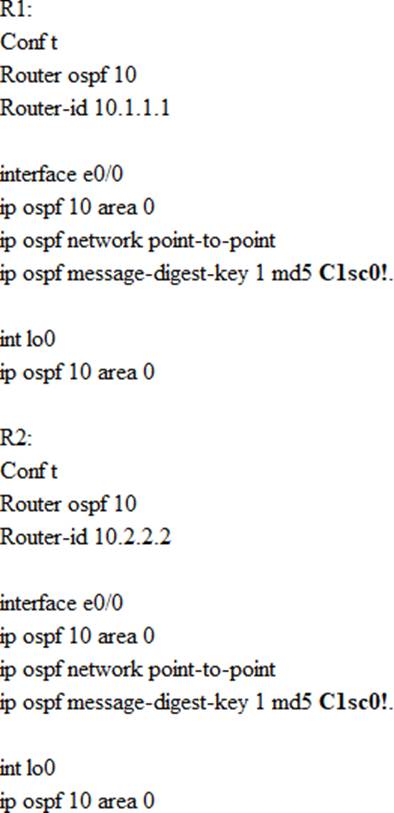
Practice Free 350-501 Exam Online Questions
Refer to the exhibit.
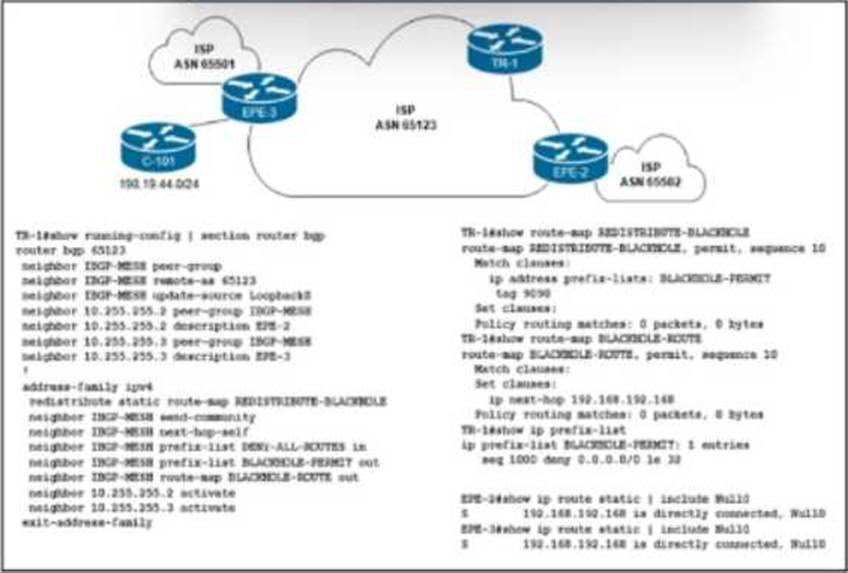
Customer C-101 in ASN 65123 requested that the ISP blackholes a host route 198.19.44.195, to which the customer is receiving a significant amount of malicious traffic.
Which configuration must the network engineer implement on the trigger router TR-1 to fulfill the request without affecting other IP destinations in the customer’s block?
- A . configure terminal
ip prefix-list BLACKHOLE-PERMIT seq 5 permit 198.19.44.0/24 le 32
ip route 198.19.44.195 255.255.255.255 Null0 tag 9090
end - B . configure terminal
ip prefix-list BLACKHOLE-PERMIT seq 5 permit 198.19.44.195/32
ip route 198.19.44.195 255.255.255.255 Null0 tag 9090
end - C . configure terminal
ip prefix-list BLACKHOLE-PERMIT permit 198.19.44.0/24 le 32
ip route 198.19.44.195 255.255.255.255 Null0 tag 9090 end - D . Configure terminal
Refer to the exhibit.
