Practice Free 350-501 Exam Online Questions
Refer to the exhibit.

Router 4 is added to the network and must be in the same area as router 1.
Which NET should the engineer assign?
- A . 49.0001.0000.0000.0004.00
- B . 49.0111.0000.0000.0001.00
- C . 49.0011.0000.0000.0003.00
- D . 49.0011.0000.0000.0002.00
B
Explanation:
Router 4 must be in the same area as Router 1, so it should have the same area address which is “49.0111”. The system ID can be different to uniquely identify the router in that area, but since there is no option with a different system ID and the same area address, option B is correct as it has both the same area address and system ID as Router 1.
Reference: = Cisco
Refer to the exhibit:

A network engineer is implementing a BGP routing policy.
Which effect of this configuration is true?
- A . All traffic that matches acl10 is allowed without any change to its local-preference
- B . All traffic that matches acl10 is dropped without any change to its local-preference
- C . If traffic matches acl10, it is allowed and its local-preference is set to 300
- D . All traffic is assigned a local-preference of 30O regardless of its destination
C
Explanation:
The configuration in the exhibit shows a route policy named “ciscotest”. According to this policy, if the destination is in acl10, then the traffic will pass without any changes. However, if the destination is not in acl10 (else condition), then the local preference will be set to 300 before it passes through. This means option C is correct as it states that if traffic matches acl10, it’s allowed without any change to its local-preference; otherwise (if not matching acl10), its local-preference is set to 300.
BGP has been implemented on a IOS XR router.
Which configuration sends BGP IPv4 labels to build inter-domain LSPs?
- A . router bgp 65515
address-family ipv4 unicast
neighbor 172.16.70.23 send-community extended - B . router bgp 65515
no bgp default ipv4-unicast - C . router bgp 65515
address-family ipv4 unicast
neighbor 172.16.70.23 send-community - D . router bgp 65515
neighbor 172.16.70.23
address-family ipv4 labeled-unicast
D
Explanation:
In Cisco IOS XR, to send BGP IPv4 labels to build inter-domain Label Switched Paths (LSPs), the configuration command used is router bgp 65515 neighbor 172.16.70.23 address-family ipv4 labeled-unicast. This command specifies that the router should use the BGP labeled unicast address family for the specified neighbor, which enables the exchange of label information along with the IPv4 routing information, facilitating MPLS LSP creation for inter-domain traffic.
Reference: Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies (SPCOR) training materials1.
Which module refers to the network automation using Ansible?
- A . the iosxr_system module to collect facts from remote devices
- B . the iosxr_user module to manage banners for users in the local database
- C . the losxr_logging module to run debugging for seventy levels 2 to 5
- D . the iosxr_command module to issue run commands on remote devices
D
Explanation:
The iosxr_command module in Ansible is used to issue commands on remote devices running Cisco IOS XR. This module allows network administrators to execute operational commands on Cisco routers and switches, which is essential for tasks such as retrieving information or applying configuration changes. It is a part of network automation using Ansible, which simplifies the management of network devices by automating repetitive tasks.
Reference: Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies (SPCOR) course and study guide
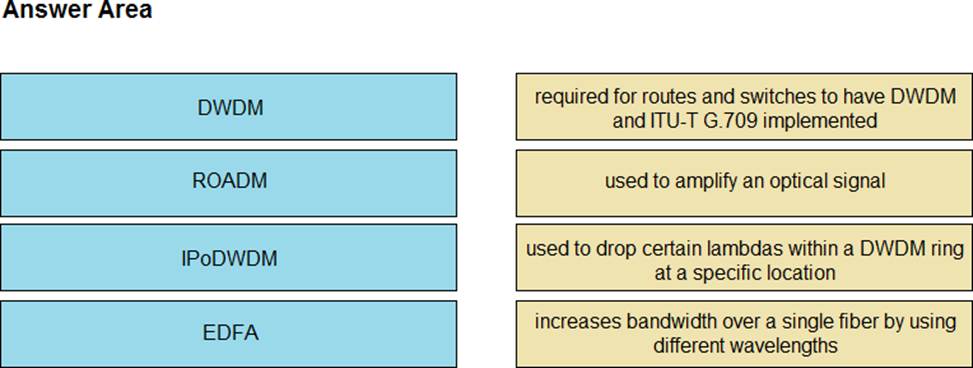
DRAG DROP
Drag and drop the technologies from the left onto the correct definitions on the right.
Refer to the exhibit.

An engineer is configuring multitiopology IS-IS for IPv6 on router R1.
Which additional configuration must be applied to complete the task?
