Practice Free AZ-104 Exam Online Questions
You have an Azure subscription that has a Recovery Services vault named Vault 1.
The subscription contains the virtual machines shown in the following table.
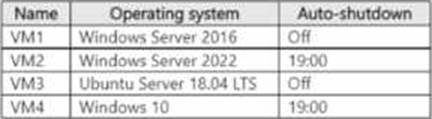
You plan to schedule backups to occur every night at 23:00.
Which virtual machines can you back up by using Azure Backup?
- A . VM1 only
- B . VM1 and VM2 only
- C . VM1 and VM3 only
- D . VM1, VM2, VM3 and VM4
HOTSPOT
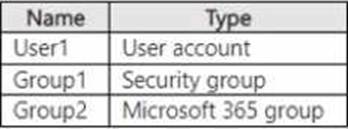
You have a Microsoft Entra tenant named adatum.com that contains the groups shown in the following table.
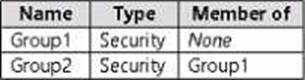
Adatum.com contains the users shown in the following table.
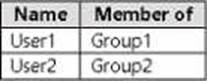
You assign a Microsoft Entra ID P2 license to Group1 as shown in the following exhibit.

Group2 is NOT directly assigned a license.
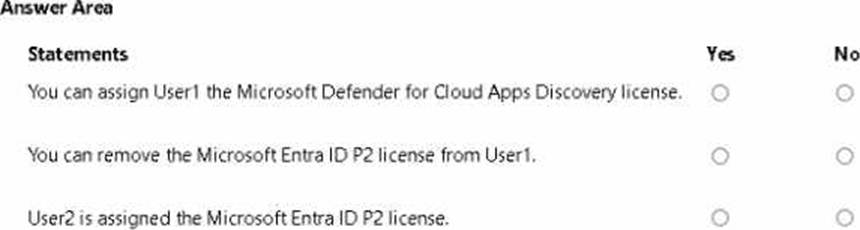
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. NOTE Each correct selection is worth one point.
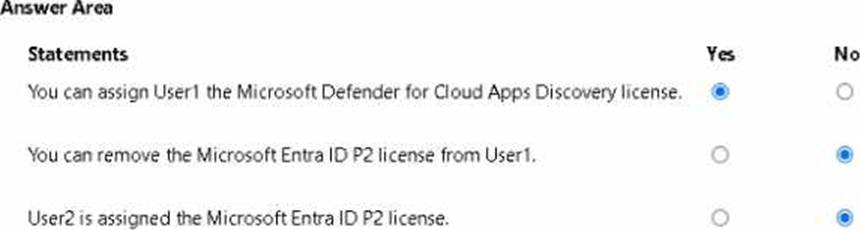
You have a Microsoft Entra tenant configured as shown in the following exhibit.
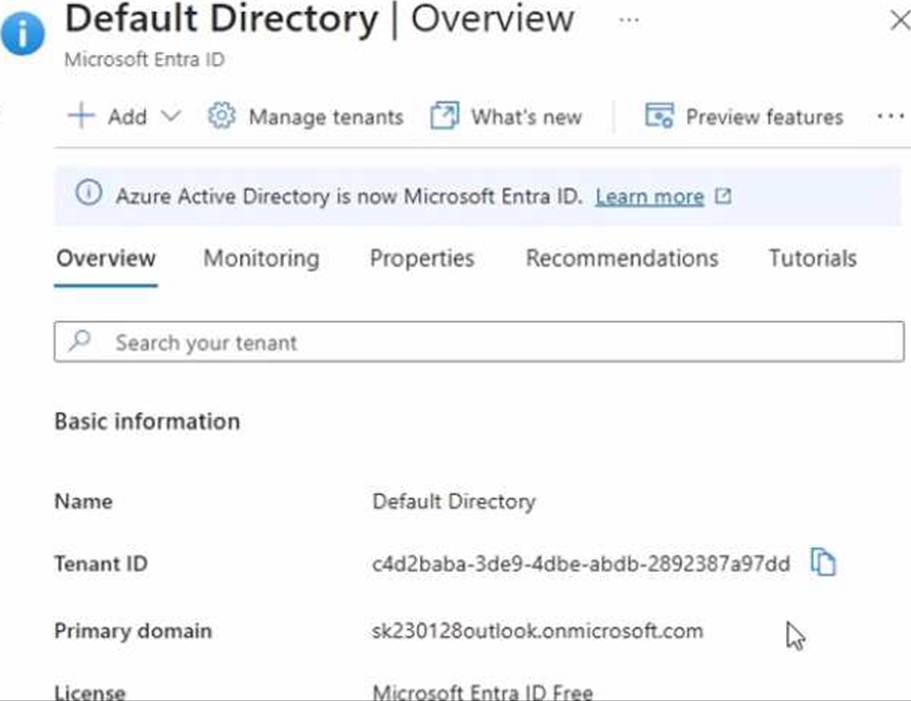
The tenant contains the identities shown in the following table.
