Practice Free 350-501 Exam Online Questions
Refer to the exhibit.
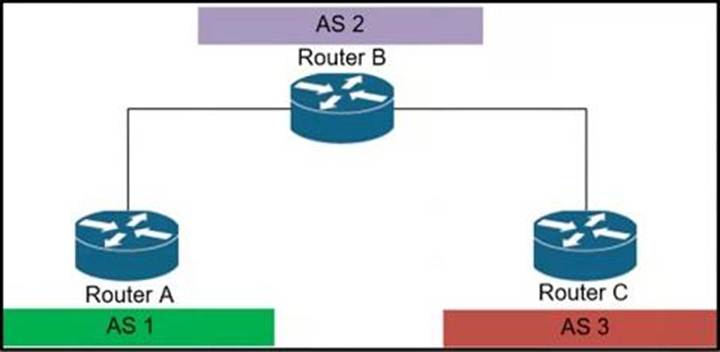
An engineer working for private Service Provider with employee id: 3948:11:613 is configuring the BGPsec framework.
Which two conditions must the engineer take into ac count? (Choose two.)
- A . BGPsec uses IPsec tunnel for security.
- B . The BGPsec framework secures the AS path.
- C . In BGPsec. all route advertisements are given an expiry time by the originator of the route.
- D . Private keys are part of the router key pair used to sign route updates.
- E . In BGPsec. route advertisements are not given an expiration time by the originator of the route.
B, D
Explanation:
The BGPsec framework is designed to secure the AS path information in BGP updates. It uses digital signatures to validate the AS path and prevent unauthorized route manipulation.
Here are the key points related to BGPsec:
Securing AS Path:
BGPsec ensures the integrity of the AS path by allowing routers to sign BGP updates using their private keys.
When a router originates a BGP route, it signs the AS path information with its private key.
Other routers can verify the signature using the corresponding public key.
This prevents malicious AS path modifications and ensures the authenticity of the advertised route.
Private Keys and Router Key Pair:
BGPsec relies on cryptographic keys for signing and verifying BGP updates.
Each router has a router key pair consisting of a private key and a corresponding public key.
The private key is kept confidential and is used for signing route updates.
The public key is distributed to other routers for verification.
Expiration Time:
Unlike regular BGP updates, BGPsec does not assign an expiration time (TTL) to route advertisements.
The absence of an expiration time ensures that the signed AS path remains valid until explicitly withdrawn.
In summary, BGPsec enhances BGP security by securing the AS path using digital signatures and private keys. It does not rely on IPsec tunnels for security1.
Reference: Cisco. (2021). Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies (SPCOR) v1.0. Cisco Learning Services.
Cisco. (2021). Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies (SPCOR) v1.1. Cisco Learning Network Store.
Cisco. (2021). BGPsec Overview. Link
Refer to the exhibit.

An engineer needs to implement this QoS policy on customer’s network due to ongoing slow network issues.
What will be the effect on the network when the engineer implements this configuration?
- A . Traffic that is identified in the ciscotest class map will be remarked from IP precedence 1 to DSCP AF11 when it enters the pos0/2/0/0 interface.
- B . Traffic that is identified in the ciscopolicy class map will be marked with IP precedence 1 when it enters the pos0/2/0/0 interface.
- C . Traffic that is identified in the ciscopolicy class map will be remarked from IP precedence 1 to DSCP AF11 when it exits the pos0/2/0/0 interface.
- D . Traffic that is identified in the ciscotest class map will be marked with IP precedence 1 when it exits the poso/2/0/0 interface.
A
Explanation:
The configuration applies a QoS policy to the pos0/2/0/0 interface, which affects traffic as it exits the interface. The policy map “ciscopolicy” references the class map “ciscotest”, where traffic matching the class map criteria will be remarked. The command set precedence 1 within the class map “ciscotest” indicates that the traffic will be remarked to IP precedence 1.
Therefore, the correct effect of this configuration is that traffic identified by the “ciscotest” class map will be remarked from its original IP precedence to IP precedence 1 when it exits the pos0/2/0/0 interface.
Reference: = This explanation is based on the QoS configuration practices as outlined in the Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies (SPCOR) course materials.
Refer to the exhibit.
![]()
What does the number 2 mean in the configuration?
