Practice Free 350-501 Exam Online Questions
Which Cisco software OS uses monolithic architecture?
- A . NX-OS
- B . IOS XE
- C . IOS XR
- D . IOS
D
Explanation:
Cisco Internetwork Operating System (IOS) is the software used on most Cisco Systems routers and current Cisco network switches. IOS is a package of routing, switching, internetworking and telecommunications functions integrated into a multitasking operating system. IOS uses a monolithic architecture, meaning that all processes run in a single address space, making it a single-image system.
Which Cisco software OS uses monolithic architecture?
- A . NX-OS
- B . IOS XE
- C . IOS XR
- D . IOS
D
Explanation:
Cisco Internetwork Operating System (IOS) is the software used on most Cisco Systems routers and current Cisco network switches. IOS is a package of routing, switching, internetworking and telecommunications functions integrated into a multitasking operating system. IOS uses a monolithic architecture, meaning that all processes run in a single address space, making it a single-image system.
An engineer must implement QoS to prioritize traffic that requires better service throughout the network. The engineer started by configuring a class map to identify the high-priority traffic.
Which additional tasks must the engineer perform to implement the new QoS policy?
- A . Attach the class map to a policy map that sets the minimum bandwidth allocated to the classified traffic and designates the action to be taken on the traffic.
- B . Attach the class map to a policy map that designates the action to be taken on the classified traffic and then attach the policy map to an interface using a service policy.
- C . Attach the class map to a policy map within a VRF to segregate the high-priority traffic and then attach the policy map to an interface in another VRF.
- D . Create a route map to manipulate the routes that are entered into the routing table and then attach the route map to an interface using a service policy.
Refer to the exhibit.
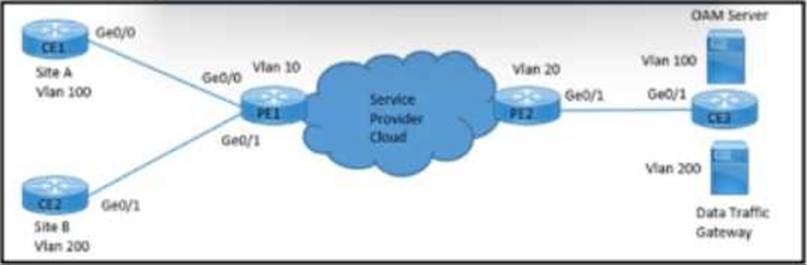
A network engineer with an employee ID: 5086:72:817 is configuring a connection to manage CE1 from the OAM server on VLAN 100. PE1 must push S-VLAN tag 10 toward PE2 while forwarding traffic from CE1 to the OAM server. PE1 must push S-VLAN tag 20 toward PE2 while forwarding traffic from CE2 to the data traffic gateway.
Which configuration must the engineer implement on PE2?
- A . interface GigE0/1
encapsulation dot1q 100
rewrite ingress tag pop 10
rewrite ingress tag push 20 - B . interface Ge0/0
encapsulation dot1q 100
rewrite ingress tag push dot1q 10 symmetric
interface Ge0/1
encapsulation dot1q 200
rewrite ingress tag push dot1q 20 symmetric - C . interface GigE0/1
encapsulation dot1q 10
rewrite ingress tag push dot1q 10 symmetric
Interface Ge0/0
encapsulation dot1q 20
rewrite ingress tag push dot1q 20 symmetric - D . Interface Ge0/1
encapsulation dot1q 100
Refer to the exhibit.
