Practice Free AIF-C01 Exam Online Questions
What is tokenization used for in natural language processing (NLP)?
- A . To encrypt text data
- B . To compress text files
- C . To break text into smaller units for processing
- D . To translate text between languages
C
Explanation:
The correct answer is C because tokenization is the NLP process of breaking down text into smaller units, such as words, subwords, or characters, that can be processed by ML models.
From AWS documentation:
"Tokenization is the process of splitting text into meaningful units, such as words or subwords, that are used as input tokens in NLP tasks. Tokenization is an essential step in preparing text data for models."
This is a foundational concept used in language models, including those on Amazon Bedrock and SageMaker.
Explanation of other options:
HOTSPOT
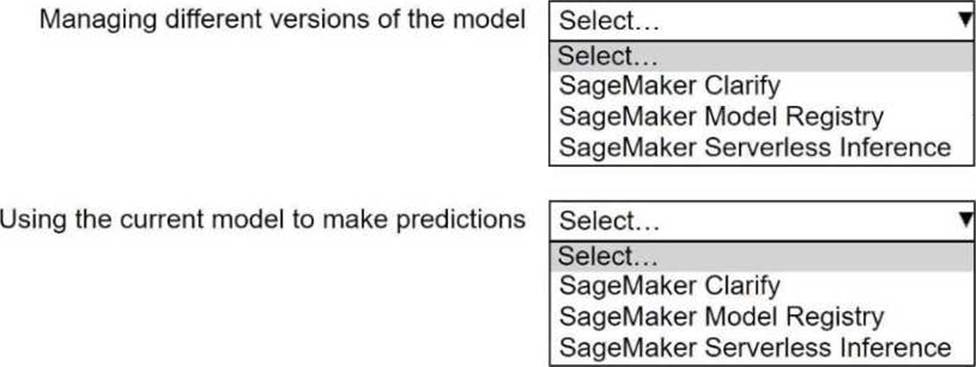
A company is using Amazon SageMaker to develop AI models.
Select the correct SageMaker feature or resource from the following list for each step in the AI model lifecycle workflow. Each SageMaker feature or resource should be selected one time or not at all. (Select TWO.)
SageMaker Clarify
SageMaker Model Registry
SageMaker Serverless Inference

Explanation:
SageMaker Model Registry, SageMaker Serverless interference
This question requires selecting the appropriate Amazon SageMaker feature for two distinct steps in the AI model lifecycle. Let’s break down each step and evaluate the options:
Step 1: Managing different versions of the model
The goal here is to identify a SageMaker feature that supports version control and management of machine learning models.
Let’s analyze the options:
SageMaker Clarify: This feature is used to detect bias in models and explain model predictions, helping with fairness and interpretability. It does not provide functionality for managing model versions.
SageMaker Model Registry: This is a centralized repository in Amazon SageMaker that allows users to catalog, manage, and track different versions of machine learning models. It supports model versioning, approval workflows, and deployment tracking, making it ideal for managing different versions of a model.
SageMaker Serverless Inference: This feature enables users to deploy models for inference without managing servers, automatically scaling based on demand. It is focused on inference (predictions), not on managing model versions.
Conclusion for Step 1: The SageMaker Model Registry is the correct choice for managing different versions of the model.
Exact Extract
Reference: According to the AWS SageMaker documentation, “The SageMaker Model Registry allows you to catalog models for production, manage model versions, associate metadata, and manage approval status for deployment.” (Source: AWS SageMaker Documentation – Model Registry, https://docs.aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/latest/dg/model-registry.html).
Step 2: Using the current model to make predictions
The goal here is to identify a SageMaker feature that facilitates making predictions (inference) with a
deployed model. Let’s evaluate the options:
SageMaker Clarify: As mentioned, this feature focuses on bias detection and explainability, not on performing inference or making predictions.
SageMaker Model Registry: While the Model Registry helps manage and catalog models, it is not used directly for making predictions. It can store models, but the actual inference process requires a deployment mechanism.
