Practice Free 350-501 Exam Online Questions
After implement MPLS protocol for multiple VRFs on a single Cisco device, the engineer notices all VRFs on the router still do to not LDP session protection feature enabled.
Which configuration must the engineer apply to enable the LDP session protection feature FOR LDP neighbors within each VRF?
- A . Configure LDP session protection globally on the device only.
- B . Configure LDP session protection globally on the device and on each neighbor that requires session protection.
- C . Configure LDP session authentication on the device to enable LDP session protection on each VRF automatically.
- D . Configure LDP session protection within the individual VRFs.
D
Explanation:
To enable LDP session protection for LDP neighbors within each VRF, the engineer should configure LDP session protection within the individual VRFs. This ensures that LDP sessions are protected at the VRF level, providing security and stability for MPLS-based services. By enabling LDP session protection within each VRF, the router will take appropriate actions to protect LDP sessions against misbehaving neighbors or potential attacks.
Reference: Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies (SPCOR) v1.0
Refer to the exhibit.
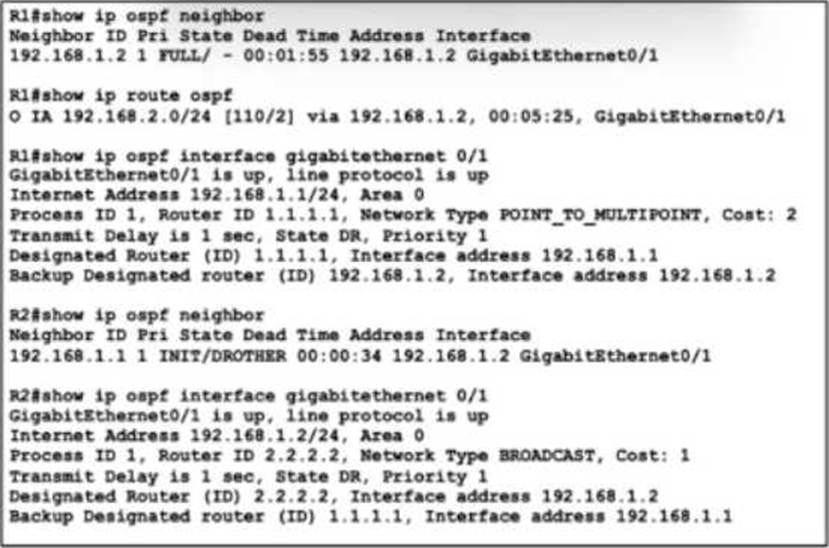
A junior network engineer has been configuring OSPF on two directly connected routers, R1 and R2, to establish a neighbor adjacency. The engineer also configured ip route 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 GigabitEthernet 0/1 10.10.10.1 on R1 to allow inbound management. After the initial configuration, the adjacency failed to form. The engineer changed the cost and area type under the OSPF configuration on R1, but the problem persists.
Which action must the engineer take to resolve the issue?
- A . Change the network type on R2 to point-to-multipoint.
- B . Remove the static route on R1 and enable OSPF under the Gi0/1 interface.
- C . Set the OSPF process ID on R1 to match the OSPF process ID on R2.
- D . Decrease the OSPF cost on R1 to match the cost on R2.
Refer to the exhibit.