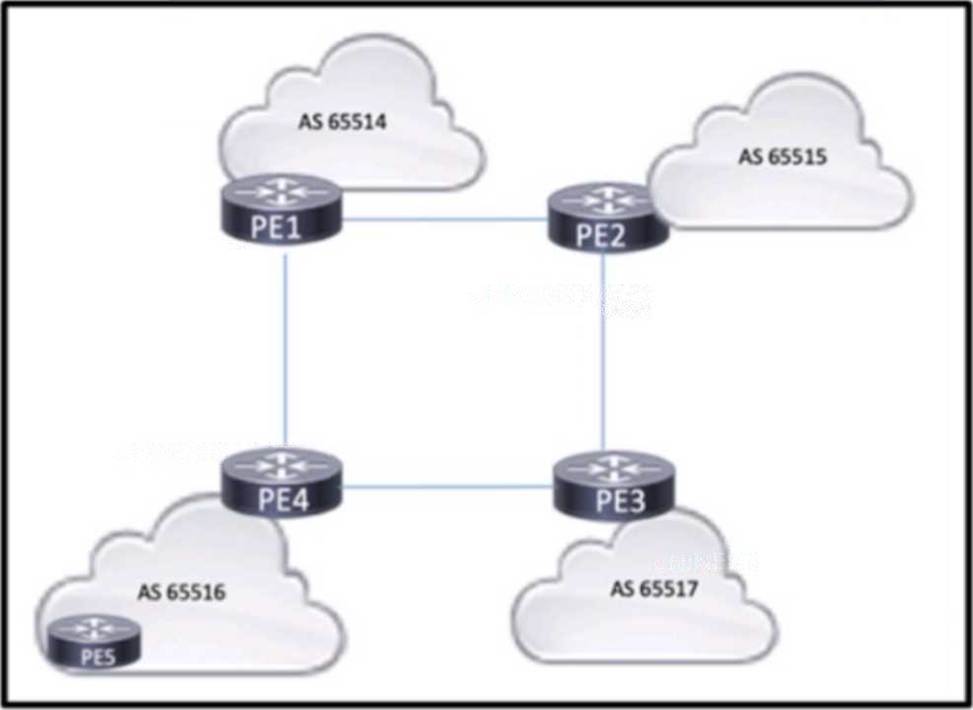
Four midsize service providers provide access to different customers that use Layer 3 VPN services to enable communication across geographic regions. The service providers are connected as shown in the exhibit, and the PEs have established eBGP relationships. PE4 has an IBGP relationship with PE5. The routes that PE4 learns from PE5 must reach the other PE routers, but they are absent from the routing tables on the other PES.
Which action should the engineers take to correct the problem?
- A . Configure a peering between all five Pes.
- B . Disable BGP synchronization on PE4.
- C . Enable BOP IPv4 unicast on PE4 and PE5
- D . Advertise the route targets for PE5 to the other PEs
D
Explanation:
The absence of routes learned by PE4 from PE5 in other PE routers’ routing tables is likely due to missing route target configurations. Route targets are crucial for importing and exporting VPN routes between VRFs in MPLS Layer 3 VPNs.
Option D is correct because advertising the route targets for PE5 to the other PEs will allow them to import routes from PE5 into their respective VRFs, facilitating communication across the Layer 3 VPN.
Reference: =
Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies (SPCOR) source book and study guide.
Refer to the exhibit.
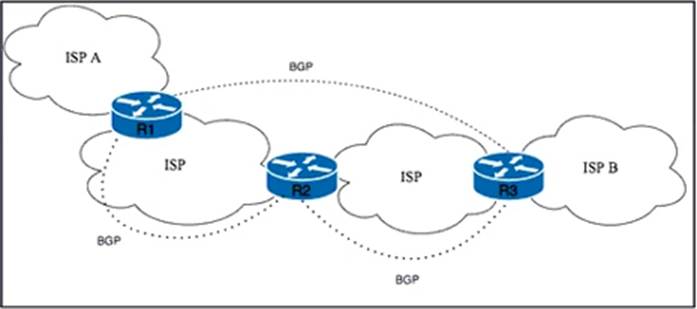
Tier 1 ISP A is connected to small Tier 3 ISP B. The EBGP routing protocol is used for route exchange. The networking team at ISP A noticed the flapping of BGP sessions with ISP B. The team decides to Improve stability on the network by suppressing the subnet for 30 minutes when a session begins to flap.
Which action must the team perform to meet this goal?
- A . Implement a BGP route-penalty timer on ISP A router R1 with the bgp penalty-timer 30 250 750 15 command.
- B . Implement BGP route dampening on ISP A router R1 with the bgp dampening 15 700 1500 30 command.
- C . Implement BGP route suppression on ISP A router R2 with the bgp suppression 30 600 1200 30 command.
- D . Implement a BGP route withdraw-delay timer on ISP B router R3 with the bgp withdraw-delay 30 15 90 30 command.
B
Explanation:
To address the issue of BGP session flapping between ISP A and ISP B, the networking team at ISP A should implement BGP route dampening. This feature helps stabilize the network by suppressing the advertisement of flapping routes. The command bgp dampening 15 700 1500 30 will set the parameters for route dampening, where routes that flap will be suppressed for 30 minutes. This action will prevent the constant advertisement and withdrawal of unstable routes, thus improving the stability of the network.
Reference: = For further details on BGP route dampening and its configuration, the Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies (SPCOR) course materials and Cisco’s official documentation provide comprehensive guidance.