You purchase a Microsoft Fabric license.
To which identities can you assign the license?
- A . User1 only
- B . User1 and Group1 only
- C . User1 and Group2 only
- D . User1. Group1. and Group2
You have an Azure virtual machine named VM1.
You use Azure Backup to create a backup of VM1 named Backup1.
After creating Backup1, you perform the following changes to VM1:
Modify the size of VM1.
– Copy a file named Budget.xls to a folder named Data.
– Reset the password for the built-in administrator account.
– Add a data disk to VM1.
An administrator uses the Replace existing option to restore VM1 from Backup1.
You need to ensure that all the changes to VM1 are restored.
Which change should you perform again?
- A . Modify the size of VM1.
- B . Add a data disk.
- C . Reset the password for the built-in administrator account.
- D . Copy Budget.xls to Data.
D
Explanation:
The scenario mentioned in the question, we are using the replace option. So in this case we would lose the existing data written to the disk after the backup was taken. The file was copied to the disk after the backup was taken. Hence, we would need to copy the file once again.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/backup/backup-azure-arm-restore-vms#replace-existing-
disks
You plan to create the Azure web apps shown in the following Table.
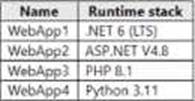
What is the minimum number of App Service plans you should create for the web apps?
- A . 1
- B . 2
- C . 3
- D . 4
B
Explanation:
NET Core 3.0: Windows and Linux ASP .NET V4.7: Windows only PHP 7.3: Windows and Linux Ruby 2.6: Linux only Also, you can’t use Windows and Linux Apps in the same App Service Plan, because when you create a new App Service plan you have to choose the OS type. You can’t mix Windows and Linux apps in the same App Service plan. So, you need 2 ASPs.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/app-service/overview
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have an Azure subscription that contains the virtual machines shown in the following table.
You deploy a load balancer that has the following configurations:
• Name: LB1
• Type: Internal
• SKU: Standard
• Virtual network: VNET1
You need to ensure that you can add VM1 and VM2 to the backend pool of LB1.
Solution: You create two Standard public IP addresses and associate a Standard SKU public IP address to the network interface of each virtual machine.
Does this meet the goal?
- A . Yes
- B . No
HOTSPOT
You have an Azure subscription that contains the Azure virtual machines shown in the following table.
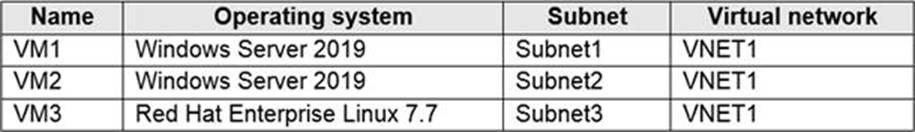
You configure the network interfaces of the virtual machines to use the settings shown in the following table
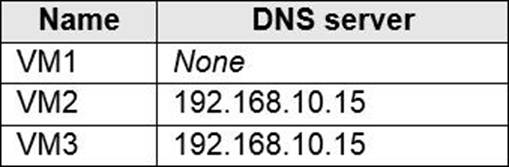
From the settings of VNET1, you configure the DNS servers shown in the following exhibit.
