Practice Free 350-501 Exam Online Questions
Form the neighbor relationship using a BGP multihop mechanism. Use minimal values to solve the issue.

Refer to the exhibit.
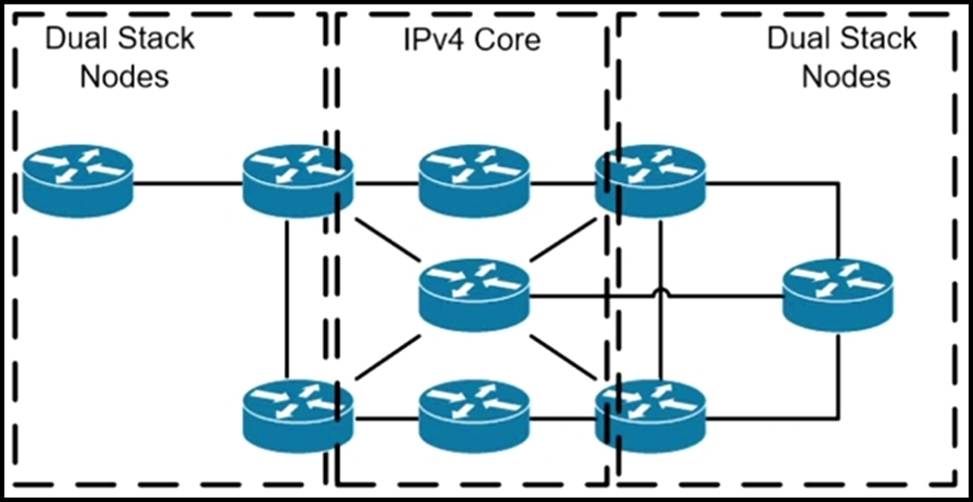
A network operator has two IPv4 and IPv6 dual-stacked network on each side of the IPv4 core network. The operator must be able to provide connectivity between them while using specific assigned IPv6 space provided from the company IP administrator team.
Which technology should the network operator use to accomplish this goal?
- A . 6rd
- B . NAT46
- C . DS-Lite
- D . NAT44
B
Explanation:
The network operator needs to provide connectivity between two IPv4 and IPv6 dual-stacked networks using specific assigned IPv6 space. NAT46 (Network Address Translation 46) is the appropriate technology for this scenario. It allows translation between IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, enabling communication between the dual-stack networks. NAT46 maps IPv6 addresses to IPv4 addresses and vice versa, facilitating seamless communication across different address families.
Reference: Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies
Refer to the exhibit.
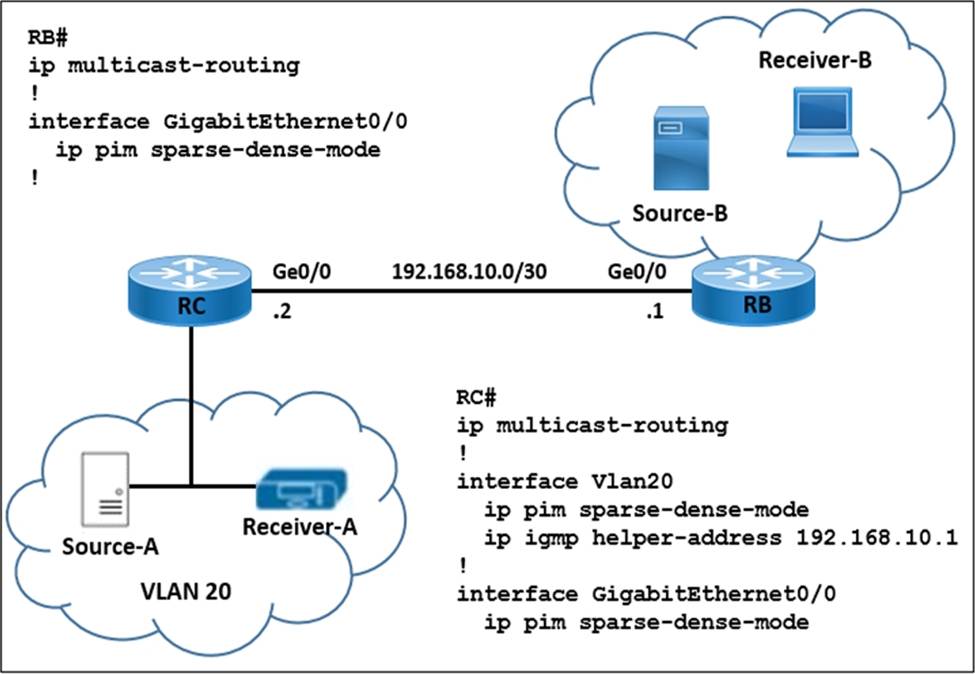
A network engineer is implementing multicast Source-A to send a multicast stream for Receiver-A, and multicast Source-B to send a multicast stream for Receiver-B. Router RC forwards the IGMP host a report and leaves messages to IP address 192.168.10.1.
