Practice Free 100-160 Exam Online Questions
Which two basic metrics should be taken into consideration when assigning a severity to a vulnerability during an assessment? (Choose 2.)
- A . The likelihood that an adversary can and will exploit the vulnerability
- B . The impacts that an exploit of the vulnerability will have on the organization
- C . The time involved in choosing replacement software to replace older systems
- D . The age of the hardware running the software that contains the vulnerability
AB
Explanation:
The CCST Cybersecurity course describes that risk scoring for vulnerabilities often involves likelihood and impact ― similar to the CVSS (Common Vulnerability Scoring System) model.
"When prioritizing vulnerabilities, assess both the likelihood of exploitation and the potential impact to the organization. Likelihood measures how easy or probable it is for an adversary to exploit the weakness, while impact measures the consequences to confidentiality, integrity, and availability if exploitation occurs." (CCST Cybersecurity, Vulnerability Assessment and Risk Management, Risk Assessment and Prioritization section, Cisco Networking Academy)
A is correct: Likelihood is a fundamental part of severity assessment.
B is correct: Impact determines how damaging an exploit would be.
C is incorrect: Time to choose replacement software is an operational consideration, not a severity metric.
D is incorrect: Hardware age may influence performance but does not directly define vulnerability severity.
DRAG DROP
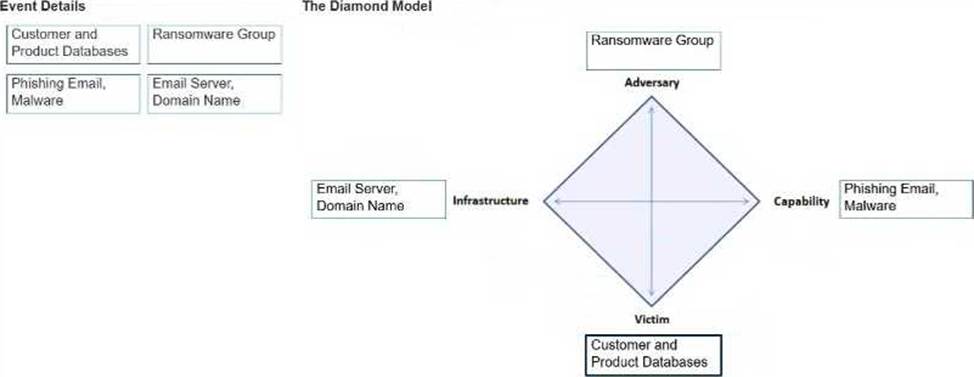
You need to diagram an intrusion event by using the Diamond Model.
Move each event detail from the list on the left to the correct location in the diagram on the right. Note: You will receive partial credit for each correct response.
Explanation:
The CCST Cybersecurity Study Guide describes the Diamond Model of Intrusion Analysis as a framework to map the relationships between four core features of an intrusion: Adversary C The threat actor or group conducting the attack.
Example: Ransomware Group
Capability C The tools, techniques, or malware the adversary uses.
Example: Phishing Email, Malware
Infrastructure C The physical or logical communication and delivery systems the adversary uses. Example: Email Server, Domain Name
Victim C The target of the attack, such as systems, organizations, or individuals.
Example: Customer and Product Databases
"The Diamond Model helps analysts connect the attacker, the tools they use, the infrastructure supporting the attack, and the victim, providing a holistic view of the intrusion event."
(CCST Cybersecurity, Incident Handling, Threat Modeling section, Cisco Networking Academy)
Which of the following is a primary purpose of software inventory in a cybersecurity program?
- A . Monitoring user access and permissions
- B . Identifying vulnerabilities and patch requirements
- C . Analyzing network traffic for potential threats
- D . Ensuring compliance with software licensing agreements
B
Explanation:
Software inventory is an essential component of a cybersecurity program as it helps in identifying the software applications installed on devices within the network. By maintaining an accurate software inventory, organizations can identify vulnerabilities and track patch requirements to keep their systems secure and up to date.
What is a common security threat in which an attacker attempts to overwhelm a targeted system by flooding it with Internet traffic?
- A . Ransomware
- B . Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack
- C . Phishing
- D . SQL injection
B
Explanation:
Option 1: Ransomware is a type of malicious software that encrypts a victim’s files and demands a ransom in exchange for the decryption key. While it can cause damage to systems, it is not specifically designed to overwhelm a system with Internet traffic.
Option 2: Correct. A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack is a common security threat in which an attacker attempts to overwhelm a targeted system by flooding it with Internet traffic. This can result in a loss of service availability for legitimate users.
