Practice Free JN0-105 Exam Online Questions
Which command displays real-time usage statistics for all interfaces?
- A . show interfaces extensive
- B . monitor interface traffic
- C . monitor traffic
- D . show interfaces
B
Explanation:
The monitor interface traffic command in Junos OS is used to view real-time interface statistics, such as bandwidth utilization (input and output rate), error counters, and packet counts. Unlike the show interfaces commands, which provide static, snapshot-based details, the monitor command displays continuously updated traffic data until the session is stopped.
From Junos OS Documentation:
“The monitor interface traffic command displays real-time statistics about traffic utilization on the specified interfaces. By default, statistics are displayed for all interfaces at regular intervals until you exit the command.”
Reference: Juniper TechLibrary C Monitoring Interfaces JNCIA-Junos Exam Objective: Operational Monitoring and Maintenance
25.11.0/24;
}
protocol icmp;
}
then {
count count-icmp; discard;
}
}
Referring to the exhibit, which two actions will occur when a packet matches the firewall filter? (Choose two.)
- A . An ICMP destination unreachable message will be returned.
- B . The packet will be forwarded.
- C . The packet will be discarded.
- D . A counter will be incremented.
CD
Explanation:
Referring to the firewall filter configuration in the exhibit, when a packet matches the specified term limit-icmp, two actions are defined in the then statement: count count-icmp and discard. The count count-icmp action means that each time a packet matches this term, a counter named count-icmp will be incremented, providing a tally of how many packets have matched the term. The discard action means that the packet will be dropped and not forwarded through the device. This effectively prevents the packet from reaching its intended destination. There is no action specified that would cause an ICMP destination unreachable message to be returned, nor is there any action that would allow the packet to be forwarded.
Which two statements are correct regarding Layer 2 network switches? (Choose two.)
- A . Switches create a single collision domain.
- B . Switches are susceptible to traffic loops.
- C . Switches flood broadcast traffic.
- D . Switches do not learn MAC addresses.
B, C
Explanation:
Layer 2 network switches are crucial components in local area networks (LANs), providing multiple functions for data packet forwarding and network segmentation. One inherent characteristic of switches is their susceptibility to traffic loops, especially in networks with redundant paths. Without proper loop prevention protocols like Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), loops can cause broadcast storms and network instability. Additionally, switches inherently flood broadcast traffic to all ports within the broadcast domain, except the port on which the broadcast was received. This is because broadcast frames are meant to be delivered to all devices within the VLAN, and the switch ensures this by flooding these frames to all ports in the VLAN, except the source port.
Exhibit.
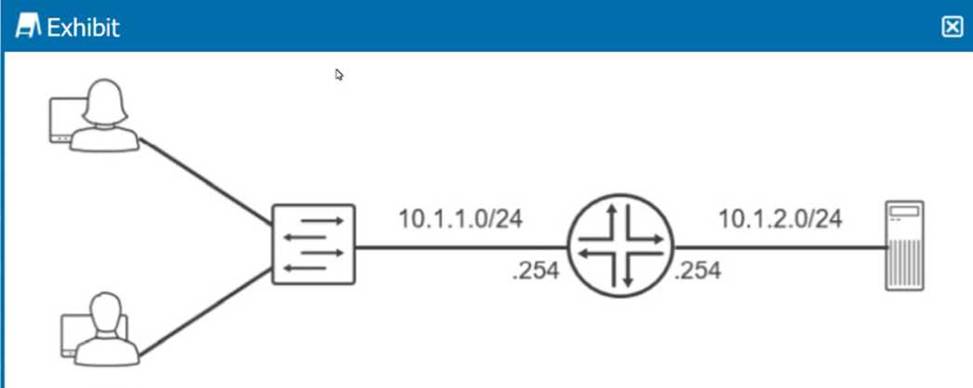
Referring to the exhibit, which routing configuration is required for these two users to access the remote server?