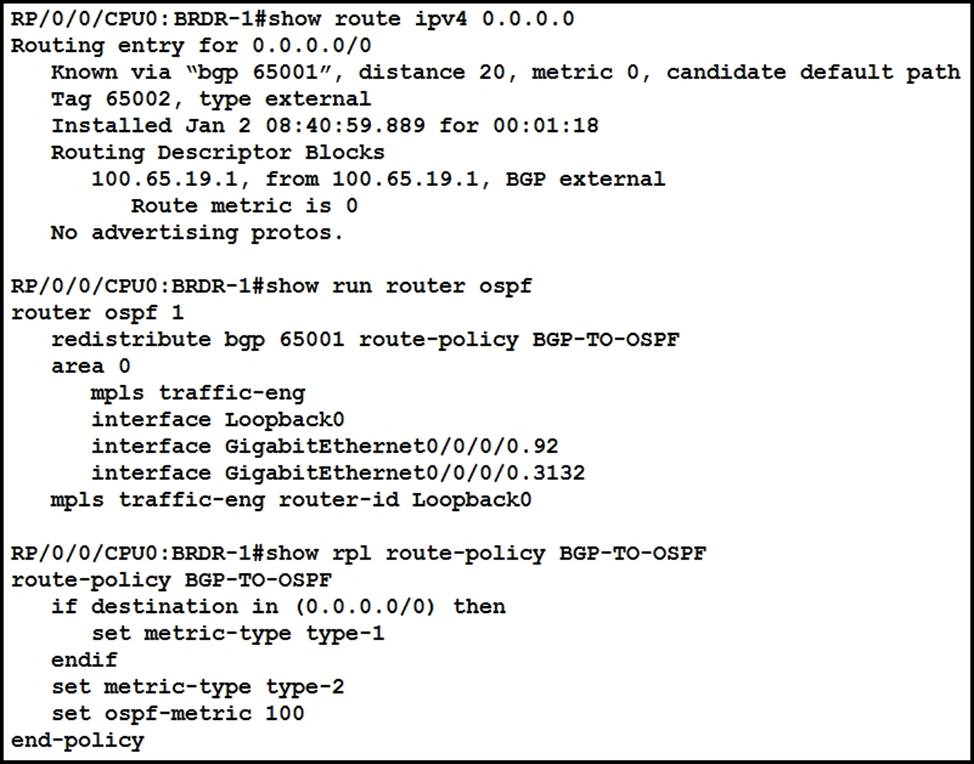
Router BRDR-1 is configured to receive the 0.0.0.0/0 and 172.17.1.0/24 network via BGP and advertise then into OSPF area 0. An engineer has noticed that the OSPF domain is receiving only the 172.17.1.0/24 route and default router 0.0.0.0/0 is still missing.
Which configuration must an engineer apply to resolve this problem?
- A . router ospf 1
default-information originate always
end - B . router ospf 1
redistribute bgp 65001 metric 100 route-policy BGP-TO-OSPF
end - C . router ospf 1
default-metric 100
end - D . router ospf 1
default-information originate
end
A
Explanation:
The issue of the OSPF domain receiving only the 172.17.1.0/24 route and not the default route 0.0.0.0/0 can be resolved by configuring OSPF to propagate default routes.
Let’s take a look at the options:
Option A: The configuration includes the following commands:
router ospf 1
default-information originate
end
This configuration generates a default route into the OSPF domain, which is missing in this scenario.
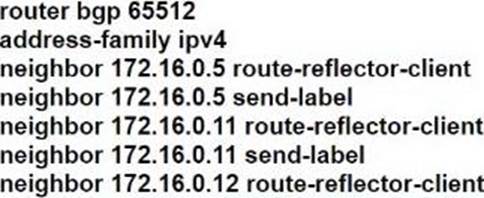
Refer to the exhibit.
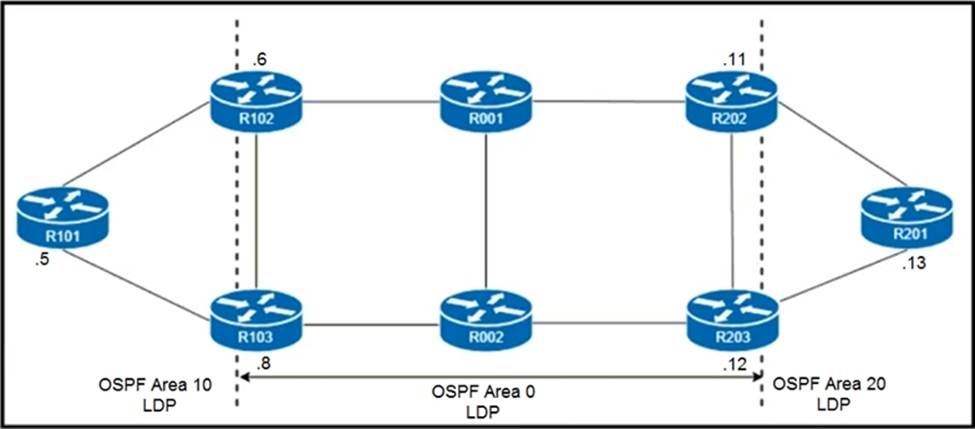
R101 is peering with R102 and R103, and R201 is peering with R202 and R203 using iBGP Labeled Unicast address families. The OSPF area 0 border routers are in a full iBGP Labeled Unicast mesh, and VPNv4 routes are exchanged directly between PE routers R101 and R201 through iBGP.
