Practice Free AIF-C01 Exam Online Questions
A manufacturing company has an application that ingests consumer complaints from publicly available sources. The application uses complex hard-coded logic to process the complaints. The company wants to scale this logic across markets and product lines.
Which advantage do generative AI models offer for this scenario?
- A . Predictability of outputs
- B . Adaptability
- C . Less sensitivity to changes in inputs
- D . Explainability
B
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact AWS AI documents:
Generative AI models offer adaptability, meaning they can generalize across:
Different markets
New product lines
Variations in language and complaint structure
Unlike hard-coded logic, generative models can adapt to new patterns and inputs without requiring extensive rule rewrites, making them ideal for scaling text-based processing applications.
Why the other options are incorrect:
Predictability (A) is typically lower in generative models.
Less sensitivity (C) is incorrect; generative models are sensitive to input variations.
Explainability (D) is generally limited in large generative models.
AWS AI document references:
Generative AI Benefits and Trade-offs
Modernizing Text Processing with Foundation Models
Scaling NLP Solutions on AWS
A company deployed an AI/ML solution to help customer service agents respond to frequently asked questions. The questions can change over time. The company wants to give customer service agents the ability to ask questions and receive automatically generated answers to common customer questions.
Which strategy will meet these requirements MOST cost-effectively?
- A . Fine-tune the model regularly.
- B . Train the model by using context data.
- C . Pre-train and benchmark the model by using context data.
- D . Use Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) with prompt engineering techniques.
D
Explanation:
RAG combines large pre-trained models with retrieval mechanisms to fetch relevant context from a knowledge base. This approach is cost-effective as it eliminates the need for frequent model retraining while ensuring responses are contextually accurate and up to date.
Reference: AWS RAG Techniques.
A financial company wants to build workflows for human review of ML predictions. The company wants to define confidence thresholds for its use case and adjust the threshold over time.
Which AWS service meets these requirements?
- A . Amazon Personalize
- B . Amazon Augmented AI (Amazon A2I)
- C . Amazon Inspector
- D . AWS Audit Manager
B
Explanation:
The correct answer is B because Amazon Augmented AI (Amazon A2I) allows developers to integrate human review workflows into ML systems. It supports defining confidence thresholds, such that only low-confidence predictions are sent to human reviewers.
From AWS documentation:
"Amazon A2I provides built-in human review workflows for ML predictions. You can configure confidence thresholds to determine when human review is triggered, enabling continual adjustment based on accuracy needs."
This supports use cases where business decisions (like financial approvals) require manual oversight for edge cases.
Explanation of other options:
A company wants to improve the accuracy of the responses from a generative AI application. The application uses a foundation model (FM) on Amazon Bedrock.
Which solution meets these requirements MOST cost-effectively?
- A . Fine-tune the FM.
- B . Retrain the FM.
- C . Train a new FM.
- D . Use prompt engineering.
D
Explanation:
The company wants to improve the accuracy of a generative AI application using a foundation model (FM) on Amazon Bedrock in the most cost-effective way. Prompt engineering involves optimizing the input prompts to guide the FM to produce more accurate responses without modifying the model itself. This approach is cost-effective because it does not require additional computational resources or training, unlike fine-tuning or retraining.
Exact Extract from AWS AI Documents:
From the AWS Bedrock User Guide:
"Prompt engineering is a cost-effective technique to improve the performance of foundation models. By crafting precise and context-rich prompts, users can guide the model to generate more accurate and relevant responses without the need for fine-tuning or retraining."
(Source: AWS Bedrock User Guide, Prompt Engineering for Foundation Models)
Detailed
Option A: Fine-tune the FM. Fine-tuning involves retraining the FM on a custom dataset, which requires computational resources, time, and cost (e.g., for Amazon Bedrock fine-tuning jobs). It is not the most cost-effective solution.
Option B: Retrain the FM. Retraining an FM from scratch is highly resource-intensive and expensive, as it requires large datasets and significant compute power. This is not cost-effective.