SageMaker Serverless Inference: This feature allows users to deploy models for inference without managing infrastructure. It automatically scales based on traffic and is specifically designed for making predictions in a cost-efficient, serverless manner.
Conclusion for Step 2: SageMaker Serverless Inference is the correct choice for using the current model to make predictions.
Exact Extract
Reference: The AWS documentation states, “SageMaker Serverless Inference is a deployment option that allows you to deploy machine learning models for inference without configuring or managing servers. It automatically scales to handle inference requests, making it ideal for workloads with intermittent or unpredictable traffic.” (Source: AWS SageMaker Documentation – Serverless Inference, https://docs.aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/latest/dg/serverless-inference.html).
Why Not Use the Same Feature Twice?
The question specifies that each SageMaker feature or resource should be selected one time or not at all. Since SageMaker Model Registry is used for version management and SageMaker Serverless Inference is used for predictions, each feature is selected exactly once. SageMaker Clarify is not applicable to either step, so it is not selected at all, fulfilling the question’s requirements.
Reference: AWS SageMaker Documentation: Model Registry (https://docs.aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/latest/dg/model-registry.html)
AWS SageMaker Documentation: Serverless Inference (https://docs.aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/latest/dg/serverless-inference.html)
AWS AI Practitioner Study Guide (conceptual alignment with SageMaker features for model lifecycle management and inference)
Let’s format this question according to the specified structure and provide a detailed, verified answer based on AWS AI Practitioner knowledge and official AWS documentation. The question focuses on selecting an AWS database service that supports storage and queries of embeddings as vectors, which is relevant to generative AI applications.
Which option is an example of unsupervised learning?
- A . A model that groups customers based on their purchase history
- B . A model that classifies images as dogs or cats
- C . A model that predicts a house’s price based on various features
- D . A model that learns to play chess by using trial and error
A
Explanation:
Unsupervised learning involves training a model on unlabeled data, letting it find patterns or groupings on its own, without explicit outputs provided. Clustering is a primary unsupervised learning technique.
Option A is correct: Grouping customers based on purchase history (without predefined categories) is clustering, a classic unsupervised task.
B and C are supervised learning (classification and regression, respectively).
D is reinforcement learning, not unsupervised learning.
"Unsupervised learning involves training on data without labels and is often used for clustering or dimensionality reduction."
(Reference: AWS Certified AI Practitioner Official Study Guide, AWS ML Concepts)
A company wants to learn about generative AI applications in an experimental environment.
Which solution will meet this requirement MOST cost-effectively?
- A . Amazon Q Developer
- B . Amazon SageMaker JumpStart
- C . Amazon Bedrock PartyRock
- D . Amazon Q Business
C
Explanation:
The correct answer is Amazon Bedrock PartyRock, a playground for building and experimenting with generative AI apps in a low-cost, no-code environment. PartyRock is designed for innovation and learning. It enables users to try out prompts, LLM apps, and templates using Amazon Bedrock under a free-tier friendly setup. According to AWS, PartyRock abstracts infrastructure and allows rapid prototyping using models from Bedrock providers. This makes it ideal for early experimentation, especially for non-developers or those not ready to invest in full production pipelines. In contrast, Amazon Q Developer is for software engineering tasks, SageMaker JumpStart focuses on deploying ML models, and Q Business targets enterprise knowledge workers. None of those are as cost-effective and experimental-focused as PartyRock.
Referenced AWS AI/ML Documents and Study Guides:
Amazon Bedrock Documentation C PartyRock Overview
AWS Generative AI Learning Path C Getting Started Tools
A company wants to identify groups for its customers based on the customers’ demographics and buying patterns.
Which algorithm should the company use to meet this requirement?
- A . K-nearest neighbors (K-NN)
- B . K-means
- C . Decision tree
- D . Support vector machine
B
Explanation:
The correct answer is B because K-means is an unsupervised learning algorithm used for clustering data points into groups (clusters) based on feature similarity. It is ideal for customer segmentation use cases where the goal is to discover natural groupings based on buying behavior and demographics without pre-labeled data.