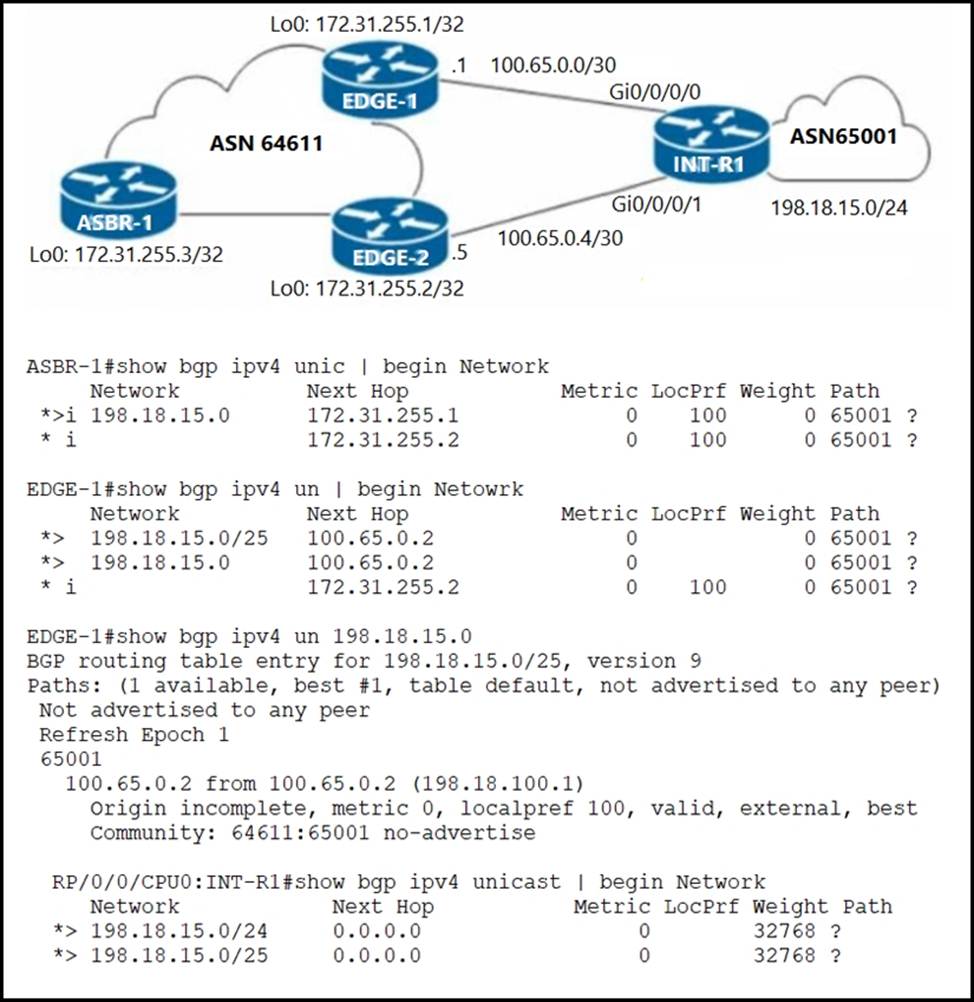
The network engineer who manages ASN 65001 is troubleshooting suboptimal routing to the 198.18.15.0/24 prefix.
According to the network requirements:
✑ Routing to IP destinations in the 198.18.15.0/25 block must be preferred via the EDGE-1 PE.
✑ Routing to IP destinations in the 198.18.15.128/25 block must be preferred via the EDGE-2 PE.
✑ More specific prefixes of the 198.18.15.0/24 block must not be advertised beyond the boundaries of ASN 64611.
✑ Routing to 198.18.15.0/24 must be redundant in case one of the uplinks on INT-R1 fails.
Which configuration must the network engineer implement on INT-R1 to correct the suboptimal routing and fix the issue?
- A . configure terminal
route-policy ASN65001-SPECIFIC-OUT
if destination in (198.18.15.0/25) then
set community (no-export, peeras:65001)
done
endif
if destination in (198.18.15.0/24) then
prepend as-path 65001 3
done
endif
drop
end-policy
!
router bgp 65001
neighbor 100.65.0.1
address-family ipv4 unicast
route-policy ASN65001-SPECIFIC-OUT out
end - B . configure terminal
route-policy ASN65001-SPECIFIC-OUT
if destination in (198.18.15.0/25) then
set community (internal, peeras:65001)
done
endif
if destination in (198.18.15.0/24) then
done
endif
drop
end-policy
!
router bgp 65001
neighbor 100.65.0.1
address-family ipv4 unicast
route-policy ASN65001-SPECIFIC-OUT out
end - C . configure terminal
route-policy ASN65001-SPECIFIC-OUT
if destination in (198.18.15.0/25) then
set community (no-advertise, peeras:65001)
done
endif
if destination in (198.18.15.128/25) then
prepend as-path 65001 3
done
endif
drop
end-policy
!
router bgp 65001
neighbor 100.65.0.1
address-family ipv4 unicast
route-policy ASN65001-SPECIFIC-OUT out
end - D . configure terminal
route-policy ASN65001-SPECIFIC-OUT
if destination in (198.18.15.0/25) then
set community (no-export, peeras:65001)
done
endif
if destination in (198.18.15.128/25) then
prepend as-path 65001 3
done
endif
drop
end-policy
!
router bgp 65001
neighbor 100.65.0.1
address-family ipv4 unicast
route-policy ASN65001-SPECIFIC-OUT in
end
Which task must be performed first to Implement BFD in an IS-IS environment?
