Practice Free 2V0-11.25 Exam Online Questions
Which tasks can be accomplished through vSphere Host Profiles?
- A . Enforcing identical network settings across multiple hosts
- B . Removing old VIBs from an ESXi host automatically
- C . Checking compliance with defined storage configurations
- D . Managing user accounts and password policies
A, C, D
Explanation:
Host Profiles allow consistent host settings (network, storage, security). They don’t typically remove VIBs automatically (B); that’s often done via CLI or vSphere Lifecycle Manager.
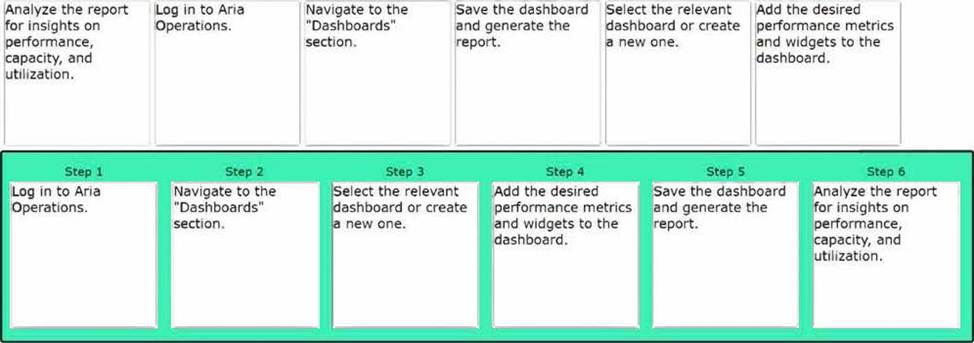
DRAG DROP
Arrange the steps in the correct order to generate a performance report in Aria Operations.
Which of the following considerations apply when deploying NSX for micro-segmentation in a vSphere environment?
- A . Distributed Firewall rules can be applied at the virtual NIC level
- B . vSphere HA must be disabled for NSX to function
- C . Proper IP addressing and VLAN design for NSX management and VXLAN traffic
- D . Using Guest Introspection services for offloaded antivirus scanning
A, C, D
Explanation:
NSX micro-segmentation uses distributed firewall rules at vNIC level (A), requires dedicated network design (C), and integrates with Guest Introspection for security (D). HA does not need to be disabled (B).
During a vMotion migration, the memory contents of a running VM are transferred between hosts.
Which vSphere feature can help accelerate this process if the source and destination hosts are using hardware-based RDMA or high-speed interconnects?
- A . vSphere vMotion with Multi-NIC support
- B . Proactive HA
- C . EVC
- D . vSphere VM Encryption
A
Explanation:
Multi-NIC vMotion can spread the memory transfer across multiple NICs (including high-speed RDMA if supported) to accelerate migration. Proactive HA (B) moves VMs off potentially failing hosts, EVC (C) handles CPU compatibility, and VM Encryption (D) secures disk data.
Which of the following best describes the fundamental function of a hypervisor in a VMware vSphere environment?
- A . It manages physical storage devices and presents logical volumes to the OS.
- B . It abstracts hardware resources so multiple VMs can run on a single physical server.
- C . It provides network routing and firewall services between virtual networks.
- D . It monitors resource usage and sends performance metrics to vRealize Operations.
B
Explanation:
A hypervisor is responsible for creating and managing virtual hardware for multiple virtual machines, allowing each VM to share the host’s physical resources securely and efficiently.
Which two operations can be completed in the SDDC Manager UI on an NSX Edge cluster after it has been deployed into a workload domain? (Choose two.)
- A . Redeploy
- B . Expand
- C . Sync
- D . Delete
- E . Shrink
B, E
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
After an NSX Edge cluster is deployed into a workload domain, SDDC Manager provides built in operations to adjust the cluster size.