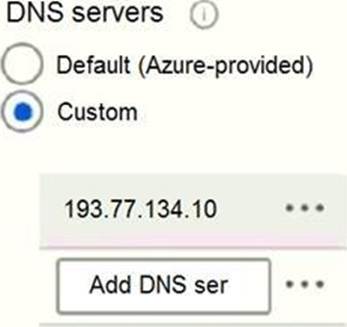
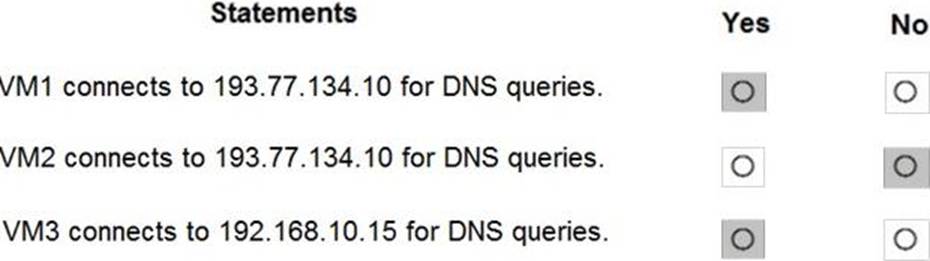
The virtual machines can successfully connect to the DNS server that has an IP address of 192.168.10.15 and the DNS server that has an IP address of 193.77.134.10.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
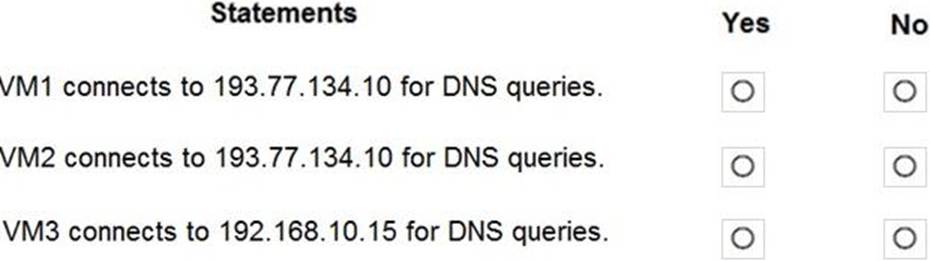
Explanation:
Box 1: Yes
You can specify DNS server IP addresses in the VNet settings. The setting is applied as the default DNS server(s) for all VMs in the VNet.
Box 2: No
You can set DNS servers per VM or cloud service to override the default network settings.
Box 3: Yes
You can set DNS servers per VM or cloud service to override the default network settings.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-network/virtual-networks-faq#name-resolution-dns
HOTSPOT
You have an Azure subscription. The subscription contains a virtual machine that runs Windows 10.
You need to join the virtual machine to an Active Directory domain.