- A . It dictates the number of sessions that will be open with the SNMP manager
- B . It represents the version of SNMP running.
- C . It indicates two SNMP managers are able to read and write with the agent using community string ciscotest.
- D . It is the numeric name of the ACL that contains the list of SNMP managers with access to the agent.
D
Explanation:
The number “2” in the SNMP server configuration “snmp-server community ciscotest ro 2” refers to the numeric name of the Access Control List (ACL) that contains the list of SNMP managers with access to the agent. In this context, “ro” stands for read-only access, meaning that SNMP managers can only read but not modify data on the device. The ACL identified by number “2” specifies which SNMP managers are authorized to access SNMP data on this device using the community string “ciscotest”.
Reference: Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies source documents or study guide.
The service provider is serving hosts with two different multicast streams from source X and source Y. Source X is multicast group 224.0.0.0/8, and source Y is multicast group 226.0.0.0/8. Multicast source X should send its stream through bidirectional RP address 10.20.1.1, and multicast source Y should send its stream through RP address 10.20.2.1.
Which configuration meets these requirements?
- A . Enable ip pim ssm default on RA and RB.
- B . Add ip pim bidir-enable in global mode on RB.
- C . Permit the source X and source Y IP addresses in the access list on RB.
- D . Set PIM sparse mode with a static RP address of 10.20.2.1 on RA and RC.
Refer to the exhibit.
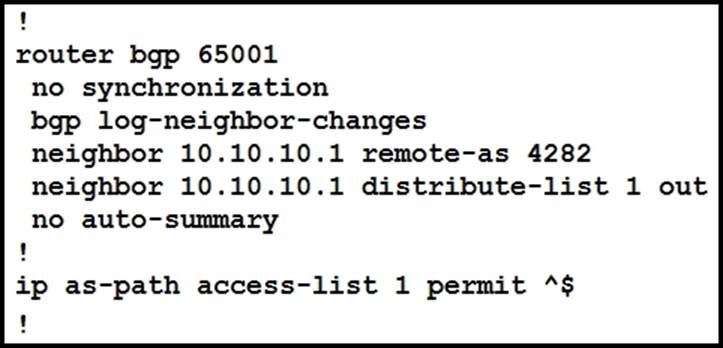
An engineer is reviewing the BGP configuration.
Which routes must be advertised to 10.10.10.1
- A . Local routes are permitted, and routes from other ASNs are denied.
- B . All routes whether local or from other ASNs are denied.
- C . Local routes are denied, and routes from other ASNs are permitted.
- D . All routes whether local or from other ASNs are permitted.
A
Explanation:
The configuration snippet shows a BGP router with AS number 65001. It has a neighbor at IP address 10.10.10.1 with remote AS number 4282, and there is an outbound distribute-list applied to this neighbor relationship (distribute-list 1 out).
The distribute list refers to access list 1, which permits any route with an AS path that starts with the local ASN (permit ^$). This means that only local routes will be advertised to the neighbor at IP address 10.10.10.1; routes from other Autonomous Systems (ASNs) will not be advertised because they would have an AS path starting with another ASN.
Reference: Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies source documents or study guide.
Drag and drop the 5G RAN architecture types from the bottom next to the corresponding topologies on the right.
