worth one point.
- A . Azure Active Directory (AD) Identity Protection and an Azure policy
- B . a Recovery Services vault and a backup policy
- C . an Azure Key Vault and an access policy
- D . an Azure Storage account and an access policy
C
Explanation:
D: Seamless SSO works with any method of cloud authentication – Password Hash Synchronization or Pass-through Authentication, and can be enabled via Azure AD Connect.
B: You can gradually roll out Seamless SSO to your users. You start by adding the following Azure AD URL to all or selected users’ Intranet zone settings by using Group Policy in Active Directory: https://autologon.microsoftazuread-sso.com
HOTSPOT
You have an Azure Storage account named storage1 that contains a blob container. The blob container has a default access tier of Hot. Storage1 contains a container named container!.
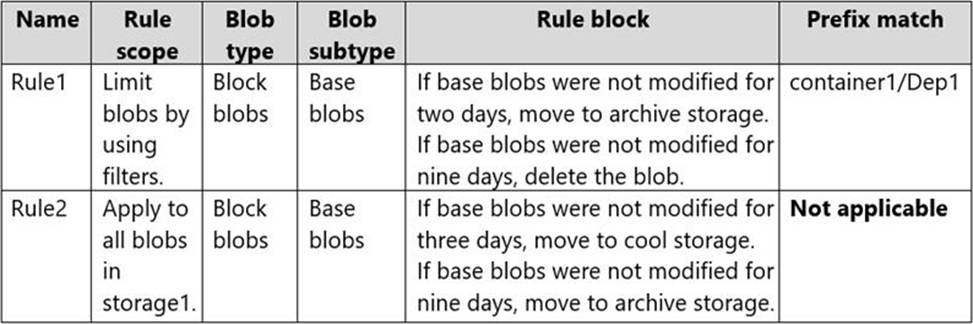
You create lifecycle management rules in storage1 as shown in the following table.
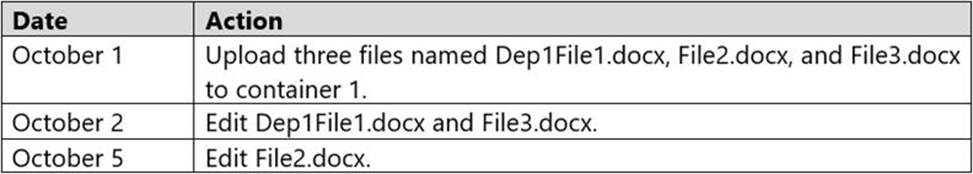
You perform the actions shown in the following table.
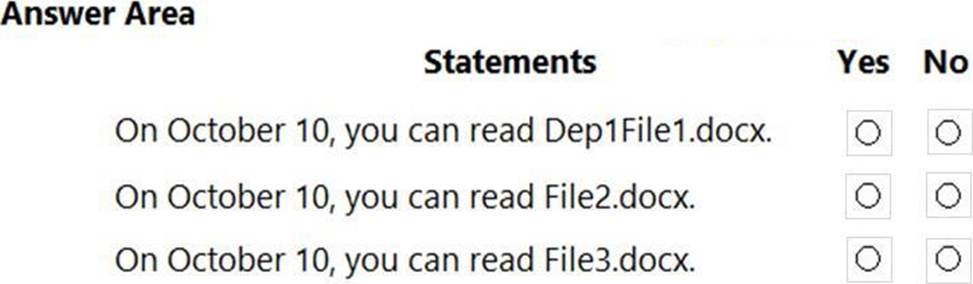
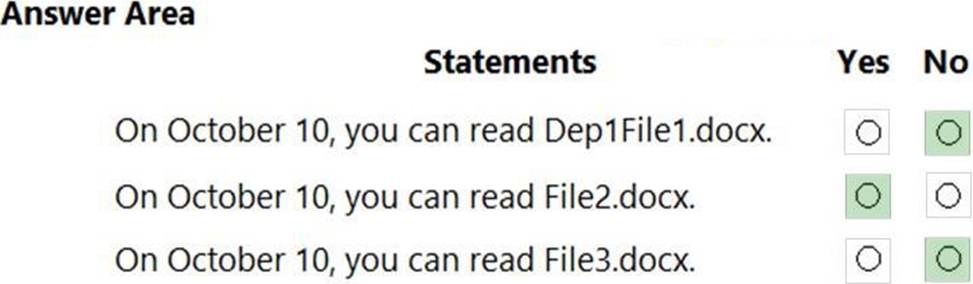
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Explanation:
On October 10, you can read Dep1File1.docx. = NO
Dep1File1.docx is a blob in container1 that was uploaded on October 1 and edited on October 2. According to the lifecycle management rule 1, any blob in container1 that has not been modified for 7 days will be moved to the archive tier. Therefore, on October 9, Dep1File1.docx will be moved to the archive tier. Blobs in the archive tier cannot be read unless they are first rehydrated, which may take several hours or days. Therefore, on October 10, you cannot read Dep1File1.docx unless you rehydrate it first.
On October 10, you can read File2.docx. = YES
File2.docx is a blob in container1 that was uploaded on October 1 and edited on October 5. According to the lifecycle management rule 1, any blob in container1 that has not been modified for 7 days will be moved to the archive tier. Therefore, on October 12, File2.docx will be moved to the archive tier. However, on October 10, File2.docx is still in the hot tier, which means it can be read without any delay or cost.
On October 10, you can read File3.docx. = NO
File3.docx is a blob in container1 that was uploaded on October 1 and edited on October 2. According to the lifecycle management rule 2, any blob in container1 that has not been modified for 5 days will be deleted. Therefore, on October 7, File3.docx will be deleted from the storage account. Therefore, on October 10, you cannot read File3.docx because it no longer exists.
HOTSPOT
You have an Azure subscription that contains a storage account named storage1. The subscription is linked to an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant named contoso.com that syncs to an on-premises Active Directory domain.
The domain contains the security principals shown in the following table.
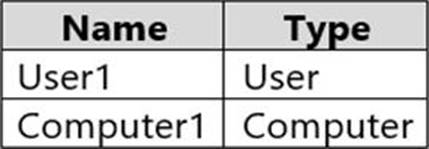
In Azure AD, you create a user named User2.
The storage1 account contains a file share named share1 and has the following configurations.

For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.


Explanation:
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/files/storage-files-identity-ad-ds-assign-permissions?tabs=azure-portal