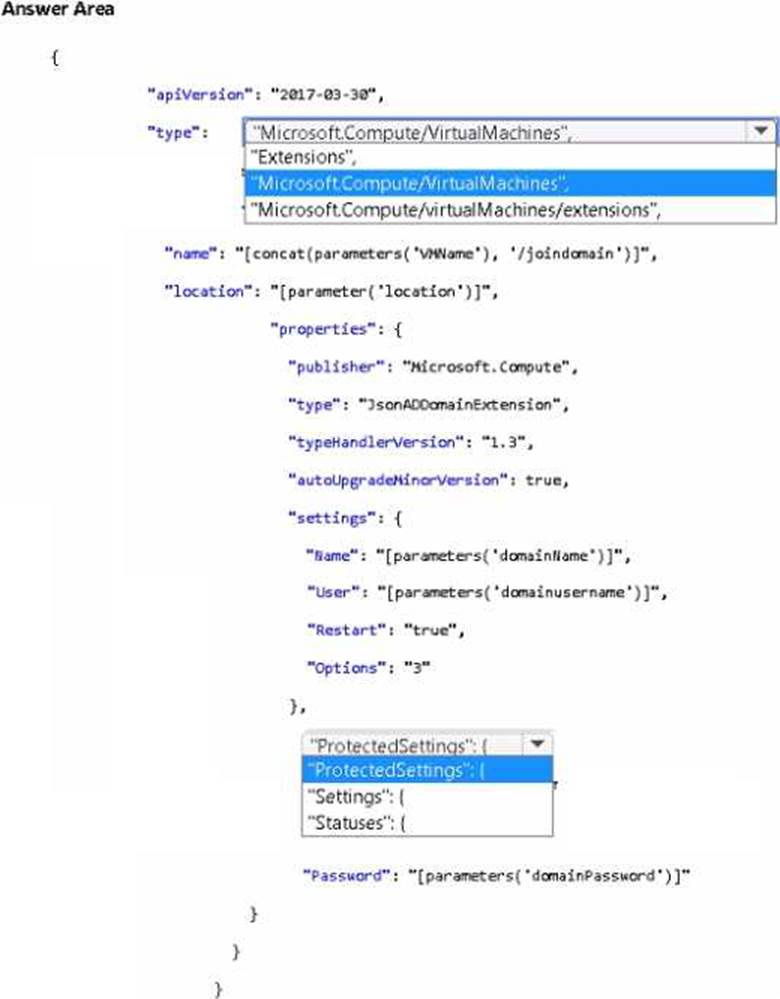
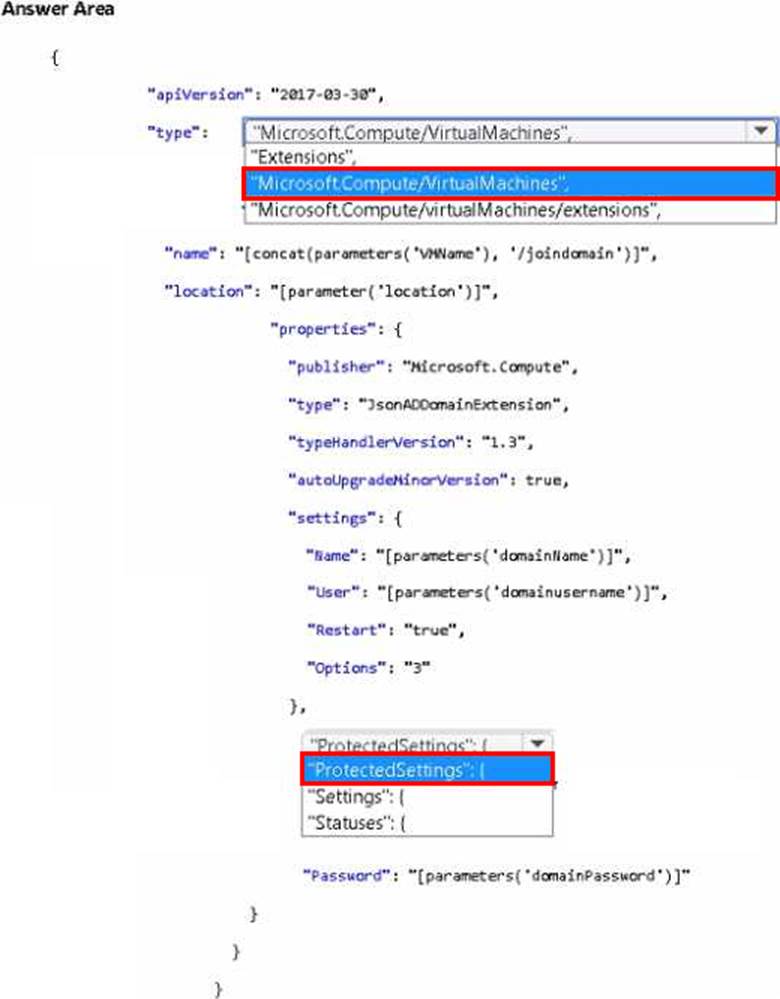
How should you complete the Azure Resource Manager (ARM) template? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
HOTSPOT
Your network contains an on-premises Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) domain named contoso.com.