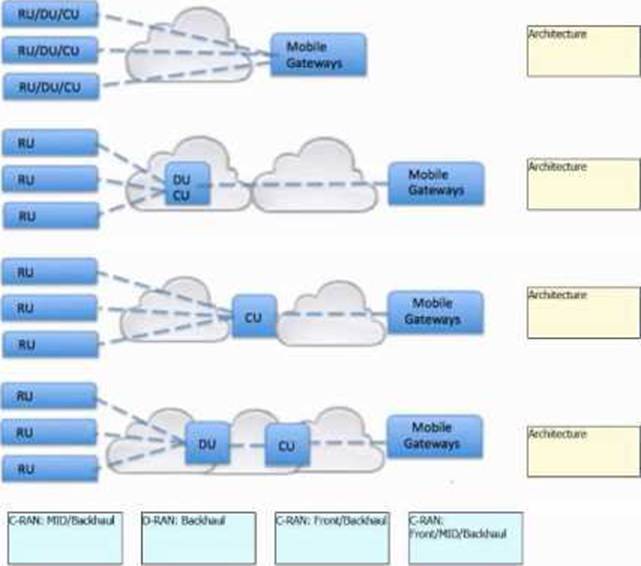
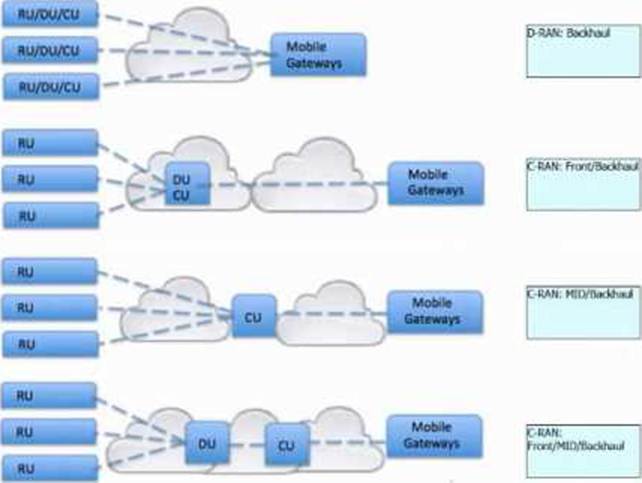
Refer to the exhibit.
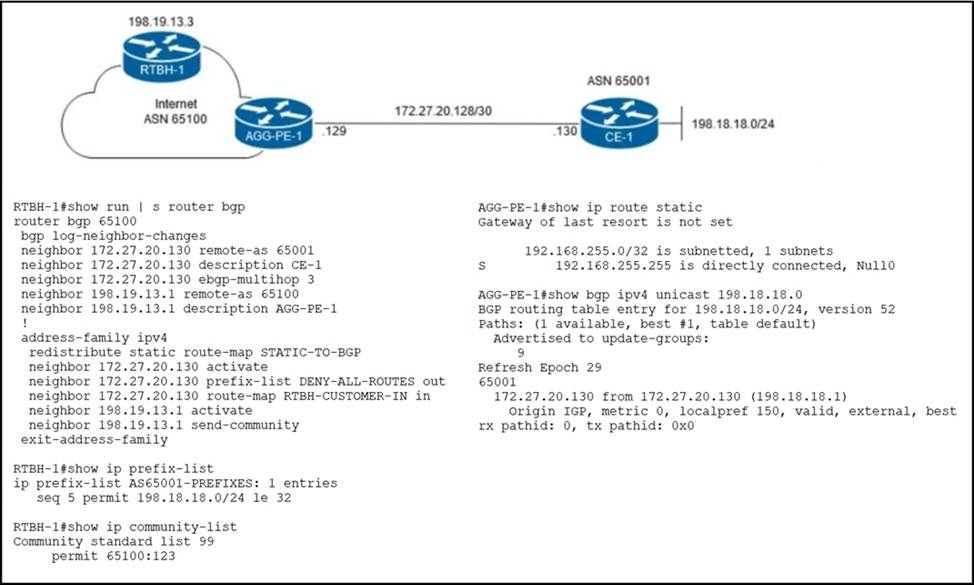
ISP ASN 65100 provides Internet services to router CE-1 and receives customer prefix 198.18.18.0/24 via eBGP. An administrator for the ISP is now provisioning RTBH services to provide on-demand data-plane security for the customer’s IP space.
Which route-map configuration must the administrator apply to router RTBH-1 to complete the implementation of RTBH services to CE-1?
- A . route-map RTBH-CUSTOMER-IN permit 10
description AS65001
match ip address prefix-list AS65001-PREFIXES
match community 99
set local-preference 200
set community no-export additive
set ip next-hop 192.168.255.255
route-map RTBH-CUSTOMER-IN deny 65535
description DEFAULT DENY - B . route-map RTBH-CUSTOMER-IN permit 10
description AS65001
match ip address prefix-list AS65001-PREFIXES
match community 99
set local-preference 200
set community local-as additive
set ip next-hop 192.168.255.255
route-map RTBH-CUSTOMER-IN deny 65535
description DEFAULT DENY - C . route-map RTBH-CUSTOMER-IN permit 10
description AS65001
match ip address prefix-list AS65001-PREFIXES
match community 99
set local-preference 200
set community no-advertise additive
set ip next-hop local-address
route-map RTBH-CUSTOMER-IN deny 65535
description DEFAULT DENY - D . route-map RTBH-CUSTOMER-IN permit 10
description AS65001
match ip address prefix-list AS65001-PREFIXES
match community 99
set local-preference 200
set community no-advertise additive
set ip next-hop 192.168.255.255
route-map RTBH-CUSTOMER-IN deny 65535
description DEFAULT DENY
Refer to the exhibit.