- A . R1# configure terminal
R1(config)# router isis area2
R1(config-router)# address-family ipv6
R1(config-router-af)# multi-topology - B . R1# configure terminal
R1(config)# router isis area1
R1(config-router)# metric-style wide level-2
R1(config-router)# address-family ipv6
R1(config-router-af)# multi-topology - C . R1# configure terminal
R1(config)# router isis area2
R1(config-router)# metric-style wide
R1(config-router)# address-family ipv6
R1(config-router-af)# multi topology - D . R1# configure terminal
R1(config)# router isis area1
R1(config-router)# metric-style wide level-1
R1(config-router)# address-family ipv6
R1(config-router-af)# multi topology
A
Explanation:
To configure multi-topology IS-IS for IPv6, the router must be configured with the ipv6 router isis command under the interface configuration mode. This command enables IS-IS for IPv6 on the interface. The ipv6 router isis command is used to enable IS-IS for IPv6 on an interface. The multi-topology keyword specifies that the interface will participate in multiple topologies. The level-1 and level-2 keywords specify the IS-IS levels for which the interface will participate. In this case, we want the interface to participate in both Level 1 and Level 2 topologies, so we use both keywords.
Refer to the exhibit.
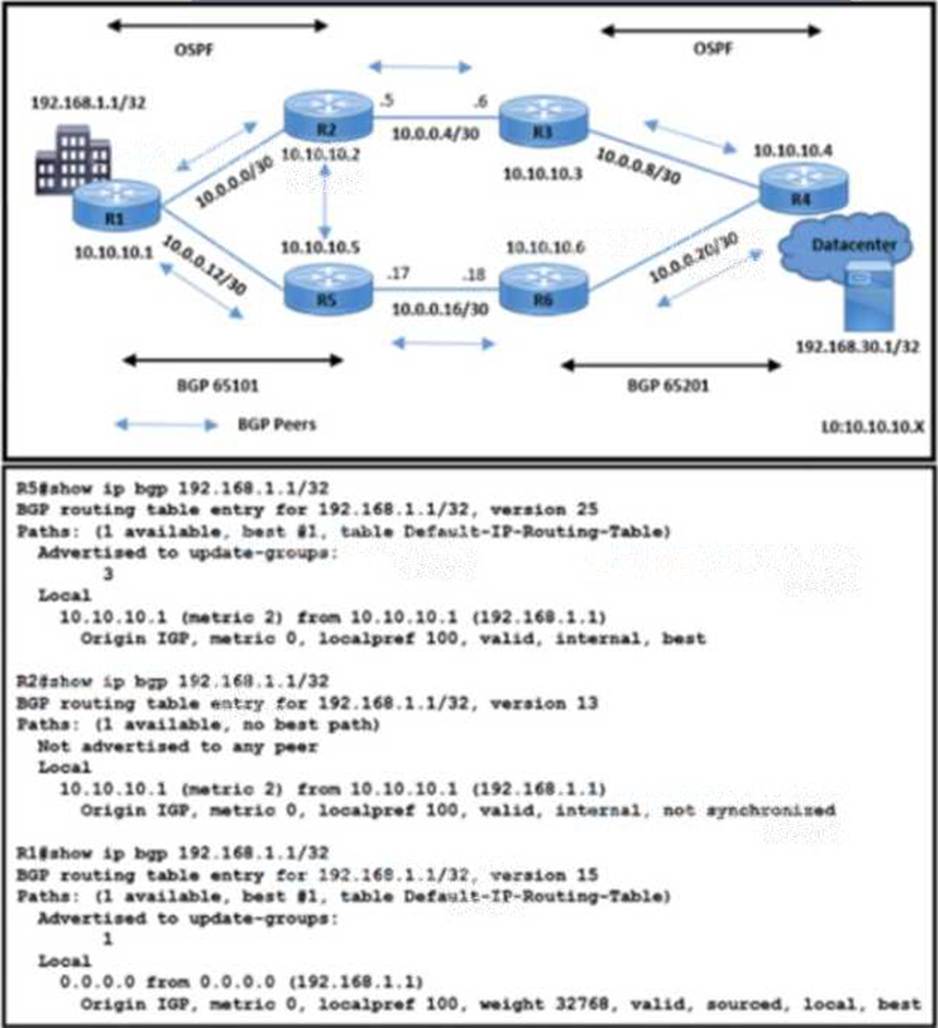
All BGP peering in AS 65101 and 65201 is enabled. The operations team is told that traffic destined to 192.168.1.1/32 from R4 does not use the path R3-R2-R1 as expected. An engineer debugs the issue and determines that 192.168.1.1/32 is advertised in the BGP routing table on R1.
Which action resolves the issue?
- A . Enable no synchronization on R2 m AS65101.