According to the VMware Cloud Foundation 5.2 documentation:
“After you create an NSX Edge cluster, you can use SDDC Manager to expand or shrink it by adding or deleting NSX Edge nodes.”
Breakdown of options:
B . Expand C You can add one or more Edge nodes to increase the cluster size.
E . Shrink C You can remove Edge nodes to decrease the cluster size.
These two actions are the only supported cluster scaling operations available in SDDC Manager post-deployment. Other operations―such as Redeploy, Sync, or Delete―are not available via the UI for a
deployed Edge cluster and are either manual or unsupported in that context.
Summary:
Selected choices B and E match the documented capability to scale an NSX Edge cluster via SDDC Manager.
No other operations (A, C, D) are supported for an existing Edge cluster through the UI.
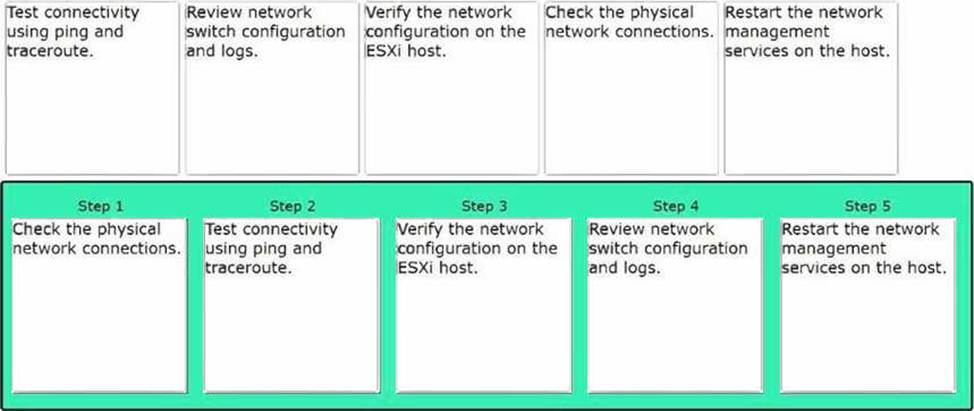
DRAG DROP
Arrange the steps in the correct order to resolve host connectivity issues.
An administrator is responsible for monitoring the logs of multiple vSphere components using VMware Aria Operations for Logs. They notice an increase in error logs for a specific ESXi host.
Which two steps should be taken to pinpoint the issue? (Choose two.)
- A . Restart the ESXi host to resolve the issue immediately
- B . Filter the loos by the ESXi host name and error severity.
- C . Correlate the error logs with recent configuration changes on the ESXi host.
- D . Check for patterns or repeated error messages over a specific time frame.
- E . Delete all old logs to free up space and generate new logs.
B, D
Explanation:
Filtering the logs by the ESXi host name and error severity helps narrow down the logs to those relevant to the specific host and allows for easier identification of significant errors.
Checking for patterns or repeated error messages over a specific time frame helps identify the root cause of the issue and determine if the errors are linked to a specific event or condition.
A VMware administrator notices that multiple VMs are experiencing high storage latency.
Which of the following is the most likely initial step in diagnosing the issue?
- A . Migrating the VMs to another vCenter
- B . Checking the performance charts in vCenter to pinpoint read/write metrics
- C . Immediately rebooting all VMs to clear potential software issues
- D . Disabling vSAN traffic
B
Explanation:
Using vCenter performance charts to monitor disk read/write latencies and IOPS is typically the first step in diagnosing storage performance problems.
Which vSphere features or settings help automate host patching and ensure all hosts in a cluster are uniformly updated?
- A . vSphere Lifecycle Manager (vLCM)
- B . Host Profiles
- C . vSphere Update Manager in older versions
- D . Enhanced vMotion Compatibility (EVC)
A, B, C
Explanation:
vSphere Lifecycle Manager (or Update Manager in older versions) automate patching, while Host Profiles help maintain consistent configurations. EVC standardizes CPU features but does not patch or update hosts.