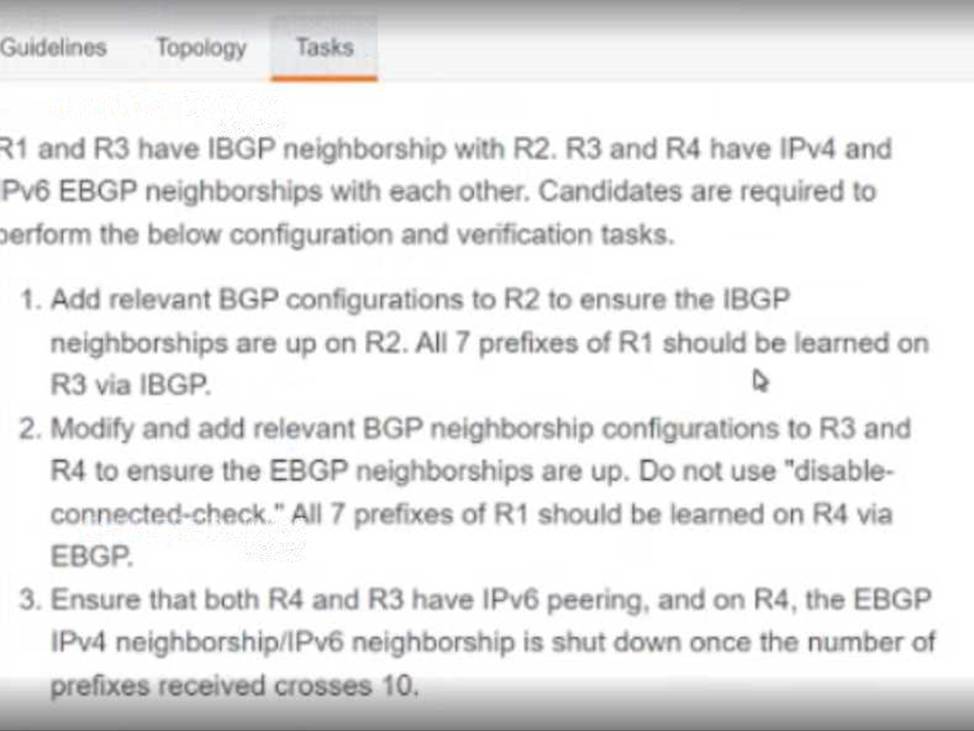
The enterprise is running BGP between sites to provide connectivity to users across the company’s geographic regions. A network engineer must update the configuration so that the operations team can confirm that BGP prefixes that are received on each router originated from the correct autonomous system.
Which configuration must the engineer apply?
- A . bgp bestpath prefix-validate disable
- B . bgp rpki server tcp 192.168.1.2 port 1029 refresh 500
- C . bgp bestpath prefix-validate allow-invalid
- D . bgp synchronization
DRAG DROP
Drag and drop the functions from the path computation element protocol roles on the right.