Option C: Train a new FM. Training a new FM is the most expensive option, as it involves building a model from the ground up, requiring extensive data, compute resources, and expertise. This is not cost-effective.
Option D: Use prompt engineering. This is the correct answer. Prompt engineering adjusts the input prompts to improve the FM’s responses without incurring additional compute costs, making it the most cost-effective solution for improving accuracy on Amazon Bedrock.
Reference: AWS Bedrock User Guide: Prompt Engineering for Foundation Models (https://docs.aws.amazon.com/bedrock/latest/userguide/prompt-engineering.html)
AWS AI Practitioner Learning Path: Module on Generative AI Optimization
Amazon Bedrock Developer Guide: Cost Optimization for Generative AI (https://aws.amazon.com/bedrock/)
A company wants to use Amazon Q Business for its data. The company needs to ensure the security and privacy of the data.
Which combination of steps will meet these requirements? (Select TWO.)
- A . Enable AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) keys for the Amazon Q Business Enterprise index.
- B . Set up cross-account access to the Amazon Q index.
- C . Configure Amazon Inspector for authentication.
- D . Allow public access to the Amazon Q index.
- E . Configure AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) for authentication.
A,E
Explanation:
The correct answers are A and E because both directly align with AWS best practices for securing generative AI services and data privacy in enterprise applications.
From the AWS Amazon Q Business documentation:
"AWS Key Management Service (KMS) integrates with Amazon Q Business to encrypt sensitive data at rest. You can use customer-managed KMS keys to meet compliance requirements."
And:
"You must configure IAM access controls to manage which users and applications can access Amazon Q Business indexes, ensuring that only authorized users can retrieve information."
Explanation of other options:
B. Cross-account access is not a common requirement for internal enterprise use of Amazon Q Business unless explicitly sharing data across organizations. It’s not a requirement for securing access.
C. Amazon Inspector is a vulnerability management tool for EC2 and containers. It is unrelated to Amazon Q authentication or security.
D. Allowing public access would violate security and privacy principles and directly contradict the stated requirement.
Referenced AWS AI/ML Documents and Study Guides:
Amazon Q Business Developer Guide C Security and Identity Management
AWS KMS Documentation C Integration with Bedrock and Amazon Q
AWS Certified Machine Learning Specialty Guide C Responsible AI and Governance Section
HOTSPOT
A company is training its employees on how to structure prompts for foundation models.
Select the correct prompt engineering technique from the following list for each prompt template. Each prompt engineering technique should be selected onetime. (Select THREE.)
• Chain-of-thought reasoning
• Few-shot learning
• Zero-shot learning

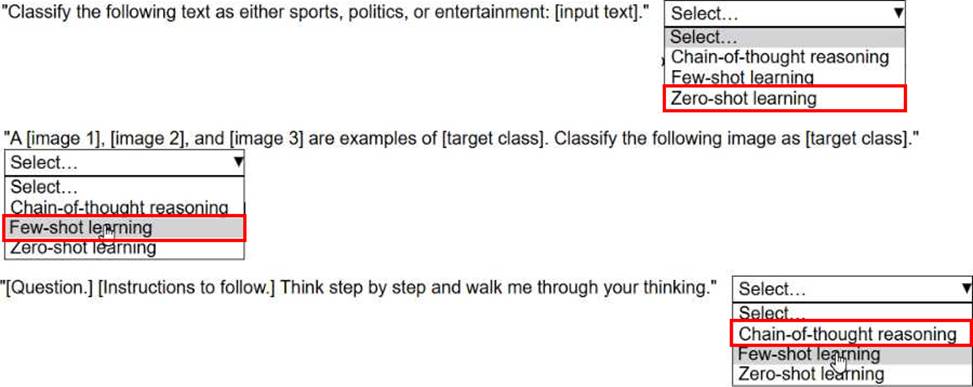
Explanation:
Zero-shot learning is when the model is asked to perform a task without being given any examples.
