Practice Free Associate Cloud Engineer Exam Online Questions
You assist different engineering teams in deploying their infrastructure on Google Cloud. Your company has defined certain practices required for all workloads. You need to provide the engineering teams with a solution that enables teams to deploy their infrastructure independently without having to know all implementation details of the company’s required practices.
What should you do?
- A . Create a service account per team, and grant the service account the Project Editor role. Ask the teams to provision their infrastructure through the Google Cloud CLI (gcloud CLI), while impersonating their dedicated service account.
- B . Provide training for all engineering teams you work with to understand the company’s required
practices. Allow the engineering teams to provision the infrastructure to best meet their needs. - C . Configure organization policies to enforce your company’s required practices. Ask the teams to provision their infrastructure by using the Google Cloud console.
- D . Write Terraform modules for each component that are compliant with the company’s required practices, and ask teams to implement their infrastructure through these modules.
D
Explanation:
The goal is to enable teams to deploy infrastructure independently while ensuring compliance with company practices, without requiring teams to understand the underlying details of those practices.
Option A provides deployment capability but doesn’t enforce practices. The Editor role is overly broad, and using the gcloud CLI directly requires knowledge of how to configure resources compliantly.
Option B requires teams to learn all the practices, contradicting the requirement that they don’t need to know the implementation details.
Option C (Organization Policies) is useful for setting constraints (e.g., disallowing public IPs, restricting regions), but it doesn’t provide pre-configured, deployable components that embody best practices. Teams still need to figure out how to build compliant resources within the policy constraints.
Option D (Terraform Modules): This approach encapsulates the company’s required practices within reusable infrastructure-as-code modules. Engineering teams can then use these modules as building blocks, providing only the necessary input parameters (like application name orsize). The module handles the compliant implementation details internally. This allows teams to deploy independently and ensures compliance without needing deep knowledge of every practice.
Using standardized, compliant modules is a common pattern for enabling self-service infrastructure deployment while maintaining standards and governance.
Reference: Terraform Modules: "Modules are containers for multiple resources that are used together… Modules allow complex resources to be abstracted away behind a clean interface." –
https://developer.hashicorp.com/terraform/language/modules
Google Cloud Architecture Framework – Security, privacy, and compliance: Recommends using IaC and pre-approved templates/modules to enforce security configurations. – https://cloud.google.com/architecture/framework/security-privacy-compliance/define-and-enforce-security-configurations
Organization Policy Service: "The Organization Policy Service gives you centralized and programmatic control over your organization’s cloud resources… define constraints…" (Focuses on constraints, not providing deployable components). – https://cloud.google.com/resource-manager/docs/organization-policy/overview
Your team has developed a stateless application which requires it to be run directly on virtual machines. The application is expected to receive a fluctuating amount of traffic and needs to scale automatically. You need to deploy the application.
What should you do?
- A . Deploy the application on a managed instance group and configure autoscaling.
- B . Deploy the application on a Kubernetes Engine cluster and configure node pool autoscaling.
- C . Deploy the application on Cloud Functions and configure the maximum number instances.
- D . Deploy the application on Cloud Run and configure autoscaling.
A
Explanation:
A managed instance group (MIG) is a group of identical virtual machines (VMs) that you can manage as a single entity. You can use a MIG to deploy and maintain a stateless application that runs directly on VMs. A MIG can automatically scale the number of VMs based on the load or a schedule. A MIG can also automatically heal the VMs if they become unhealthy or unavailable. A MIG is suitable for applications that need to run on VMs rather than containers or serverless platforms.
B is incorrect because Kubernetes Engine is a managed service for running containerized applications on a cluster of nodes. It is not necessary to use Kubernetes Engine if the application does not use containers and can run directly on VMs.
C is incorrect because Cloud Functions is a serverless platform for running event-driven code in response to triggers. It is not suitable for applications that need to run continuously and handle HTTP requests.
D is incorrect because Cloud Run is a serverless platform for running stateless containerized applications. It is not suitable for applications that do not use containers and can run directly on VMs.
Managed instance groups documentation
Choosing a compute option for Google Cloud
You are building a backend service for an ecommerce platform that will persist transaction data from mobile and web clients. After the platform is launched, you expect a large volume of global transactions. Your business team wants to run SQL queries to analyze the data. You need to build a highly available and scalable data store for the platform.
What should you do?
- A . Create a multi-region Cloud Spanner instance with an optimized schema.
- B . Create a multi-region Firestore database with aggregation query enabled.
- C . Create a multi-region Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL database with optimized indexes.
- D . Create a multi-region BigQuery dataset with optimized tables.