- A . Disable Cisco Express Forward.ng on all interfaces running routing protocols other than IS-IS
- B . Configure BFD under the IS-IS process
- C . Configure all ISIS routers as Level 2 devices
- D . Configure BFD in an interface configuration mode
D
Explanation:
To implement Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) in an IS-IS environment, the first task is to configure BFD in an interface configuration mode. This involves setting up BFD parameters on the interfaces where IS-IS is running to enable quick failure detection.
Reference: Implementing BFD in an IS-IS Environment – Exam-Answer3.
Refer to the exhibit.
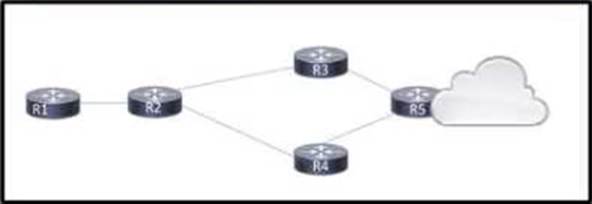
An engineer is scripting ACLs to handle traffic on the given network. The engineer must block users on the network between R1 and R2 from leaving the network through R5. but these users must still be able to access all resources within the administrative domain.
How must the engineer implement the ACL configuration?
- A . Configure an ACL that permits traffic to any internal address, and apply it to the R5 interfaces to R3 and R4 in the egress direction
- B . Configure a permit any ACL on the R1 interface to R2 in the egress direction, and a deny any ACL on the interface in the ingress direction
- C . Configure an ACL that permits traffic to all internal networks and denies traffic to any external address, and apply it to the R2 interface to R1 in the ingress direction.
- D . Configure an ACL that denies traffic to any internal address and denies traffic to any external address, and apply it to the R5 interfaces to R3 and R4 in the ingress direction
C
Explanation:
In the given scenario, the goal is to restrict users on the network between R1 and R2 from accessing the external network through R5, while still allowing them access to all resources within the administrative domain. The correct approach is to configure an Access Control List (ACL) that permits traffic to all internal networks and denies traffic to any external address. This ACL should be applied to the R2 interface that connects to R1 in the ingress direction. By doing so, traffic originating from users between R1 and R2 destined for external networks will be blocked, while internal traffic will be allowed.
Reference: This explanation is derived from the Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies (SPCOR) study materials, which cover the configuration and application of ACLs in a service provider network environment.
Refer to the exhibit:

Which effect of this configuration is true?
- A . R1 can support a peer that is configured for LDP SSO/NSF as the peer recovers from an outage
- B . R1 can failover only to a peer that is configured for LDP SSO/NSF
- C . R1 can failover to any peer
- D . R1 can support a graceful restart operation on the peer, even if graceful restart is disabled on the peer
D
Explanation:
The configuration in the exhibit shows that R1 is configured with “mpls ldp graceful-restart”, which enables LDP Graceful Restart on the router. This means that R1 can support a graceful restart operation on the peer, even if graceful restart is disabled on the peer. This feature allows LDP to recover from failures without affecting the forwarding plane, ensuring network stability and minimal packet loss during failovers.
Reference: Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies (SPCOR) – Cisco SPCOR Training & Certification
Refer to the exihibit.