The prompt simply describes the task and relies on the model’s pre-trained knowledge.
(Reference: Amazon Bedrock Prompt Engineering Guide)
Few-shot learning provides a few examples (shots) in the prompt to show the model how to solve the task before asking it to complete a similar task.
(Reference: Amazon Bedrock Prompt Engineering Guide)
Chain-of-thought reasoning encourages the model to reason step by step and explain its thinking for more complex or logical tasks.
(Reference: AWS Chain-of-Thought Prompting)
An AI practitioner is developing a prompt for an Amazon Titan model. The model is hosted on Amazon Bedrock. The AI practitioner is using the model to solve numerical reasoning challenges. The AI practitioner adds the following phrase to the end of the prompt: "Ask the model to show its work by explaining its reasoning step by step."
Which prompt engineering technique is the AI practitioner using?
- A . Chain-of-thought prompting
- B . Prompt injection
- C . Few-shot prompting
- D . Prompt templating
A
Explanation:
Chain-of-thought prompting is a prompt engineering technique where you instruct the model to explain its reasoning step by step, which is particularly useful for tasks involving logic, math, or reasoning.
A is correct: Asking the model to "explain its reasoning step by step" directly invokes chain-of-thought prompting, as documented in AWS and generative AI literature.
B is unrelated (prompt injection is a security concern).
C (few-shot) provides examples, but doesn’t specifically require step-by-step reasoning.
D (templating) is about structuring the prompt format.
"Chain-of-thought prompting elicits step-by-step explanations from LLMs, which improves performance on complex reasoning tasks."
(Reference: Amazon Bedrock Prompt Engineering Guide, AWS Certified AI Practitioner Study Guide)
A company wants to make a chatbot to help customers. The chatbot will help solve technical problems without human intervention.
The company chose a foundation model (FM) for the chatbot. The chatbot needs to produce responses that adhere to company tone.
Which solution meets these requirements?
- A . Set a low limit on the number of tokens the FM can produce.
- B . Use batch inferencing to process detailed responses.
- C . Refine the prompt until the FM produces the desired responses.
- D . Define a higher number for the temperature parameter.
C
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact AWS AI documents:
Prompt engineering is the primary method for controlling tone, style, and behavior of foundation model responses.
AWS generative AI guidance explains that:
Prompts can define tone, voice, and response structure
Iterative refinement ensures consistent outputs
Prompt refinement requires no model retraining
Why the other options are incorrect:
Token limits (A) affect length, not tone.
Batch inferencing (B) affects processing mode, not response style.
Higher temperature (D) increases randomness, reducing consistency.
AWS AI document references:
Prompt Engineering Best Practices
Controlling Model Output Tone
Using Prompts with Foundation Models on AWS
HOTSPOT
A company wants to build an ML application.
Select and order the correct steps from the following list to develop a well-architected ML workload. Each step should be selected one time. (Select and order FOUR.)
• Deploy model
• Develop model
• Monitor model
• Define business goal and frame ML problem
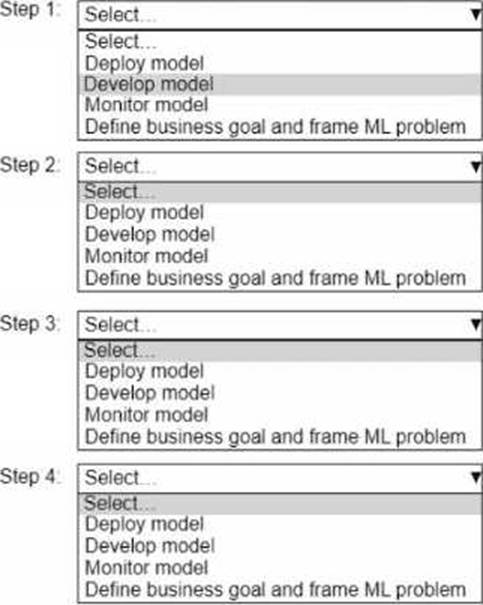

Explanation:
Building a well-architected ML workload follows a structured lifecycle as outlined in AWS best practices. The process begins with defining the business goal and framing the ML problem to ensure the project aligns with organizational objectives. Next, the model is developed, which includes data preparation, training, and evaluation. Once the model is ready, it is deployed to make predictions in a production environment. Finally, the model is monitored to ensure it performs as expected and to address any issues like drift or degradation over time. This order ensures a systematic approach to ML development.