From AWS documentation:
"K-means is a clustering algorithm that assigns data points to one of K groups based on feature similarity. It is commonly used in marketing and customer segmentation to group users with similar characteristics."
Explanation of other options:
A company is exploring Amazon Nova models in Amazon Bedrock. The company needs a multimodal model that supports multiple languages.
- A . Nova Lite
- B . Nova Pro
- C . Nova Canvas
- D . Nova Reel
B
Explanation:
Amazon Nova Pro is a multimodal foundation model in Amazon Bedrock that supports text, images, and multiple languages.
Nova Lite is optimized for lightweight, faster inference at lower cost.
Nova Canvas is a creative tool for visual design.
Nova Reel is optimized for video-related use cases.
Reference: AWS Documentation C Amazon Nova Models
A real estate company is developing an ML model to predict house prices by using sales and marketing data. The company wants to use feature engineering to build a model that makes accurate predictions.
Which approach will meet these requirements?
- A . Understand patterns by providing data visualization.
- B . Tune the model’s hyperparameters.
- C . Create or select relevant features for model training.
- D . Collect data from multiple sources.
C
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact AWS AI documents:
Feature engineering focuses on:
Creating new features
Selecting the most relevant existing features
Improving model signal and accuracy
AWS ML best practices identify feature engineering as a key driver of predictive performance.
Why the other options are incorrect:
Visualization (A) helps understanding, not feature creation.
Hyperparameter tuning (B) optimizes models, not features.
Data collection (D) expands datasets but does not engineer features.
AWS AI document references:
Feature Engineering Best Practices
Improving Model Accuracy on AWS
ML Model Development Lifecycle
Which statement presents an advantage of using Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) for natural language processing (NLP) tasks?
- A . RAG can use external knowledge sources to generate more accurate and informative responses
- B . RAG is designed to improve the speed of language model training
- C . RAG is primarily used for speech recognition tasks
- D . RAG is a technique for data augmentation in computer vision tasks
A
Explanation:
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) integrates external knowledge sources (databases, vector stores, document repositories) with LLMs, enabling them to generate contextually accurate and up-to-date responses without retraining.
B is incorrect: RAG does not speed up training; it improves inference results.
C is incorrect: speech recognition is not an RAG use case.
D is incorrect: computer vision augmentation is unrelated to RAG.
Reference: AWS Documentation C Knowledge Bases for RAG in Amazon Bedrock
An online learning company with large volumes of education materials wants to use enterprise
search.
- A . Amazon Comprehend
- B . Amazon Textract
- C . Amazon Kendra
- D . Amazon Personalize
C
Explanation:
The correct answer is C C Amazon Kendra, AWS’s enterprise search service designed for organizations with large, diverse document repositories. Kendra uses machine learning and natural language understanding (NLU) to provide semantic search, meaning it retrieves results based on meaning rather than keyword matching. According to AWS documentation, Kendra is ideal for educational, enterprise, and knowledge-management scenarios where users need fast, accurate retrieval across PDFs, HTML, Office documents, FAQs, and multimedia transcripts. Kendra connectors can index content from S3, SharePoint, LMS platforms, and internal databases, making it perfect for large volumes of training materials. Amazon Comprehend (A) is for NLP tasks like entity extraction, not enterprise search. Amazon Textract (B) extracts text from PDFs and scanned materials but does not provide search capabilities. Amazon Personalize (D) is for personalized recommendations, not document retrieval. Kendra is purpose-built for enterprise search and aligns directly with the company’s needs.
Referenced AWS Documentation:
Amazon Kendra Developer Guide C Enterprise Search
AWS ML Specialty Guide C Intelligent Search Systems
A company uses Amazon SageMaker and various models fa Its AI workloads. The company needs to understand If Its AI workloads are ISO compliant.
Which AWS service or feature meets these requirements?
- A . AWS Audit Manager
- B . Amazon SageMaker Model Cards
- C . Amazon SageMaker Model Monitor
- D . AWS Artifact
