Practice Free 350-501 Exam Online Questions
Refer to the exhibit.
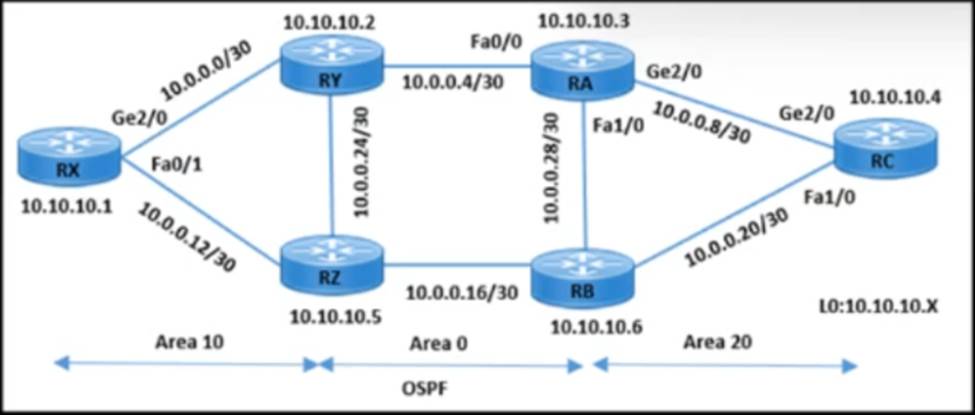
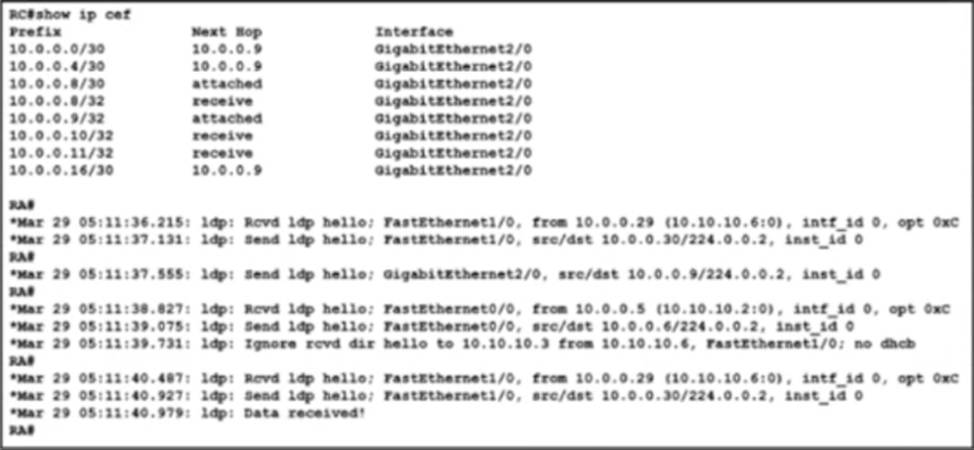
The operations team is implementing an LDP-based configuration in the service-provider core network with these requirements:
• RC must establish LDP peering with the loopback IP address as its Router ID.
• RA must establish LDP peering with RB, RC, and RY.
How must the team update the network configuration to successfully enable LDP peering between RA and RC?
- A . Enable the mpls ip command on RC interface Gi2/0. DUMPS
- B . Configure the mpls Idp router-Id loopback0 command on RA and RC.
- C . Implement LDP session protection on RA.
- D . DUMPS Reset the discover hello hold time and interval to their default values.
B
Explanation:
To establish LDP peering with the loopback IP address as its Router ID, both RA and RC need to configure their LDP router IDs to use their respective loopback addresses. This is done by applying the ‘mpls ldp router-id loopback0’ command on both routers. This configuration ensures that LDP peering uses the loopback addresses, which is a requirement for the service-provider core network.
Reference: = This explanation is based on the concepts outlined in Cisco’s Implementing and Operating Service Provider Network Core Technologies (SPCOR) course, which provides in-depth knowledge on service provider infrastructure. For further study, refer to the official Cisco documentation and training materials available on the Cisco Learning Network Store.
Refer to the exhibit:
![]()
What does this value mean when it is received in XML?
- A . It shows the ending of the script
- B . It indicates a break in a sequence
- C . It indicates a value assigned by a network administrator to tag a route
- D . It means a data field is blank
D
Explanation:
In XML, a self-closing tag such as <tag/> indicates that the element does not contain any data, hence the data field is considered blank. This is a common way to represent empty elements in XML documents.
Reference: For further details, you can refer to XML-related sections in the Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies (SPCOR) materials, which explain the structure and usage of XML in network configurations.
How do CSC VPN services use BGP to support connectivity between customer sites?
- A . BGP uses address families for IPv6 support in networks that use IPv4 and IPv6 between customers in different geographies.
- B . The BGP AS-Override feature allows the CSC network to use the same autonomous system number.
- C . BGP eliminates the need for an IGP to run within the backbone carrier core and provides more efficient label distribution.
- D . BGP sends labels to the CSC-PE router so that traffic can traverse the backbone carrier.
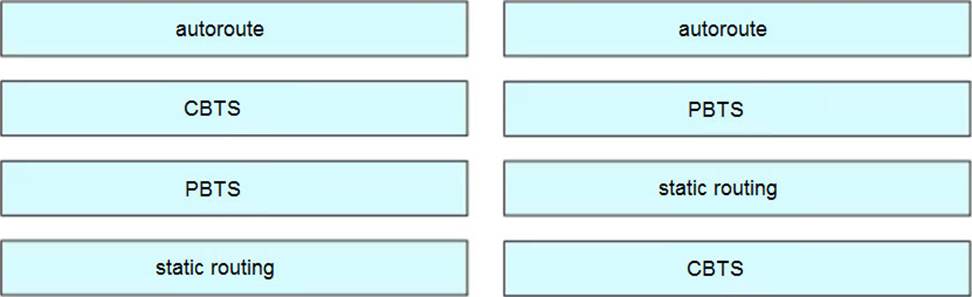
DRAG DROP
Drag and drop the methods of Cisco MPLS TE tunnel traffic assignment from the left onto their characteristics on the right.