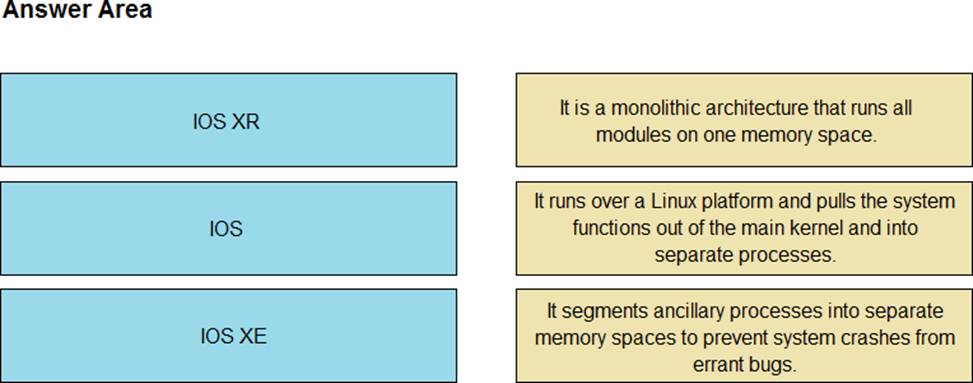
DRAG DROP
Drag and drop the OSs from the left onto the correct deceptions on the right.
Refer to the exhibit:

Export statistics received do not include the BGP next hop.
Which statement about the NetFlow export statistics is true?
- A . Only the origin AS of the source router will be included in the export statistics.
- B . Loopback 0 must be participating in BGP for it to be included in the export statistics.
- C . The origin AS and the peer-as will be included in the export statistics.
- D . To include the BGP next hop in the export statistics, those keywords must be included with the version 9 entry.
D
Explanation:
In NetFlow export statistics, the BGP next hop information is not included by default. To include the BGP next hop in the export statistics, specific keywords related to BGP next hop must be configured with the version 9 NetFlow entry. This configuration allows for the measurement of network traffic on a per-BGP next hop basis, which is essential for detailed traffic analysis and accounting1.
Reference: Configuring NetFlow BGP Next Hop Support for Accounting and Analysis – Cisco Systems1.
Refer to the exhibit.
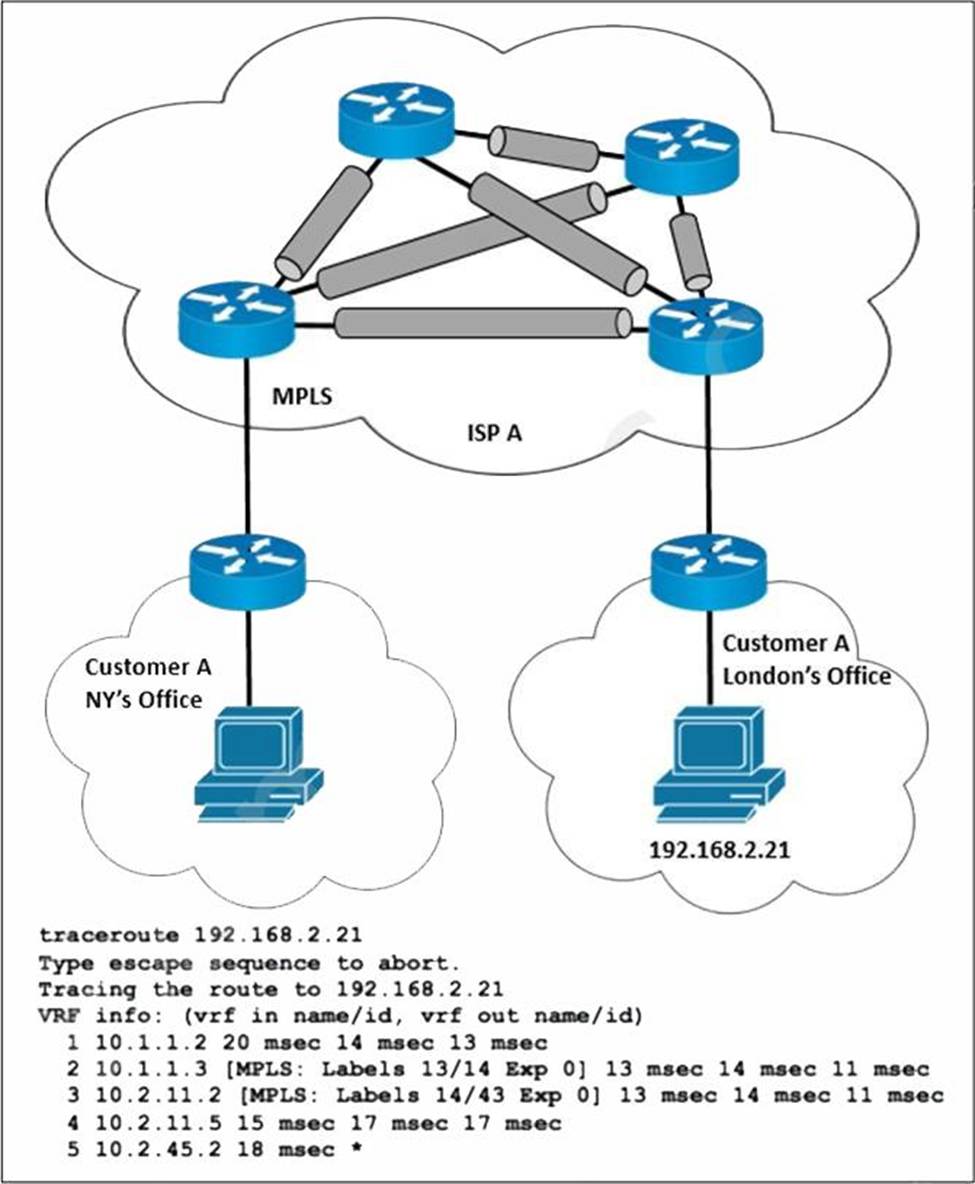
ISP A provides MPLS L3VPN service to customer A with BGP as the external routing protocol. Customer A has just opened a new branch office in London and requested the service provider to implement lossless service between its two offices. The LDP is enabled over the MPLS backbone and label exchange is working normally.