You have an instance group that you want to load balance. You want the load balancer to terminate the client SSL session. The instance group is used to serve a public web application over HTTPS. You want to follow Google-recommended practices.
What should you do?
- A . Configure an HTTP(S) load balancer.
- B . Configure an internal TCP load balancer.
- C . Configure an external SSL proxy load balancer.
- D . Configure an external TCP proxy load balancer.
A
Explanation:
Reference: https://cloud.google.com/load-balancing/docs/https/
According to this guide for setting up an HTTP (S) load balancer in GCP: The client SSL session terminates at the load balancer. Sessions between the load balancer and the instance can either be HTTPS (recommended) or HTTP.
https://cloud.google.com/load-balancing/docs/ssl
You have an instance group that you want to load balance. You want the load balancer to terminate the client SSL session. The instance group is used to serve a public web application over HTTPS. You want to follow Google-recommended practices.
What should you do?
- A . Configure an HTTP(S) load balancer.
- B . Configure an internal TCP load balancer.
- C . Configure an external SSL proxy load balancer.
- D . Configure an external TCP proxy load balancer.
A
Explanation:
Reference: https://cloud.google.com/load-balancing/docs/https/
According to this guide for setting up an HTTP (S) load balancer in GCP: The client SSL session terminates at the load balancer. Sessions between the load balancer and the instance can either be HTTPS (recommended) or HTTP.
https://cloud.google.com/load-balancing/docs/ssl
You have a Dockerfile that you need to deploy on Kubernetes Engine.
What should you do?
- A . Use kubectl app deploy <dockerfilename>.
- B . Use gcloud app deploy <dockerfilename>.
- C . Create a docker image from the Dockerfile and upload it to Container Registry. Create a Deployment YAML file to point to that image. Use kubectl to create the deployment with that file.
- D . Create a docker image from the Dockerfile and upload it to Cloud Storage. Create a Deployment YAML file to point to that image. Use kubectl to create the deployment with that file.
C
Explanation:
Reference: https://cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine/docs/tutorials/hello-app
You are building a pipeline to process time-series data.
Which Google Cloud Platform services should you put in boxes 1,2,3, and 4?
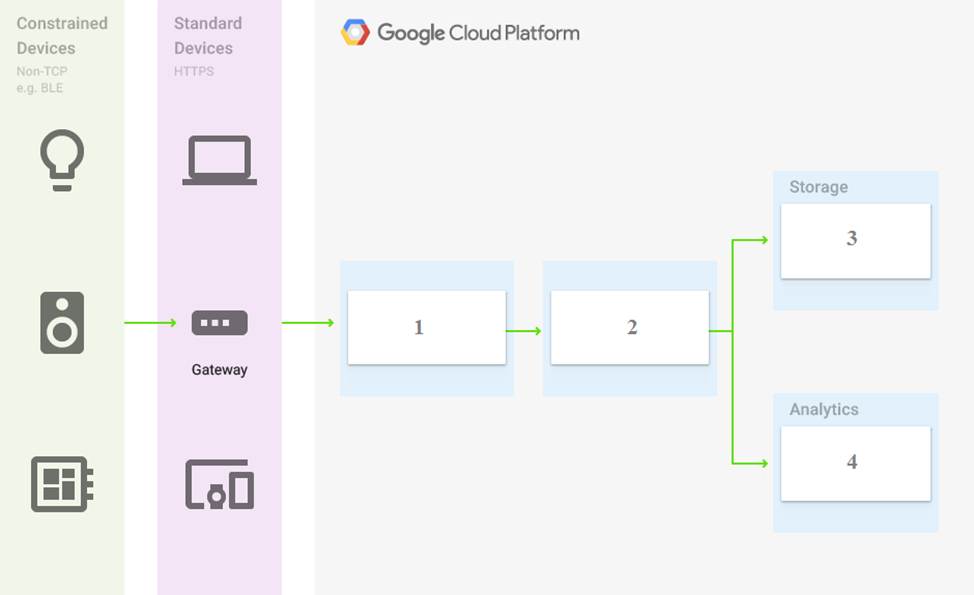
- A . Cloud Pub/Sub, Cloud Dataflow, Cloud Datastore, BigQuery
- B . Firebase Messages, Cloud Pub/Sub, Cloud Spanner, BigQuery
- C . Cloud Pub/Sub, Cloud Storage, BigQuery, Cloud Bigtable
- D . Cloud Pub/Sub, Cloud Dataflow, Cloud Bigtable, BigQuery
D
Explanation:
Reference:
https://cloud.google.com/solutions/correlating-time-series-dataflow
https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/data-analytics/handling-duplicate-data-in-streaming-pipeline-using-pubsub-dataflow
https://cloud.google.com/bigtable/docs/schema-design-time-series