How must the multicast features be implemented to prevent RB from receiving multicast flooding from Source-A?
- A . Change the helper-address value to 192.168.10.2 on RC.
- B . Enable ip pim neighbor-filter on RC interface Ge0/0.
- C . Configure PIM-SSM on RB and RC interface Ge 0/0.
- D . Enable ip pim passive on RB interface Ge0/0.
DRAG DROP
Drag and drop the descriptions from the left onto the corresponding OS types on the right.
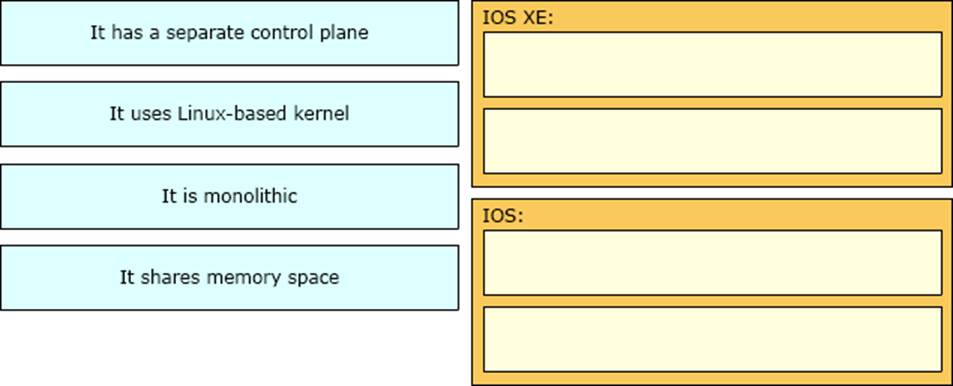

Explanation:
IOS XE:
It uses Linux-based kernel
It has a separate control plane
IOS:
It is monolithic
It shares memory space
Refer to the exhibit.
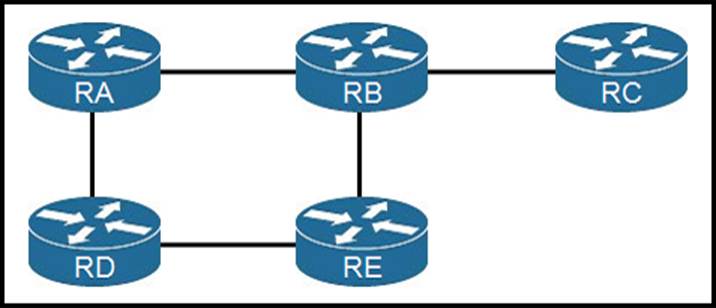
If RC is a stub router, which entry must be injected so that it will send traffic outside the OSPF domain?
- A . virtual link between RB and RC
- B . sham link
- C . more specific route
- D . default route
D
Explanation:
If RC is a stub router in an OSPF network, it requires a default route to be injected so that it can send traffic outside the OSPF domain. In OSPF, stub routers do not have any routes external to the OSPF domain in their routing tables. To allow these routers to reach networks outside of their OSPF domain, a default route should be injected into the stub area by the Area Border Router (ABR). This allows all routers in the stub area, including RC, to forward traffic for unknown destinations to the ABR, which then forwards it appropriately.
Reference: Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies source documents or study guide
Refer to the exhibit:

Which purpose of implementing NSF with this configuration is true?
