Practice Free AZ-104 Exam Online Questions
DRAG DROP
You have an Azure subscription named Sub1 that contains two users named User1 and User2. You need to assign role-based access control (RBAC) roles to User1 and User2.
The users must be able to perform the following tasks in Sub1:
• User1 must view the data in any storage account.
• User2 must assign users the Contributor role for storage accounts. The solution must use the principle of least privilege.
Which RBAC role should you assign to each user? To answer, drag the appropriate roles to the correct users. Each role may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
Explanation:
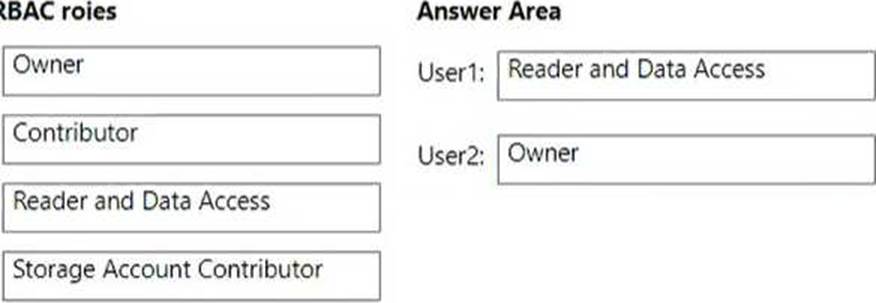
User1: You should assign the Reader and Data Access role to User1. This role grants read access to Azure resources and data, including the data in any storage account1. This role is suitable for User1’s task of viewing the data in any storage account, and it follows the principle of least privilege by not granting any write or delete permissions.
User2: You should assign the Storage Account Contributor role to User2. This role grants full access to manage storage accounts and their data, including the ability to assign roles in Azure RBAC2. This role is suitable for User2’s task of assigning users the Contributor role for storage accounts, and it follows the principle of least privilege by not granting access to other types of resources.
You have an Azure subscription that contains the virtual machines shown in the following table.
You deploy a load balancer that has the following configurations:
• Name: LB 1
• Type: Internal
• SKU: Standard
• Virtual network: VNET1
You need to ensure that you can add VM1 and VM2 to the backend pool of L81.
Solution: You create two Standard SKU public IP addresses and associate a Standard SKU public IP address to the network interface of each virtual machine.
Does this meet the goal?
- A . Yes
- B . No
HOTSPOT
You have an Azure subscription that contains the virtual networks shown in the following table.
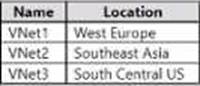
The subscription contains the subnets shown in the following table.

The subscription contains the storage accounts shown in the following table.
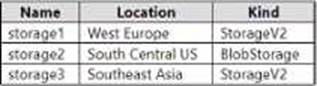
You create a service endpoint policy named policy1 in the South Central US Azure region to allow connectivity to all the storage accounts in the subscription.
Fow each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.


Explanation:
Policy1 can be applied to Subnet3. = YES
Only storage1 and storage2 can be accessed from VNet2. = NO
Only storage2 can be accessed from VNet3. = Yes
According to the Microsoft documentation, a service endpoint policy can be applied to any subnet in a virtual network that has a service endpoint enabled for the same service as the policy. In your scenario, Subnet3 has a service endpoint enabled for Microsoft. Storage, which is the same service as policy1. Therefore, policy1 can be applied to Subnet3.
According to the Microsoft documentation, when you configure network rules for a storage account, you can limit access to your storage account to requests that come from specified IP addresses, IP ranges, subnets in an Azure virtual network, or resource instances of some Azure services. In your scenario, storage1 and storage2 have network rules that allow access from Subnet1 and Subnet2 respectively. However, this does not mean that only these subnets can access the storage accounts. Other subnets or resources that have the same IP range or resource ID as Subnet1 or Subnet2 can also access the storage accounts. For example, Subnet4 in VNet2 has the same IP range as Subnet1 in VNet1, so it can also access storage1. Similarly, Subnet5 in VNet3 has the same IP range as Subnet2 in VNet1, so it can also access storage2. Therefore, only storage1 and storage2 cannot be accessed from VNet2.
According to the Microsoft documentation, when you create a private endpoint for a storage account, you assign a private IP address from your virtual network to the storage account. This enables secure traffic between your virtual network and the storage account over a private link. In your scenario, you have created a private endpoint for storage2 in Subnet6 of VNet3. This means that only Subnet6 can access storage2 over the private link. However, this does not mean that only Subnet6 can access storage2 at all. Other subnets or resources that have the same IP range or resource ID as Subnet6 can also access storage2 over the public endpoint of the storage account. For example, Subnet7 in VNet4 has the same IP range as Subnet6 in VNet3, so it can also access storage2 over the public endpoint. Therefore, only storage2 cannot be accessed from VNet3.
You have an Azure subscription that contains a storage account named storage 1 in the North Europe A2ure region.
You need to ensure that when blob data is added to storage1, a secondary copy is created in the East US region. The solution must minimize administrative effort.
What should you configure?
- A . operational backup
- B . a lifecycle management rule
- C . object replication
- D . geo-redundant storage (GRS)
You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that contains the resources shown in the following table.
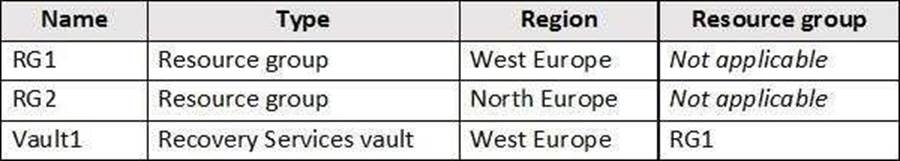
You create virtual machines in Subscription1 as shown in the following table.
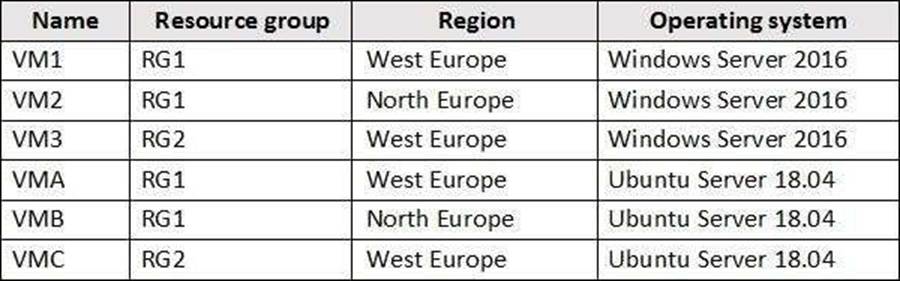
You plan to use Vault1 for the backup of as many virtual machines as possible.
Which virtual machines can be backed up to Vault1?
- A . VM1, VM3, VMA, and VMC only
- B . VM1 and VM3 only
- C . VM1, VM2, VM3, VMA, VMB, and VMC
- D . VM1 only
- E . VM3 and VMC only
A
Explanation:
To create a vault to protect virtual machines, the vault must be in the same region as the virtual machines. If you have virtual machines in several regions, create a Recovery Services vault in each region.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/bs-cyrl-ba/azure/backup/backup-create-rs-vault
You have the Azure virtual networks shown in the following table.

