Practice Free NSE5_FSM-6.3 Exam Online Questions
If an incident’s status is Cleared, what does this mean?
- A . Two hours have passed since the incident occurred and the incident has not reoccurred.
- B . A clear condition set on a rule was satisfied.
- C . A security rule issue has been resolved.
- D . The incident was cleared by an operator.
B
Explanation:
Incident Status in FortiSIEM: The status of an incident indicates its current state and helps administrators track and manage incidents effectively.
Cleared Status: When an incident’s status is "Cleared," it means that a specific condition set to clear the incident has been satisfied.
Clear Condition: This is typically a predefined condition that indicates the issue causing the incident has been resolved or no longer exists.
Automatic vs. Manual Clearance: While some incidents may be cleared automatically based on clear conditions, others might be manually cleared by an operator.
Reference: FortiSIEM 6.3 User Guide, Incident Management section, detailing the various incident statuses and the conditions that lead to an incident being marked as "Cleared."
In the rules engine, which condition instructs FortiSIEM to summarize and count the matching evaluated data?
- A . Time Window
- B . Aggregation
- C . Group By
- D . Filters
B
Explanation:
Rules Engine in FortiSIEM: The rules engine evaluates incoming events based on defined conditions to detect incidents and anomalies.
Aggregation Condition: The aggregation condition instructs FortiSIEM to summarize and count the matching evaluated data.
Function: Aggregation is used to group events based on specified criteria and then perform operations such as counting the number of occurrences within a defined time window.
Purpose: This allows for the detection of patterns and anomalies, such as a high number of failed login attempts within a short period.
Reference: FortiSIEM 6.3 User Guide, Rules Engine section, which explains how aggregation is used to summarize and count matching data.
Which protocol do collectors use to communicate with a FortiSIEM cluster?
- A . Syslog
- B . SNMP
- C . HTTPS
- D . SMTP
Where do you configure rule notifications and automated remediation on FortiSIEM?
- A . Notification policy
- B . Remediation policy
- C . Notification engine
- D . Remediation engine
A
Explanation:
Rule Notifications and Automated Remediation: In FortiSIEM, notifications and automated remediation actions can be configured to respond to specific incidents or alerts generated by rules.
Notification Policy: This is the section where administrators configure the settings for notifications and specify the actions to be taken when a rule triggers an alert.
Configuration Options: Includes defining the recipients of notifications, the type of notifications (e.g., email, SMS), and any automated remediation actions that should be executed.
Importance: Proper configuration of notification policies ensures timely alerts and automated responses to incidents, enhancing the effectiveness of the SIEM system.
Reference: FortiSIEM 6.3 User Guide, Notifications and Automated Remediation section, which details how to configure notification policies for rule-triggered actions and responses.
What does the Frequency field determine on a rule?
- A . How often the rule will evaluate the subpattern.
- B . How often the rule will trigger for the same condition.
- C . How often the rule will trigger.
- D . How often the rule will take a clear action.
C
Explanation:
Rule Evaluation in FortiSIEM: Rules in FortiSIEM are evaluated periodically to check if the defined conditions or subpatterns are met.
Frequency Field: The Frequency field in a rule determines the interval at which the rule’s subpattern will be evaluated.
Evaluation Interval: This defines how often the system will check the incoming events against the rule’s subpattern to determine if an incident should be triggered.
Impact on Performance: Setting an appropriate frequency is crucial to balance between timely detection of incidents and system performance.
Examples:
If the Frequency is set to 5 minutes, the rule will evaluate the subpattern every 5 minutes.
This means that every 5 minutes, the system will check if the conditions defined in the subpattern are met by the incoming events.
Reference: FortiSIEM 6.3 User Guide, Rules and Incidents section, which explains the Frequency field and how it impacts the evaluation of subpatterns in rules.
When configuring collectors located in geographically separated sites, what ports must be open on a front end firewall?