Which action must the ISP engineering team take to enable the service?
- A . Configure LDP and redistribute the route from EIGRP.
- B . Configure BGP address family VPNv4.
- C . Configure IGP and redistribute the route from BGP.
- D . Configure IGP LDP synchronization
Refer to the exhibit.
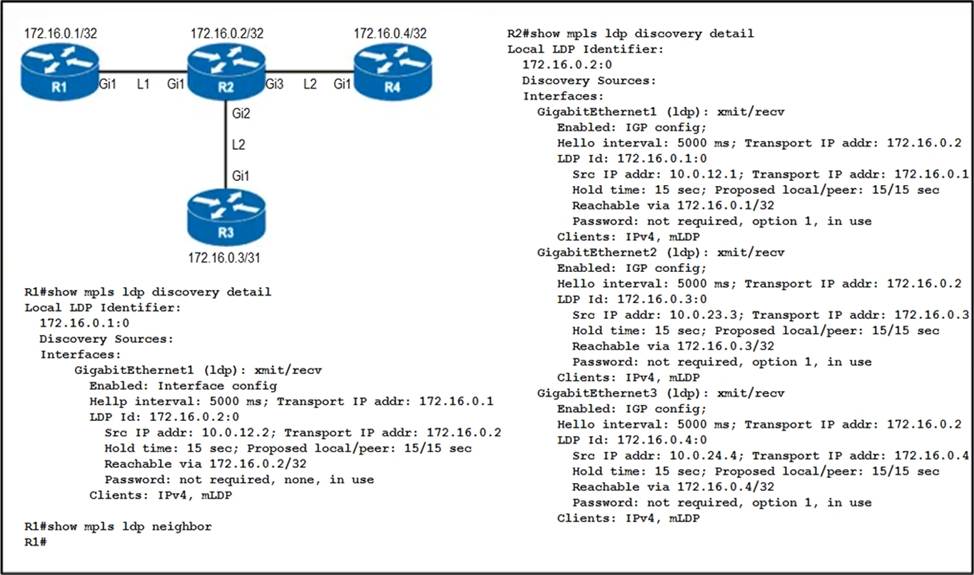
An engineer began to configure LDP between R1 and R2, but R1 and R2 cannot yet establish an LDP TCP connection.
Which additional task must be completed to finish the implementation?
- A . Configure the mpls Idp neighbor 172.16.0.1 password command on R1
- B . Configure the mpls Idp neighbor 10.0.12.1 password command on R1
- C . Configure the no mpls Idp password option 1 command on R2
- D . Configure the no mpls Idp password option 1 command on R1
C
Explanation:
The issue here is that R1 and R2 cannot yet establish an LDP TCP connection. From the exhibit, it’s clear that the password is not required as it states “Password: not required, none, in use”. So, option C “Configure the no mpls Idp password option 1 command on R2” would be the correct answer to allow the establishment of an LDP TCP connection without requiring a password. This aligns with Cisco’s guidelines on configuring MPLS LDP where passwords might not be necessary for establishing connections between routers.
Reference: Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies (SPCOR) – Cisco SPCOR