To which virtual networks can you establish a peering connection from VNet1?
- A . VNet2, VNet3, and VNet4
- B . VNet2only
- C . VNet3 and VNet4 only
- D . VNet2 and VNet3 only
You need to move the blueprint files to Azure.
What should you do?
- A . Generate a shared access signature (SAS). Map a drive, and then copy the files by using File Explorer.
- B . Use the Azure Import/Export service.
- C . Generate an access key. Map a drive, and then copy the files by using File Explorer.
- D . Use Azure Storage Explorer to copy the files.
D
Explanation:
Azure Storage Explorer is a free tool from Microsoft that allows you to work with Azure Storage data on Windows, macOS, and Linux. You can use it to upload and download data from Azure blob storage.
Scenario:
Planned Changes include: move the existing product blueprint files to Azure Blob storage.
Technical Requirements include: Copy the blueprint files to Azure over the Internet.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/machine-learning/team-data-science-process/move-data-to-azure-blob-using-azure-storage-explorer
You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that is used be several departments at your company.
Subscription1 contains the resources in the following table:
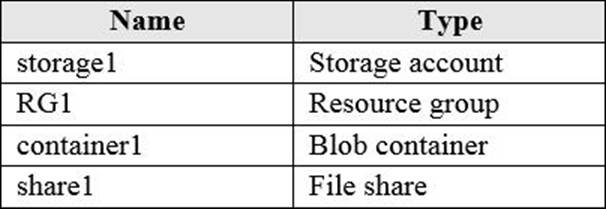
Another administrator deploys a virtual machine named VM1 and an Azure Storage account named Storage2 by using a single Azure Resource Manager template.
You need to view the template used for the deployment.
From which blade can you view the template that was used for the deployment?
- A . RG1
- B . VM1
- C . Storage1
- D . Container1
A
Explanation:
You have an Azure subscription that contains the resources in the following table.
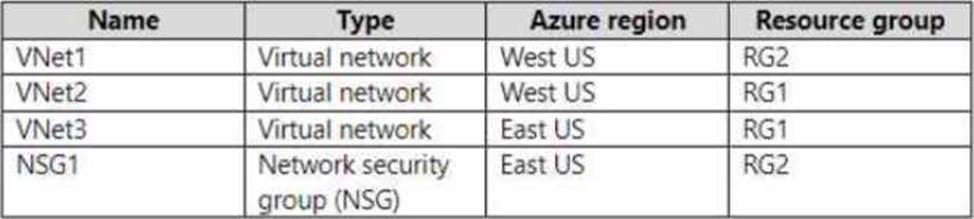
To which subnets can you apply NSG1?
- A . the subnets on VNet1 only
- B . the subnets on VNet2 only
- C . the subnets on VNet3 only
- D . the subnets on VNet2 and VNet3 only
- E . the subnets on VNet1 VNet2, and VNet3
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have an Azure virtual machine named VM1. VM1 was deployed by using a custom Azure Resource Manager template named ARM1.json.
You receive a notification that VM1 will be affected by maintenance.
You need to move VM1 to a different host immediately.
Solution: From the Overview blade, you move the virtual machine to a different subscription.
Does this meet the goal?
- A . Yes
- B . No
B
Explanation:
Moving the virtual machine to a different subscription does not change the host that the virtual machine runs on. It only changes the billing and management of the resources. To move the virtual machine to a different host, you need to redeploy it or use Azure Site Recovery.
Then, Reference: [Move resources to new resource group or subscription] [Redeploy Windows VM to new Azure node] [Use Azure Site Recovery to migrate Azure VMs between Azure regions]