The domain contains the servers shown in the following table.

You plan to migrate contoso.com to Azure.
You create an Azure virtual network named VNET1 that has the following settings:
• Address space: 10.0.0.0/16
• Subnet:
o Name: Subnet1
o IPv4: 10.0.1.0/24
You need to move DC1 to VNET1. The solution must ensure that the member servers in contoso.com can resolve AD DS DNS names.
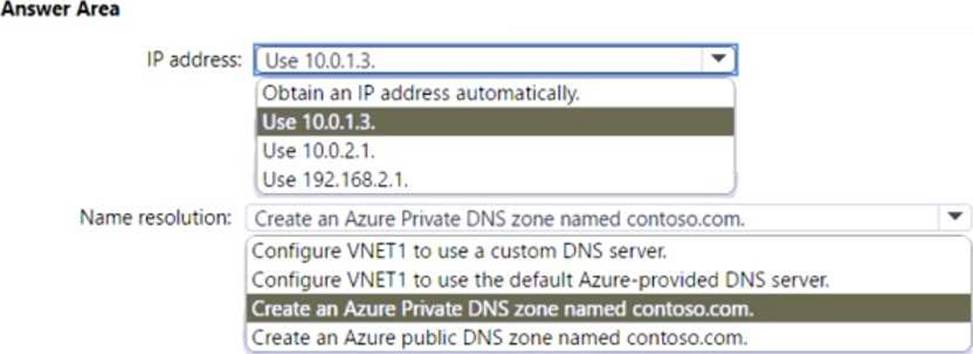
How should you configure DC1? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Explanation:
IP address: You should use 10.0.1.3 as the IP address for DC1. This is because DC1 needs to have a static IP address within the subnet range of VNET1, which is 10.0.1.0/241. You cannot use 10.0.2.1 or 192.168.2.1, as they are outside of the subnet range of VNET1. You also cannot obtain an IP address automatically, as this may cause DC1 to lose its IP address and break the DNS resolution for the domain members2.
Name Resolution: You should configure VNET1 to use a custom DNS server that points to the IP address of DC1, which is 10.0.1.33. This is because DC1 is the domain controller and DNS server for contoso.com, and it needs to resolve the AD DS DNS names for the domain members that are in Azure or on-premises. You cannot use the default Azure-provided DNS server, as it does not support AD DS DNS names. You also do not need to create an Azure Private DNS zone or an Azure public DNS zone named contoso.com, as these are not required for AD DS DNS resolution.
HOTSPOT
You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that contains the resources shown in the following table.
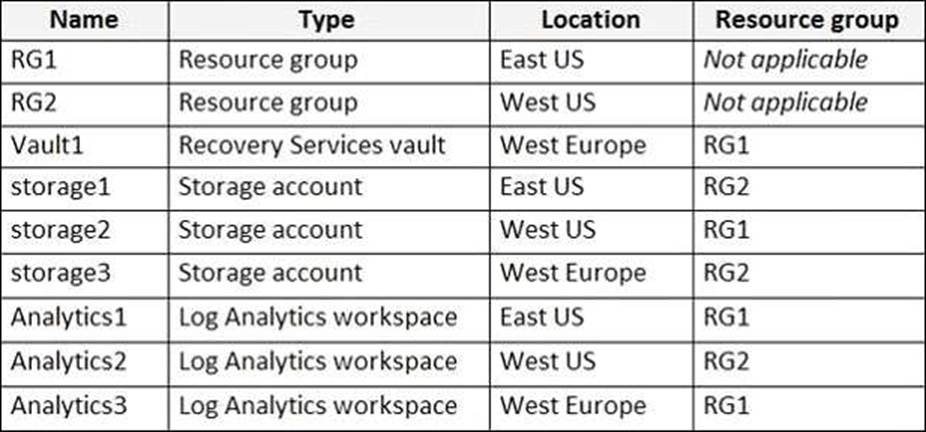
You plan to configure Azure Backup reports for Vault1.