Option 3: Phishing is a type of social engineering attack in which an attacker masquerades as a trustworthy entity to trick individuals into providing sensitive information. It does not involve overwhelming a system with Internet traffic.
Option 4: SQL injection is a type of web application attack in which an attacker manipulates a SQL query to gain unauthorized access to a database. It does not involve overwhelming a system with Internet traffic.
Vulnerability refers to:
- A . The degree to which a threat is capable of causing damage.
- B . The likelihood of a security incident occurring.
- C . The potential for loss or harm as a result of a threat exploiting a vulnerability.
- D . The exploitation of a vulnerability by a threat.
D
Explanation:
Vulnerability refers to a weakness or flaw in a system that can be exploited by a threat. It is the state of being exposed to the possibility of being attacked or harmed.
During an incident response, the security team needs to isolate a compromised server from the rest of the network but still allow forensic analysis.
Which action should they take?
- A . Power off the server immediately.
- B . Disconnect the server from the network and connect it to an isolated forensic network.
- C . Delete suspicious files from the server.
- D . Reset all user passwords on the server.
B
Explanation:
The CCST Cybersecurity course notes that isolation is a key part of the containment phase of incident response. The goal is to prevent the compromised system from communicating with the attacker or spreading malware, while preserving it for analysis.
"Containment often involves removing an affected system from the production network and connecting it to a controlled forensic environment to preserve evidence and prevent further compromise."
(CCST Cybersecurity, Incident Handling, Containment Procedures section, Cisco Networking Academy)
Which data type is protected through hard disk encryption?
- A . Data in process
- B . Data in transit
- C . Data in use
- D . Data at rest
D
Explanation:
The CCST Cybersecurity Study Guide explains that hard disk encryption is a method used to protect data stored on a physical device from unauthorized access.
"Data at rest refers to data stored on a device, such as files on a hard drive, SSD, or removable media. Hard disk encryption protects data at rest by converting it into an unreadable format unless accessed with the correct decryption key."
(CCST Cybersecurity, Essential Security Principles, Data States and Protection Methods section, Cisco Networking Academy)
Data in process refers to data actively being handled by applications in memory (RAM), which is not the primary target of disk encryption.
Data in transit is protected via encryption methods such as TLS, not disk encryption.
Data in use is accessed and manipulated by programs in real-time, also not the primary scope of disk encryption.
Data at rest is the correct answer, as hard disk encryption directly safeguards stored files.
What is the purpose of app distribution in cybersecurity?
- A . Deploying network firewalls
- B . Testing the security of applications
- C . Configuring access control policies
- D . Distributing security patches and updates
D
Explanation:
App distribution in cybersecurity refers to the process of distributing security patches and updates for applications. This is vital in maintaining the security of software and preventing vulnerabilities from being exploited. By regularly distributing and installing updates, organizations can address known security flaws, improve application performance, and ensure that their systems remain protected against emerging threats.
Which of the following is an example of a source of evidence (artifact) in a cybersecurity investigation?
- A . Firewall logs recording network traffic.
- B . Configuration files of network devices.
- C . Security policy documents.
- D . Training materials for security awareness.
A
Explanation:
In a cybersecurity investigation, evidence or artifacts play a crucial role in determining the nature of an incident. Firewall logs recording network traffic can provide valuable information regarding communication between systems, including IP addresses, ports, protocols, and timestamps. Analyzing these logs can help identify potential threats or suspicious activities within a network.
A threat actor sets up a rogue access point (AP) at a local cafe. The rogue AP captures traffic and then forwards the traffic to the cafe AP.
Which type of attack does this scenario describe?
- A . Reconnaissance
- B . Man-in-the-middle
- C . DDoS
- D . Ransomware
B
Explanation:
The CCST Cybersecurity Study Guide describes a man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack as an attack where the adversary secretly intercepts and possibly alters communications between two parties, making them believe they are communicating directly. A rogue AP configured to pass traffic through itself before sending it on is a classic wireless MITM method.
"In a MITM attack, the attacker places themselves between the sender and receiver, intercepting and possibly altering data in transit. Rogue access points can facilitate MITM attacks in wireless environments."
(CCST Cybersecurity, Basic Network Security Concepts, Wireless Threats section, Cisco Networking Academy)
A is incorrect: Reconnaissance is information gathering, not active interception.
B is correct: This is a wireless MITM attack.
C is incorrect: DDoS aims to overwhelm a service, not intercept data.
D is incorrect: Ransomware encrypts data for extortion.