Refer to the exhibit.

A network engineer at a large ISP Is configuring telemetry streams to monitor the health status of PE routers on the network using gRPC dial-out. The PE routers are located at several data centers in different physical locations, and they are using IS-IS and BGP for routing.
Which additional configuration must the engineer implement on the PE routers to meet the goal?
A)

B)

C)

D)

Refer to the exhibit:
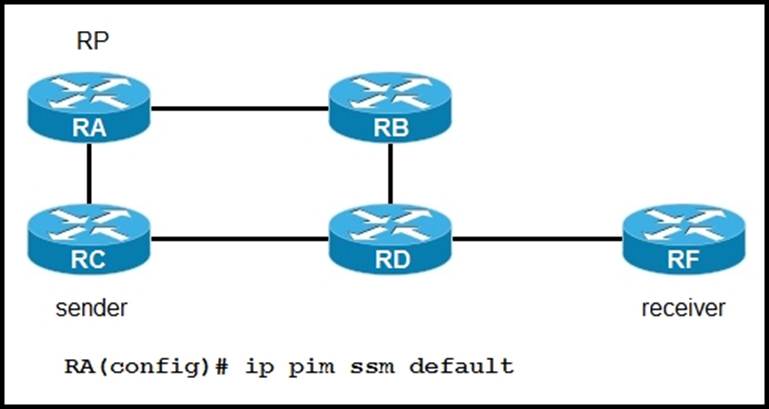
If router RA is configured as shown, which IPv4 multicast address space does it use?
- A . 224.0. 0.0/8
- B . 225.0. 0.0/8
- C . 232.0. 0.0/8
- D . 239.0. 0.0/8
C
Explanation:
The router RA is configured with the command “ip pim ssm default”. This configuration enables Source-Specific Multicast (SSM) for the default range of 232.0.0.0/8, which is the IPv4 multicast address space reserved for SSM by IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority). In SSM, data traffic is delivered to a specific group of subscribers identified by the combination of both source and multicast addresses, enhancing efficiency and security.
Reference: Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies
Which two features will be used when defining SR-TE explicit path hops if the devices are using IP unnumbered interfaces? (Choose two.)
- A . router ID
- B . labels
- C . node address
- D . next hop address
- E . output interface
A, B
Explanation:
In Segment Routing Traffic Engineering (SR-TE), when defining explicit path hops for devices using IP unnumbered interfaces, the router ID and labels are crucial. The router ID uniquely identifies a router in the network, while labels are used to direct packets along a specific path without relying on IP addresses, which is essential in unnumbered interface scenarios
Refer to the exhibit.
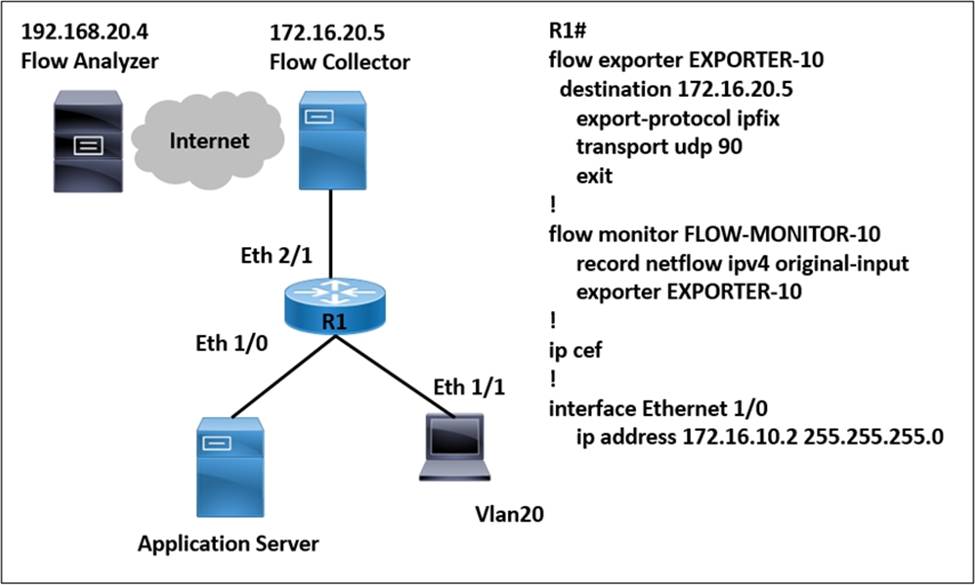