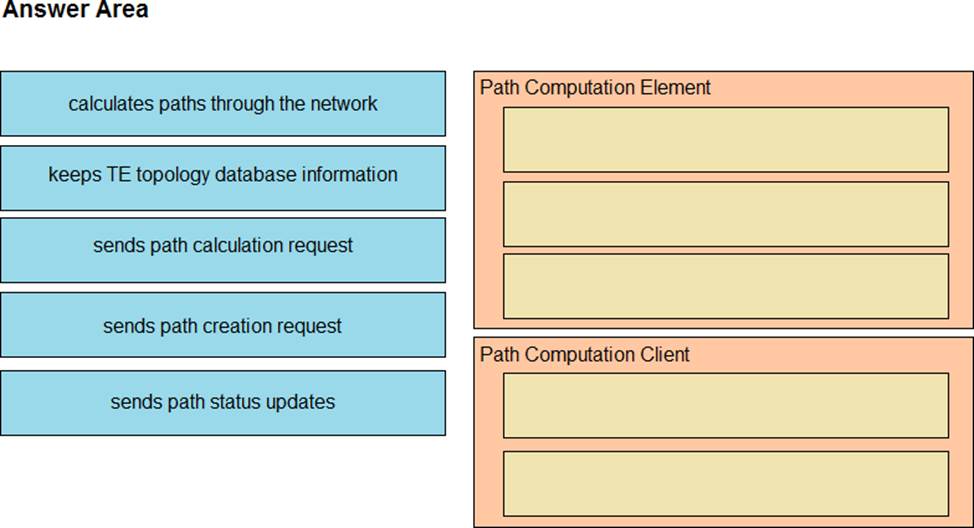

Explanation:

SIMULATION
Simulation 8
Refer to the exhibit.
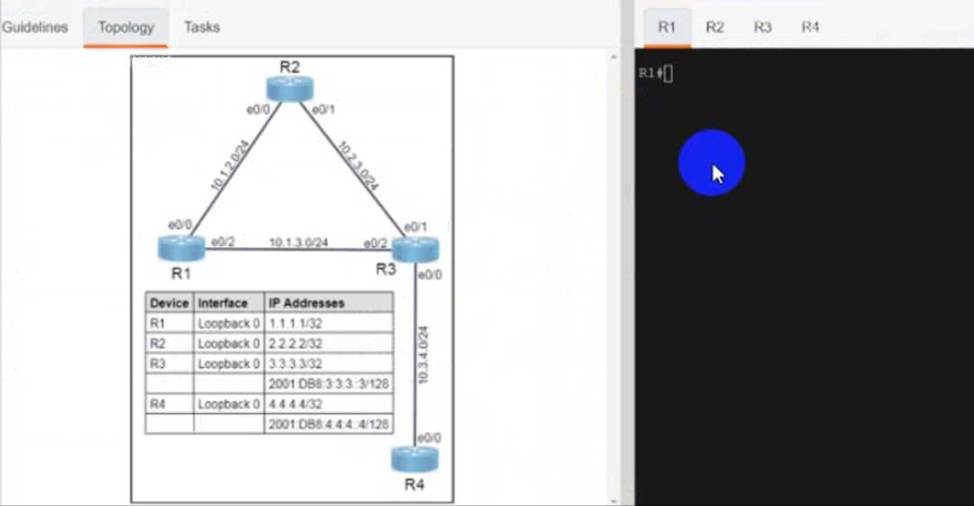

R3
router bgp 65413
add ipv4
nei 2.2.2.2 allowas-in
nei 4.4.4.4 allowas-in
add ipv6
nei 2001:db8:4:4:4::4 allowas-in
end
copy run start
=======================
R2
router bgp 65413
nei 1.1.1.1 as-override
nei 3.3.3.3 as-override
end
copy run start
=======================
R3
router bgp 65413
nei 10.3.4.2 remot 65412
nei 2001:db8:3:4::2 remot 65412
nei 2001:db8:4:4:4:4::4 remot 65412
nei 2001:db8:4:4:4:4::4 ebgp-multihop 10
add ip4
nei 10.3.4.2 act
ex
add ipv6
nei 2001:db8:4:4:4:4::4 activate
nei 2001:db8:4:4:4:4::4 ebgp-multihop 10
nei 2001:db8:3:4::2 act
end
copy run start
===================
R4
router bgp 65412
nei 10.3.4.1 remot 65413
nei 2001:db8:3:3:3:3::3 remot 65413
nei 2001:db8:3:3:3:3::3 ebgp-multihop 10
nei 2001:db8:3:4::1 remot 65413
add ipv4
nei 10.3.4.1 remot act
nei 10.3.4.1 prefix-limit 10
add ipv6
nei 2001:db8:3:3:3:3::3 activate
nei 2001:db8:3:3:3:3::3 ebgp-multihop 10
nei 2001:db8:3:3:3:3::3 prefix-limit 10
nei 2001:db8:3:4::1 activate
nei 2001:db8:3:4::1 prefix-limit 10
end
copy run start