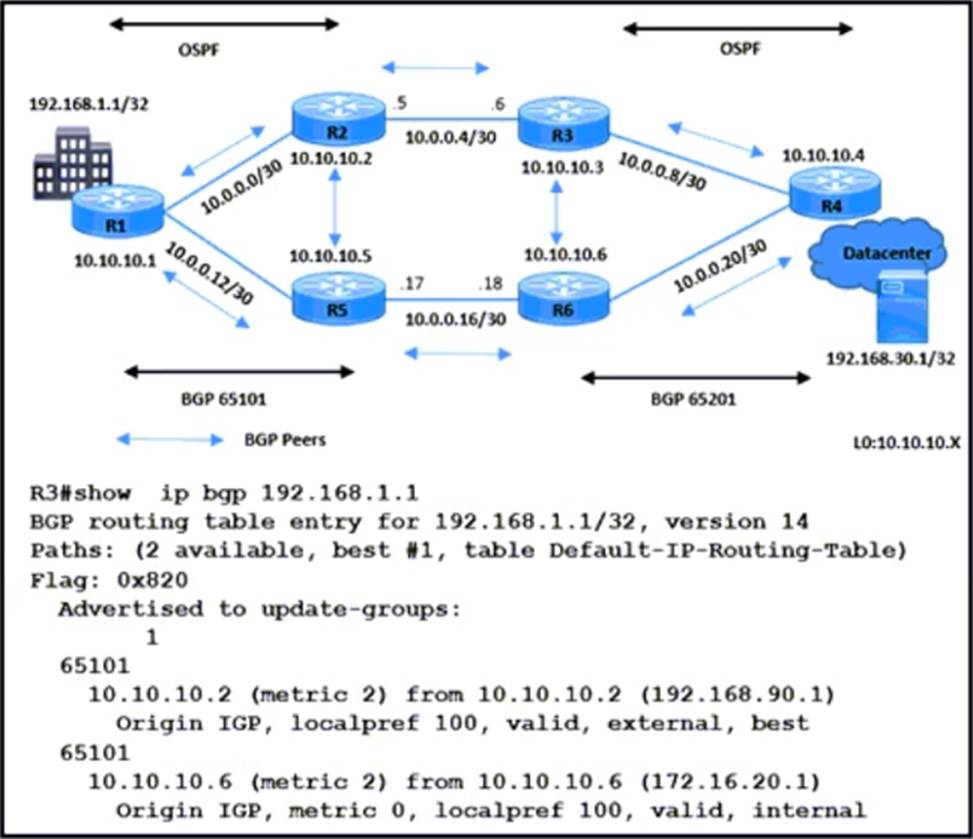
A network engineer is implementing BGP in AS 65101 and AS 65201. R3 sends data traffic to 192.168.1.1 /32 via the path R3-R2-R1. The traffic must travel via alternate path R6-R5 for prefix 192.168.1.1/32.
Which action must be taken to meet the requirement?
- A . Apply route-map HIGH-MED out on R2 for neighbor R3.
- B . Apply route-map HIGH-LP in on R3 for neighbor R6
- C . Apply route-map LOW-LP out on R2 for neighbor R3.
- D . Apply route-map LOW-MED in on R5 for neighbor R2
B
Explanation:
To ensure that traffic for the prefix 192.168.1.1/32 travels via the alternate path R6-R5, a route-map with a higher local preference should be applied inbound on R3 for neighbor R6. This will make the path through R6-R5 more preferable, thus meeting the requirement.
Reference: = Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies
A network engineer is deploying VPLS configuration between multiple PE routers so that customer’s remote offices have end-to-end LAN connectivity.
Which additional configuration should the engineer perform on the PE routers to enable the virtual switch instance?
A)
![]()
B)

C)

D)
![]()
- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
A
Explanation:
In the context of VPLS (Virtual Private LAN Service) configuration, the engineer should perform additional configurations to enable the virtual switch instance. The correct answer is Option A, which likely involves configuring interface VLAN and associating it with xconnect vfi to establish end-to-end LAN connectivity between customer’s remote offices. This is essential for enabling VPLS, which allows geographically dispersed sites to be connected over a service provider’s network as if they were on the same local area network.
Reference: Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies (SPCOR) – Cisco SPCOR Training & Certification
Refer to the exhibit.

An engineer is configuring router R1 for OSPFv3 as shown.
Which additional configuration must be performed so that the three active interfaces on the router will advertise routes and participate in OSPF IPv6 processes?