A network engineer wants to monitor traffic from the application server and send the output to the external monitoring device at 172.16.20.5. Application server traffic should pass through the R1 Eth2/1 interface for further analysis after it is monitored.
Which configuration must be applied on the R1 router?
- A . Configure the FLOW-MONITOR-20 command.
- B . Configure the flow exporter EXPORTER-10 destination 192.168.20.4 command.
- C . Configure the ip flow monitor FLOW-MONITOR-10 input command on the Ethernet1/0 interface.
- D . Configure the ip flow monitor FLOW-MONITOR-10 output command on the Ethernet 2/1 interface.
What are the four primary components of an API?
- A . methods, actions, objects, and formats
- B . GET, PUT, DELETE, and SET
- C . Modularity, Abstraction, Stability, and Resources
- D . running config, startup config, VLAN database, and routing database
Company A is implementing VoIP services across the company. The network architect designed a QoS policy to allow only specific IP subnets and mark the signaling flow with DSCP 36. The solution should be as secure as possible. Phones receive their IP addresses from the 172.184.12.0/24 pool and are assigned by the RADIUS server to VLAN 1021. Skinny Client Control Protocol is used as a signaling protocol in the network. For security reasons, switchport port-security maximum 1 vlan voice has been preconfigured on the switch side.
Which two tasks must an engineer perform on SW_1 to achieve this goal? (Choose two.)
- A . Implement a class map with the set dscp af42 command.
- B . Implement a class map with the set dscp af43 command.
- C . Implement an ACL with the set dscp af41 command.
- D . Implement an ACL with the permit udp 172.184.12.0 0.0.0.255 any range 2000 2002 command.
- E . Implement an ACL with the permit tcp 10.124.121.0 0.0.0.255 range 16384 32767 command.