- A . The router uses NSF to load balance traffic between two links, with the primary link alternating every 90 seconds
- B . The router uses NSF to reduce neighbor-relationship downtime during RP switchover
- C . The router uses NSF to load balance traffic on a routed EtherChannel
- D . The router uses NSF to handle RP switchover while allowing neighbor relationships to remain up
B
Explanation:
The configuration in the exhibit shows the implementation of Nonstop Forwarding (NSF) with OSPF. NSF is used to minimize the downtime of neighbor relationships during a Route Processor (RP) switchover. The nsf command enables NSF, and ietf specifies the use of the IETF standard for graceful restart in OSPF. The restart interval 90 sets the time, in seconds, within which the restarting router should complete its restart, helping to maintain uninterrupted forwarding despite the switchover.
Reference: Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies (SPCOR v1.0); Cisco SPCOR
Training & Certification.
A network engineer must enable the helper router to terminate the OSPF graceful restart process if it detects any changes in the LSA.
Which command enables this feature?
- A . nsf ietf helper disable
- B . nsf cisco enforce global
- C . nsf ietf helper strict-lsa-checking
- D . nsf Cisco helper disable
C
Explanation:
The command nsf ietf helper strict-lsa-checking is used to configure the router to terminate the OSPF graceful restart process if it detects any changes in the LSA during the restart. This ensures that the network remains stable and consistent by preventing the use of outdated or incorrect routing information.
A network administrator must monitor network usage to provide optimal performance to the network end users when the network is under heavy load. The administrator asked the engineer to install a new server to receive SNMP traps at destination 192.168.1.2.
Which configuration must the engineer apply so that all traps are sent to the new server?
- A . snmp-server enable traps entity
snmp-server host 192.168.1.2 public - B . snmp-server enable traps bgp
snmp-server host 192.168.1.2 public - C . snmp-server enable traps isdn
snmp-server host 192.168.1.2 public - D . snmp-server enable traps
snmp-server host 192.168.1.2 public
The network team is planning to implement IPv6 on the company’s existing IPv4 network infrastructure. The network currently uses IS-IS to share routes between peers.
Which task must the team perform so that IS-IS will run in multitopology mode on the updated IPv6 network?
- A . Configure the links between the network routers as point-to-point.
- B . Configure the network routers to use metric-style wide.
- C . Configure the network routers as Level 2 routers.
- D . Configure the IS-IS IPv6 metric on the dual-stack links.
A network engineer must implement an ACL-based solution to mitigate availability issues on a web service that is hosted on a server at IP address 172.16.15.18/23. Access to the web server should be allowed over HTTP from RFC 1918 addresses only. The network architect has already enabled PMTUD in the network.
Which ACL configuration must the engineer implement to complete the task?
- A . access-list 198 deny ip any host 172.16.15.18 fragments
access-list 198 permit 6 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 172.16.15.18 0.0.1.255 eq 80
access-list 198 permit 6 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 172.16.15.18 0.0.1.255 eq 80
access-list 198 permit 6 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255 172.16.15.18 0.0.1.255 eq 80
access-list 198 deny ip any any - B . access-list 198 deny ip any host 172.16.15.18 ip-fragments
access-list 198 permit 18 10.10.0.0 0.0.255.0 172.16.15.18 255.255.254.0
access-list 198 permit 18 172.16.0.0 255.255.0 172.16.15.18 255.255.254.0
access-list 198 permit 18 192.168.0.0 255.255.0 172.16.15.18 255.255.254.0
access-list 198 deny tcp any any - C . access-list 199 deny ip any host 172.16.15.18 tcp-fragments
access-list 199 permit tcp 10.0.0.0 0.0.255.255 172.16.15.18 0.0.254.255 eq 80
access-list 199 permit tcp 172.16.0.0 0.0.0.255 172.16.15.18 0.0.254.255 eq 80
access-list 199 permit tcp 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255 172.16.15.18 0.0.254.255 eq 80
access-list 199 deny ip any any - D . access-list 199 deny tcp any host 172.16.15.18 http-fragments
access-list 199 permit 16 10.10.0.0 0.255.255.255 172.16.15.18 0.0.2.253 eq 80
access-list 199 permit 16 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 172.16.15.18 0.0.2.253 eq 80
access-list 199 permit 16 192.168.0.0 0.0.255 172.16.15.18 0.0.2.253 eq 80
access-list 199 deny tcp any any