Which address family-level configuration must be applied on ABR R102 on ABR R102 to support a Unified MPLS routing architecture with partitioned IGP domains?
A)
B)

C)

D)

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
A
Explanation:
In a Unified MPLS routing architecture with partitioned IGP domains, it is essential to ensure that the iBGP Labeled Unicast address families are correctly configured to facilitate the exchange of VPNv4 routes directly between PE routers. In this case, ABR R102 should be configured with the address family-level configuration depicted in Option A to support this architecture. This configuration ensures that R101 can peer with both R102 and R103, and similarly, R201 can peer with R202 and R203 using iBGP Labeled Unicast address families.
Reference: = Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies
Refer to the exhibit.
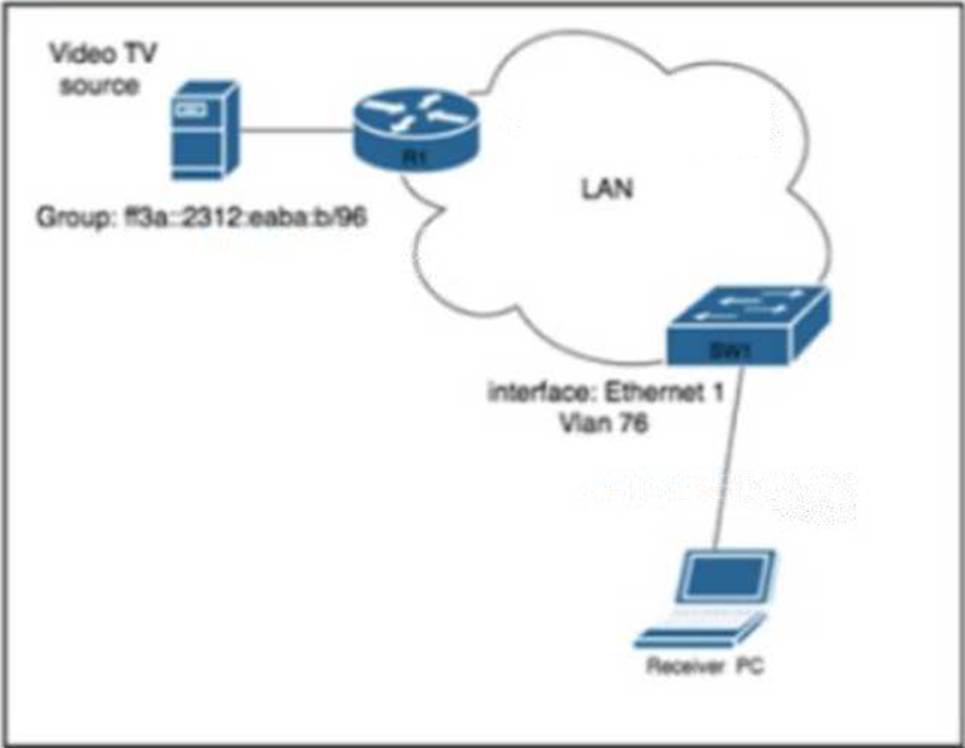
A network engineer working for a telecommunication company with an employee ID: 4602:62:646 is configuring security controls for the IPv6 multicast group, which is used for video TV. The solution from the engineer should reduce network usage and minimize the leave latency for the user that is connected to VLAN 76.
Which two configurations meet this goal? (Choose two.)
A)
![]()
B)
![]()
C)
![]()
D)
![]()
E)
![]()
- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
- E . Option E
A, C
Explanation:
To reduce network usage and minimize leave latency for users connected to VLAN 76, the configurations should focus on efficient multicast traffic management.