- A . HTTPS, from the collector to the worker upload settings address only
- B . HTTPS, from the collector to the supervisor and worker upload settings addresses
- C . HTTPS, from the Internet to the collector
- D . HTTPS, from the Internet to the collector and from the collector to the FortiSIEM cluster
B
Explanation:
FortiSIEM Architecture: In FortiSIEM, collectors gather data from various sources and send this data to supervisors and workers within the FortiSIEM architecture.
Communication Requirements: For collectors to effectively send data to the FortiSIEM system, specific communication channels must be open.
Port Usage: The primary port used for secure communication between the collectors and the FortiSIEM infrastructure is HTTPS (port 443).
Network Configuration: When configuring collectors in geographically separated sites, the HTTPS port must be open for the collectors to communicate with both the supervisor and the worker upload settings addresses. This ensures that the collected data can be securely transmitted to the appropriate processing and analysis components.
Reference: FortiSIEM 6.3 Administration Guide, Network Ports section details the necessary ports for communication within the FortiSIEM architecture.
Where must you configure rule notifications and automated remediation on FortiSIEM?
- A . Notification engine
- B . Response policies
- C . Email and scripting alerts
- D . Notification policy
Which two FortiSIEM components work together to provide real-time event correlation?
- A . Supervisor and worker
- B . Collector and Windows agent
- C . Worker and collector
- D . Supervisor and collector
C
Explanation:
FortiSIEM Architecture: The FortiSIEM architecture includes several components such as Supervisors, Workers, Collectors, and Agents, each playing a distinct role in the SIEM ecosystem.
Real-Time Event Correlation: Real-time event correlation is a critical function that involves analyzing and correlating incoming events to detect patterns indicative of security incidents or operational issues.
Role of Supervisor and Worker:
Supervisor: The Supervisor oversees the entire FortiSIEM system, coordinating the processing and analysis of events.
Worker: Workers are responsible for processing and correlating the events received from Collectors
and Agents.
Collaboration for Correlation: Together, the Supervisor and Worker components perform real-time event correlation by distributing the load and ensuring efficient processing of events to identify incidents in real-time.
Reference: FortiSIEM 6.3 User Guide, Event Correlation and Processing section, details how the Supervisor and Worker components collaborate for real-time event correlation.
Refer to the exhibit.
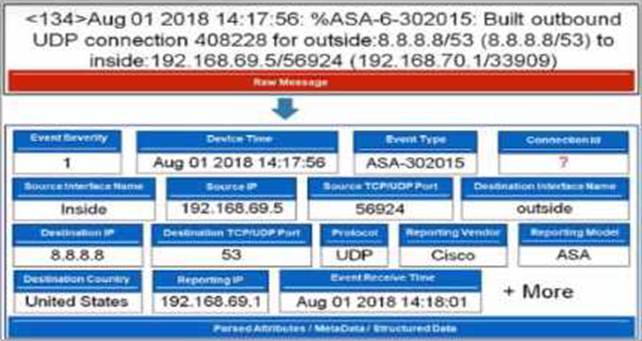
Which value will FortiSIEM use to populate the Connection Id field?
- A . 33909
- B . 134
- C . The connection ID is not in the raw message.
- D . 408228
An administrator is using SNMP and WMI credentials to discover a Windows device.
How will the WMI method handle this?
- A . WMI method will collect only traffic and IIS logs.
- B . WMI method will collect only DNS logs.
- C . WMI method will collect only DHCP logs.
- D . WMI method will collect security, application, and system events logs.
A
Explanation:
WMI Method: Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) is a set of specifications from Microsoft for consolidating the management of devices and applications in a network.
Log Collection: WMI is used to collect various types of logs from Windows devices.
Security Logs: Contains records of security-related events such as login attempts and resource access.
Application Logs: Contains logs generated by applications running on the system.
System Logs: Contains logs related to the operating system and its components.
Comprehensive Data Collection: By using WMI, FortiSIEM can gather a wide range of event logs that are crucial for monitoring and analyzing the security and performance of Windows devices.
Reference: FortiSIEM 6.3 User Guide, Data Collection Methods section, which details the use of WMI for collecting event logs from Windows devices.