Exact Extract from AWS AI Documents:
From the AWS AI Practitioner Learning Path:
"The machine learning lifecycle typically follows these stages: 1) Define the business goal and frame the ML problem, 2) Develop the model (including data preparation, training, and evaluation), 3) Deploy the model to production, and 4) Monitor the model for performance and drift to ensure it continues to meet business needs."
(Source: AWS AI Practitioner Learning Path, Module on Machine Learning Lifecycle)
Detailed
Step 1: Define business goal and frame ML problem This is the first step in any ML project. It involves understanding the business objective (e.g., reducing churn) and framing the ML problem (e.g., classification or regression). Without this step, the project lacks direction. The hotspot lists this option as "Define business goal and frame ML problem," which matches this stage.
Step 2: Develop model After defining the problem, the next step is to develop the model. This includes collecting and preparing data, selecting an algorithm, training the model, and evaluating its performance. The hotspot lists "Develop model" as an option, aligning with this stage.
Step 3: Deploy model Once the model is developed and meets performance requirements, it is deployed to a production environment to make predictions or automate decisions. The hotspot includes "Deploy model" as an option, which fits this stage.
Step 4: Monitor model After deployment, the model must be monitored to ensure it performs well over time, addressing issues like data drift or performance degradation. The hotspot lists "Monitor model" as an option, completing the lifecycle.
Hotspot Selection Analysis:
The hotspot provides four steps, each with the same dropdown options: "Select…," "Deploy model," "Develop model," "Monitor model," and "Define business goal and frame ML problem." The correct selections are:
Step 1: Define business goal and frame ML problem
Step 2: Develop model
Step 3: Deploy model
Step 4: Monitor model
Each option is used exactly once, as required, and follows the logical order of the ML lifecycle.
Reference: AWS AI Practitioner Learning Path: Module on Machine Learning Lifecycle
Amazon SageMaker Developer Guide: Machine Learning Workflow (https://docs.aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/latest/dg/how-it-works-mlconcepts.html)
AWS Well-Architected Framework: Machine Learning Lens (https://docs.aws.amazon.com/wellarchitected/latest/machine-learning-lens/)
A company stores millions of PDF documents in an Amazon S3 bucket. The company needs to extract the text from the PDFs, generate summaries of the text, and index the summaries for fast searching.
Which combination of AWS services will meet these requirements? (Select TWO.)
- A . Amazon Translate
- B . Amazon Bedrock
- C . Amazon Transcribe
- D . Amazon Polly
- E . Amazon Textract
B,E
Explanation:
Amazon Textract (E) automatically extracts text and structured data from scanned documents, such as PDFs.
Amazon Bedrock (B) offers access to LLMs (such as Amazon Titan or Anthropic Claude) for tasks like summarization and generating embeddings for search.
Workflow:
Amazon Textract extracts text from PDFs in S3.
Amazon Bedrock LLMs summarize the extracted text.
(Optional: Summaries can be indexed using Amazon OpenSearch or another search solution.)
A (Translate) is for language translation, not extraction or summarization.
C (Transcribe) is for audio to text, not PDFs.
D (Polly) is for text-to-speech.
“Amazon Textract extracts text, forms, and tables from scanned documents… Bedrock provides generative AI models to perform summarization and other text generation tasks.”
(Reference: Amazon Textract, Amazon Bedrock, AWS GenAI RAG Reference)