A)

B)

C)

D)

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
A
Explanation:
OSPFv3 is used for routing IPv6 prefixes and requires that each interface intended to participate in OSPFv3 has the protocol enabled. This involves specifying the OSPF process ID and the area ID that the interface belongs to. The process ID links the interface to a specific OSPFv3 process running on the router, and the area ID determines the area within the OSPF topology that the interface is part of. Without this configuration, the interfaces will not actively participate in OSPFv3 route advertisement or neighbor relationships12.
Reference: =
Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies (SPCOR) course materials3.
Cisco OSPFv3 configuration guides and examples
Refer to the exhibit.
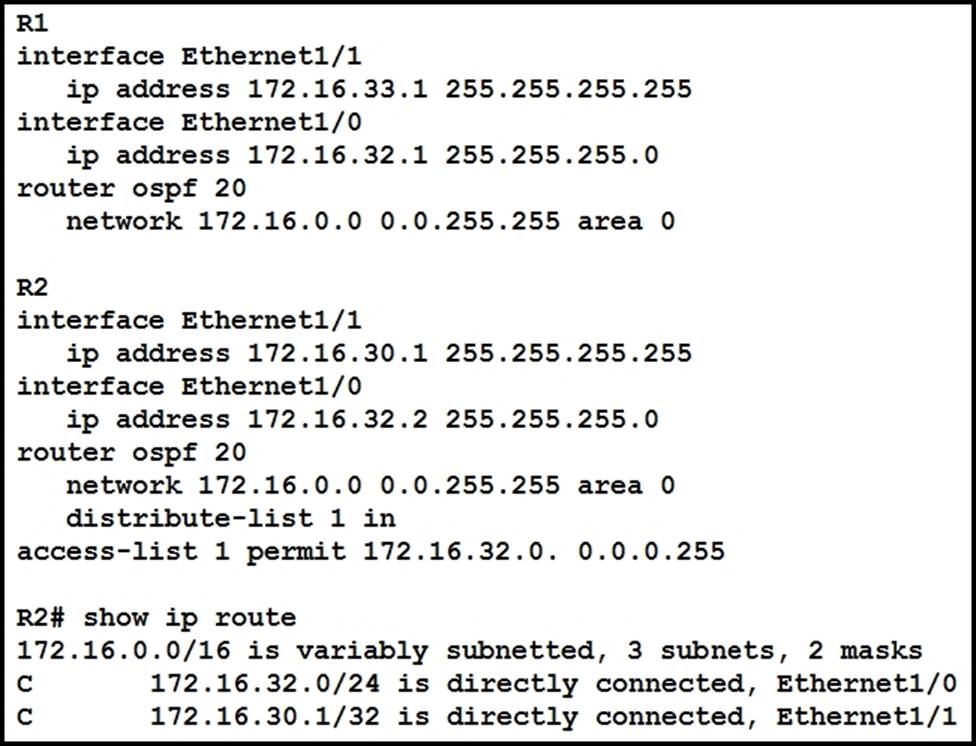
A network engineer notices that router R2 is failing to install network 172.16.33.1/32 in the routing table.
Which configuration must the engineer apply to R2 to fix the problem?
- A . R2(config)# access-list 1 permit 172.16.33.0 255.0.0.0
- B . R2(config)# access-list 1 permit 172,16,33.0 255,255,255,0
- C . R2(config)# access-list 1 permit 172.16.33.0 0.0.0.255
- D . R2(config)# access-list 1 permit 172,16,33.0 255.255,0,0
C
Explanation:
The issue is that router R2 is not installing the network 172.16.33.1/32 in the routing table due to an incorrect access list configuration. The correct answer is option C, which will allow the network to be installed in the routing table by permitting addresses from 172.16.33.0 to 172.16.33.255 with a wildcard mask of 0.0.0.255.
The current access list on R2, “access-list 1 permit 172,16,32,0 0,0,0,255”, only permits addresses from the range of 172,16,32,0 to 172,16,32,255 due to its wildcard mask of “0,.0,.0,.255”. This does not include the address “172,.16,.33,.1”.
Reference: Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies (SPCOR) study guide or course materials available on Cisco’s official website or authorized training partners.