You are configuring the Diagnostics settings for the AzureBackupReports log.
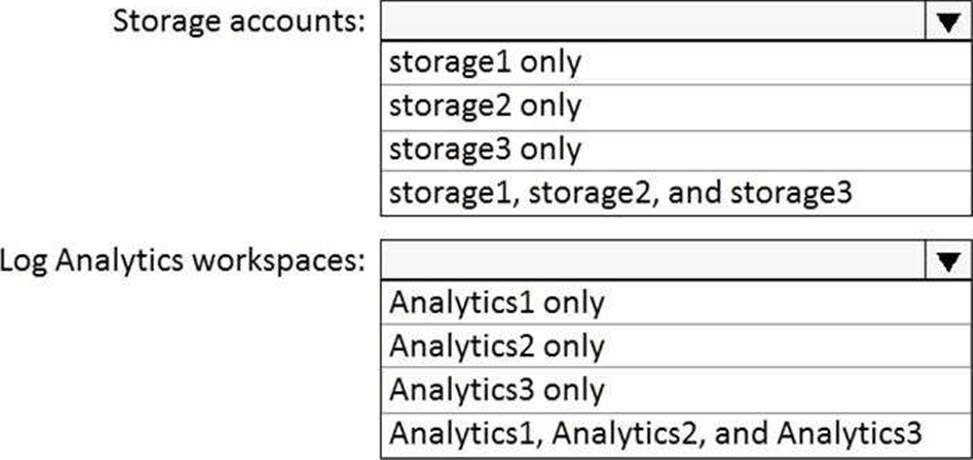
Which storage accounts and which Log Analytics workspaces can you use for the Azure Backup reports of Vault1? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Explanation:
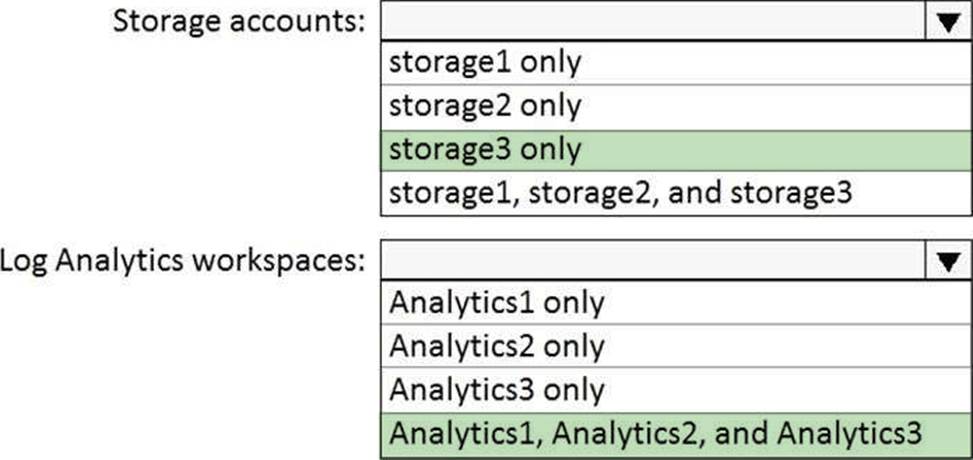
Box 1: storage3 only
Vault1 and storage3 are both in West Europe.
Box 2: Analytics1, Analytics2, Analytics3
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/backup/backup-create-rs-vault
https://docs.microsoft.com/de-de/azure/backup/configure-reports