- A . Users must connect directly to the router.
- B . Users and the server require a default gateway.
- C . Trunk ports must be enabled on the switch.
- D . A routing protocol must be enabled on the router.
B
Explanation:
For the users in the 10.1.1.0/24 subnet and the server in the 10.1.2.0/24 subnet to communicate with each other, they need to route packets through the router that connects these two subnets. Each user and the server need to have their default gateway set to the IP address of the router interface on their respective subnet (.254). This ensures that packets destined for other subnets are sent to the router, which then routes them to the correct destination subnet.
Reference: Juniper official documentation: Configuring Basic Routing.
General networking principles.
Which command modifier would you use to see all possible completions for a specific command?
- A . |
- B . detail
- C . ?
- D . extensive
C
Explanation:
In Junos OS, the ? command modifier is used to display all possible completions for a specific command. This helps users understand the available options and syntax for a command they are trying to use.
Reference: Juniper Networks CLI Documentation "Use the ? command modifier to display all possible completions for a specific command."
Which two statements are true about the candidate configuration? (Choose two.)
- A . Candidate configuration changes are automatically applied.
- B . You can deploy multiple changes at the same time.
- C . Multiple users cannot modify the same candidate configuration.
- D . You can discard changes before committing them.
B, D
Explanation:
The candidate configuration in Junos OS is a temporary configuration that allows network administrators to make and stage multiple configuration changes before applying them to the device. This approach enables the deployment of multiple changes in a single operation, ensuring that all configurations work together as intended before making them active. Additionally, the candidate configuration can be discarded if the administrator decides not to apply the staged changes, allowing for a "trial and error" approach without affecting the currently active configuration. This feature provides flexibility and reduces the risk of disruptive changes to the network.
Which statement is correct when multiple users are configuring a Junos device using the configure private command?
- A . A commit by any user will commit changes made by all active users.
- B . A commit will not succeed until there is only a single user in configuration mode.
- C . Each user gets their own candidate configuration.
- D . Each user shares the same candidate configuration.
C
Explanation:
When multiple users are configuring a Junos device using the "configure private" command, each user gets their own candidate configuration (C). This allows for isolated configuration sessions, where changes made by one user do not impact or interfere with the changes made by another user in their private session.
What is the protocol data unit (PDU) of the Data Link Layer?
- A . segment
- B . byte
- C . frame
- D . bit
C
Explanation:
In the OSI model, the Data Link Layer is responsible for node-to-node delivery of data. It frames the packets received from the Network Layer and prepares them for physical transmission. The Protocol Data Unit (PDU) for the Data Link Layer is called a "frame." Frames encapsulate the network layer packets, adding a header and a trailer that include the hardware addresses of the source and destination, among other things, facilitating the data link layer services like frame synchronization, flow control, and error checking.
You have logged on to a Junos device and are at the operational mode prompt.
Which two commands are used at this prompt? (Choose two.)
- A . show interface ge-0/0/0
- B . request system shutdown
- C . set interface ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet
- D . run show interface terse
AB
Explanation:
At the operational mode prompt on a Junos device, you can use various commands to view the device’s status and request system operations. The show interface ge-0/0/0 command is used to display information about a specific interface, while the request system shutdown command is used to properly shut down the device. The set command is used in configuration mode, not operational mode, and the run command is used to execute operational mode commands from configuration mode.
What are two functions of the Routing Engine? (Choose two.)
- A . It processes all management traffic.
- B . It runs the Junos operating system.
- C . It evaluates firewall filters for transit traffic.
- D . It processes transit traffic.
AB
Explanation:
The Routing Engine (RE) in Junos OS has several critical functions, including processing all management traffic (A) and running the Junos operating system (B). The RE handles system management tasks, user interfaces, system services, and routing protocol processes. It does not directly process transit traffic or evaluate firewall filters for transit traffic, as these tasks are handled by the Packet Forwarding Engine (PFE).