- B . Apply route-map High-LP out for prefix 192.168.1.1/32 on R1 with R2 BGP peering.
- C . Apply redistribute ospf 10 on R1 in BGP AS 65101.
- D . Configure network 192.168.1.1 mask 255.255.255.255 in BGP AS 65101 on R2
B
Explanation:
The issue described indicates that the preferred BGP path for traffic destined to 192.168.1.1/32 is not being used. By applying a route-map with a higher Local Preference (LP) on R1 for the prefix 192.168.1.1/32, the BGP path attributes can be manipulated to prefer the path through R2. Local Preference is a BGP attribute that determines the preferred exit path out of an AS. A higher Local Preference value is preferred over a lower one. Therefore, configuring the route-map High-LP with a higher Local Preference on R1’s BGP peering with R2 will influence the BGP path selection process, ensuring that traffic for 192.168.1.1/32 prefers the path R3-R2-R1 as expected.
Reference: The solution utilizes the BGP path selection process and the manipulation of BGP attributes, as taught in the Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies (SPCOR) course
Which two IS-IS parameters must match before two Level 2 peers can form an adjacency? (Choose two)
- A . authentication settings
- B . area ID
- C . system ID
- D . MTU
- E . hello timer setting
A, E
Explanation:
In IS-IS, Level 2 peers must have matching authentication settings to ensure security and integrity of the routing domain. The hello timer setting must also match to ensure that the peers can maintain a consistent adjacency state. Mismatched hello timers could lead to adjacency flaps or failure to form an adjacency.
Reference: The information is based on the IS-IS protocol’s use of TLVs (Type-Length-Value) which makes it highly extensible. As new features come in, they can be added to the protocol with TLVs. This includes authentication mechanisms and timer settings that ensure secure and stable adjacencies between Level 2 peers
An engineer needs to implement QOS mechanism on customer’s network as some applications going over the internet are slower than others are.
Which two actions must the engineer perform when implementing traffic shaping on the network in order to accomplish this task? (Choose two)
- A . Configure a queue with sufficient memory to buffer excess packets.
- B . Configure the token values in bytes.
- C . Implement packet remarking for excess traffic.
- D . Implement a scheduling function to handle delayed packets.
- E . Configure a threshold over which excess packets are discarded.
A, B
Explanation:
When implementing traffic shaping on a network, the goal is to control the rate of traffic being sent into the network to avoid congestion. This is done by buffering excess packets and then scheduling them to be sent out at a steady rate.
Option A is correct because traffic shaping requires a queue with sufficient memory to buffer excess packets. When the traffic rate exceeds the configured maximum rate (shaping rate), the excess packets are temporarily stored in the queue until they can be sent out, ensuring a smooth flow of traffic without overwhelming the network1.
Option B is also correct as traffic shaping involves configuring token values in bytes. Tokens are used to represent permission to send a certain amount of data. The token bucket is filled with tokens at a steady rate, and packets can only be sent if there are enough tokens in the bucket. The token values determine the size of the bucket and the rate at which it is refilled, which in turn controls the rate of traffic1.
Option C is incorrect because packet remarking for excess traffic is not a component of traffic shaping. Packet remarking is typically used in conjunction with policing, where packets that exceed the rate limit can be remarked to a lower priority for downstream handling1.
Option D is incorrect in the context of traffic shaping. While a scheduling function is used to handle the packets that are delayed due to buffering, the scheduling itself is not part of the shaping mechanism but rather a function of the queuing system that works alongside shaping1.
Option E is incorrect as it pertains to traffic policing, not shaping. In traffic policing, packets that exceed a certain threshold are discarded or remarked, whereas shaping delays excess packets by buffering them1.
Reference: The information provided here is based on the Quality of Service (QoS) Configuration Guide from Cisco, which details the components and implementation of QoS, including traffic shaping1.
A network engineer is configuring Flexible NetFlow and enters these commands

What are two results of implementing this feature instead of traditional NetFlow? (Choose two.)
- A . CPU and memory utilization are reduced.
- B . Only the flows of top 100 talkers are exported.
- C . The data export flow is more secure
- D . The number of packets to be analyzed are reduced.
- E . The accuracy of the data to be analyzed is improved.
A, D
Explanation:
Flexible NetFlow improves on traditional NetFlow by providing more flexibility and efficiency in collecting and analyzing network flow data. In this specific configuration, the “mode random one-out-of-100” command is used, which means that only one out of every 100 packets is sampled. This leads to reduced CPU and memory utilization (Option A) because fewer packets are being processed. Additionally, because fewer packets are being analyzed (only one out of every 100), the number of packets to be analyzed is significantly reduced (Option D), leading to further efficiencies.
Reference: =
Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies
On-Demand E-Learning