Option A likely involves enabling IPv6 MLD snooping, which restricts multicast traffic to only the ports that have members interested in receiving the traffic, thus reducing unnecessary network usage.
Option C might include configuring fast-leave processing, which allows the switch to immediately stop forwarding multicast traffic to a port when the last member of a multicast group leaves, reducing leave latency.
Reference: = Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies (SPCOR)
A mid-size service provider uses L2VPN as its standard for connectivity between offices. A small company wants the service provider to connect the company’s two sites across the service provider core. To meet service requirements, the service provider must extend the Layer 2 domain between the company’s two locations.
Which configuration must the engineer apply to implement an attachment circuit between the two sites using a VLAN tag of 12?
- A . interface TenGigE0/0/0/1.0 12transport
encapsulation dot1q 12 - B . interface TenGigE0/0/0/1.0 12transport
encapsulation dot1q 12
rewrite ingress tag push dot1q 21 symmetric - C . interface TenGigE0/0/0/1.0 12transport
encapsulation dot1q 12
rewrite ingress tag pop 13 - D . interface TenGigE0/0/0/1.0 12transport
encapsulation dot1q 12
rewrite ingress tag translate 1-to-1 dot1q 2
Refer to the exhibit.
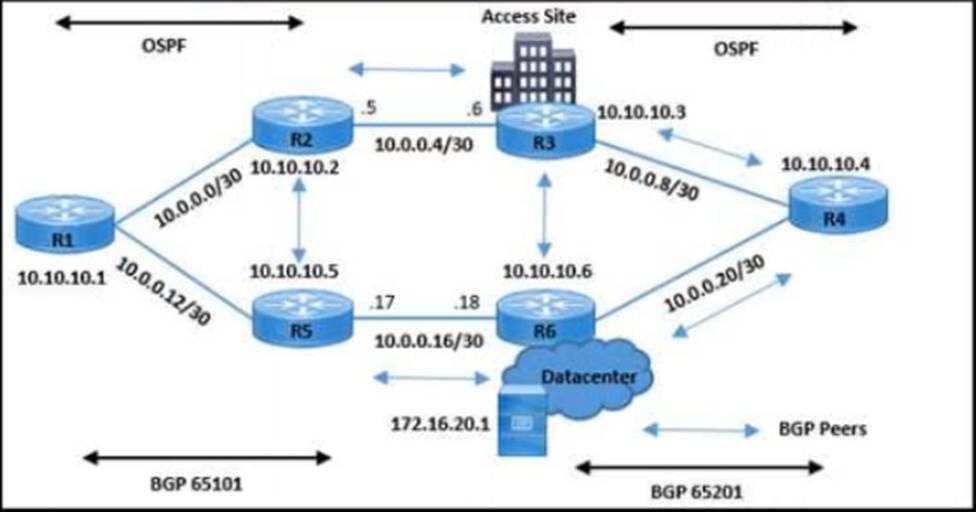
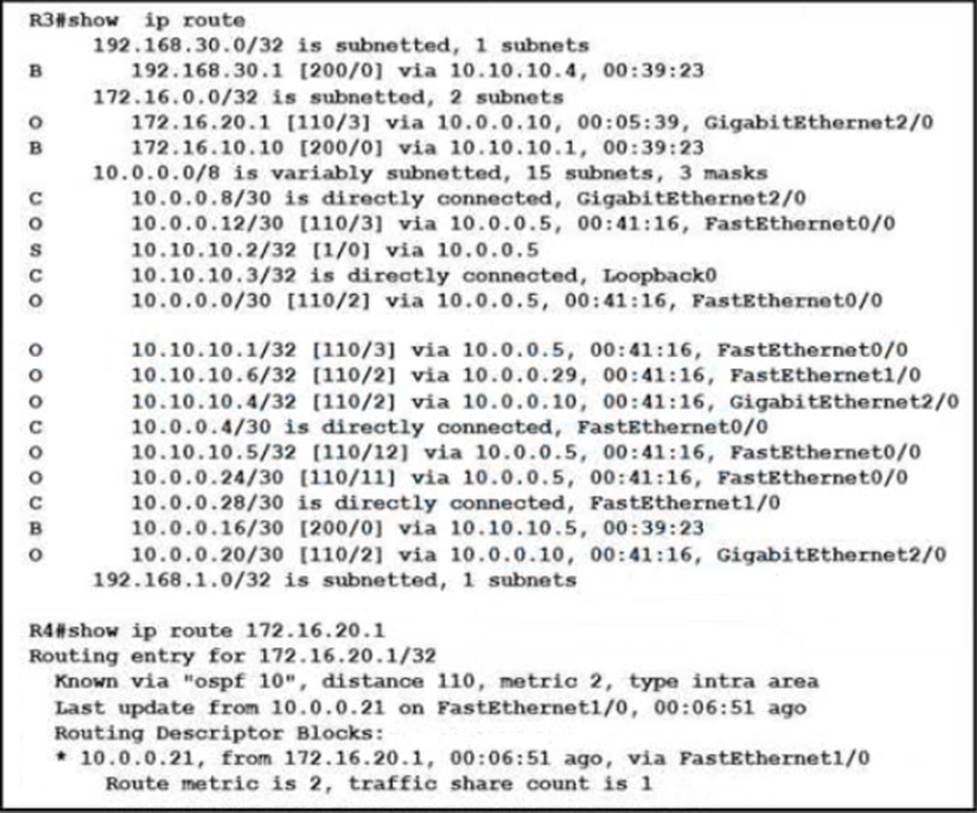
The network operations team reported that the access site that is connected to R3 is not connecting to the application server in the data center and that all packets that are sent from the application server to the access site are dropped. The team verified that OSPF and BGP peerings are up in BGP AS 65101 and BGP AS 65201. R4 is expected to receive traffic from the application server route via OSPF.
Which action resolves this issue?
- A . Remove the route-map on R4 when advertising 172.16.20.1 in BGP to R3.
- B . Advertise application server 172.16.20.1 in the OSPF routing table on R6.
- C . Allow 172.16.20.1 in the BGP advertisement on R3 in the route-map.
- D . Add the next-hop-self command on R6 to enable R3 iBGP peering.
C
Explanation:
The issue described involves packets being dropped when sent from the application server to the access site. Since OSPF and BGP peerings are confirmed to be operational, the problem likely lies within the route advertisement. Allowing 172.16.20.1 in the BGP advertisement on R3 by adjusting the route-map will likely resolve the issue, ensuring that traffic destined for 172.16.20.1 is not being inadvertently filtered or blocked.
Reference: Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies (SPCOR) course provides insights into configuring, verifying, troubleshooting, and optimizing Service Provider IP network infrastructures, which includes understanding and implementing BGP routing and route maps1.
The official Cisco certification exam overview for SPCOR, which includes topics on BGP routing and route maps, can also serve as a reference
What is the main purpose of EVPN?
- A . to provide simplified and flexible underlay connectivity for private VPN services
- B . to provide scalable, interoperable multitenancy in data center and cloud networks
- C . to provide advanced security features for IoT devices
- D . to provide application-aware networking capabilities in a cloud environment
A network administrator is planning a new network with a segment-routing architecture using a distributed control plane.
How is routing information distributed on such a network?
- A . Each segment is signaled by a compatible routing protocol, and each segment makes its own steering decisions based on SR policy.
- B . Each segment is signaled by MPLS, and each segment makes steering decisions based on the routing policy pushed by BGP.
- C . Each segment is signaled by an SR controller, but each segment makes its own steering decisions based on SR policy.
- D . Each segment is signaled by an SR controller that makes the steering decisions for each node.
A network operator with an employee ID 4531 26:504 must implement a PIM-SSM multicast configuration on the customer’s network so that users in different domains are able to access and stream live traffic. The IGMP version must be enabled to support the SSM implementation.
Which action must the engineer perform on R1 to complete the SSM implementation?
A)

B)

C)

D)

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
C
Explanation:
To implement a PIM-SSM (Protocol Independent Multicast – Source Specific Multicast) configuration for streaming live traffic across different domains, the network operator must ensure that IGMPv3 (Internet Group Management Protocol version 3) is enabled on R1. IGMPv3 is required for SSM because it allows the receiver to specify the source IP address of the desired traffic, which is a key feature of SSM. The operator would configure IGMPv3 on the interfaces that connect to the users who will be accessing the multicast stream. Additionally, PIM-SSM must be enabled on the router, and the multicast sources and groups must be properly defined.
Reference: The explanation is based on the concepts outlined in the Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies (SPCOR) course
Enable OSPF MD5 Authentication between both routers at the interface level with password C1sc0!.